Abstract
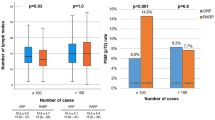
Our aim is to report our preliminary experience of a proctor-based team approach in robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy (RALP) for the treatment of localized prostate cancer. Data was collected between December 2008 and February 2012. RALP was performed on 100 consecutive patients with prostate cancer by a team of five urologists proctored by two fellowship-trained surgeons from a single hospital. Clinical and pathological data of these patients were reviewed. The mean age of the patients was 66 years (range 48–76). Clinical stages were 82 % cT1c, 3 % cT1b, 13 % cT2a and 2 % cT3a disease. Preoperative mean prostate-specific antigen level was 11.33 ng/ml (SD 10.47). Mean operative time was 342 min and mean blood loss was 717 ml (SD 988). Mean hospital stay and duration of the indwelling catheter were 3.2 days (SD 1.8) and 12.6 days (SD 8.5), respectively. Pathological staging showed 65 patients with pT2a (65 %) disease and 33 patients with pT3a (33 %) disease. Thirty-five patients (35 %) had positive surgical margins. Eighteen patients underwent adjuvant radiotherapy. Overall postoperative complication rate was 14 %. There were six Clavien grade 1 complications, seven Clavien grade 2 complications and one Clavien grade 3 complication. At mean follow-up of 36 months, 100 % of patients remained free of biochemical recurrence with continence at 70 %. Our proctor-based team approach will continue to improve each surgeon’s technical competency. He or she will continue to improve and gradually move on to achieving his or her outcomes learning curve.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singapore Cancer Registry Interim Report (2010) Trends in cancer incidence in Singapore 2004–2008. Singapore Cancer Registry
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T et al (2008) Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin 58:71–96
Catalona WJ, Smith DS, Ratliff TL, Basler JW (1993) Detection of organ-confined prostate cancer is increased through prostate-specific antigen-based screening. JAMA 270:948–954
Frota R, Turna B, Barros R, Gill IS (2008) Comparison of radical prostatectomy techniques: open, laparoscopic and robotic assisted. Int Braz J Urol 34:259–269
Hakimi A, Feder M, Ghavamian R (2007) Minimally invasive approaches to prostate cancer. A review of the current literature. Urol J 4:130–137
Singh I, Hemal AK (2010) Robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy in 2010. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 10:671–682
Herrell SD, Smith JA Jr (2005) Robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy: what is the learning curve? Urology 66:105–107
D’Amico AV, Cote K, Loffredo M, Renshaw AA, Schultz D (2002) Determinants of prostate cancer specific survival after radiation therapy for patients with clinically localized prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 20:4567–4573
Menon M, Shrivastava A, Kaul S, Badani KK, Fumo M, Bhandari M et al (2007) Vattikuti Institute prostatectomy: contemporary technique and analysis of results. Eur Urol 51:648–658
Sundaram CP, Koch MO, Gardner T, Bernie JE (2005) Utility of the fourth arm to facilitate robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. BJU Int 95:183–186
Guillonneau B, Vallancien G (2000) Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: the Montsouris technique. J Urol 163:1643–1649
Van Velthoven RF, Ahlering TE, Peltier A, Skarecky DW, Clayman RV (2003) Technique for laparoscopic running urethrovesical anastomosis: the single knot method. Urology 61:699–702
Sur RL, Wagner AA, Albala DM, Su LM (2008) Critical role of the assistant in laparoscopic and robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. J Endourol 22:587–589
Patel VR, Kenneth JP, Coughlin G, Samavedi S (2008) Robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: perioperative outcomes of 1500 cases. J Endourol 22:2299–2305
Stolzenburg JU, Qazi HAR, Holze S, Mende M, Nicolaus M, Franz T (2013) Evaluating the learning curve of experienced laparoscopic surgeons in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. J Endourol 27:80–85
Menon M, Shrivastava A, Sarle R, Hemal A, Tewari A (2003) Vattikuti Institute prostatectomy: a single-team experience of 100 cases. J Endourol 17:785–790
Ficarra V, Cavalleri S, Novara G, Aragona M, Artibani W (2007) Evidence from robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: a systematic review. Eur Urol 51:45–56
Epstein JI, Partin AW, Sauvageot J, Walsh PC (1996) Prediction of progression following radical prostatectomy. A multivariate analysis of 721 men with long-term follow-up. Am J Surg Pathol 20:286–292
Sim HG, Yip SK, Lau WK, Tan YH, Wong MY, Cheng CW (2006) Team-based approach reduces learning curve in robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Int J Urol 13:560–564
Sim HG, Yip SK, Lau WK, Tan JK, Cheng CW (2004) Early experience with robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Asian J Surg 27:321–325
Yip SKh, Sim HG (2010) Robotic radical prostatectomy in East Asia: development, surgical results and challenges. Curr Opin Urol 20:80–85
Lee JY, Mucksavage P, Sundaram CP, McDougall EM (2011) Best practices for robotic surgery training and credentialing. J Urol 185:1191–1197
Davis JW, Kamat A, Munsell M, Pettaway C, Pisters L, Matin S (2010) Initial experience of teaching robot-assisted radical prostatectomy to surgeons-in-training: can training be evaluated and standardized? BJU Int 105:1148–1154
Rashid HH, Leung YY, Rashid MJ, Oleyourryk G, Valvo JR, Eichel L (2006) Robotic surgical education: a systematic approach to training urology residents to perform robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Urology 68:75–79
Zorn KC, Gautam G, Shalhav AL, Clayman RV, Ahlering TE, Albala DM (2009) Training, credentialing, proctoring and medicolegal risks of robotic urological surgery: recommendations of the society of urologic robotic surgeons. J Urol 182:1126–1132
Conflict of interest
Dr. Shieh Ling Bang: no conflict of interest. Dr. Keng Siang Png: no conflict of interest. Dr. Yu Yi Yeow: no conflict of interest. Dr. Gerald Yau Min Tan: no conflict of interest. Dr. Yew Lam Chong: no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bang, S.L., Png, K.S., Yeow, Y.Y. et al. Developing technical expertise in robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy in a moderate-volume center through a proctor-based team approach . J Robotic Surg 8, 245–250 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-014-0460-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-014-0460-5