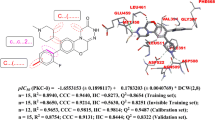
Abstract
This research, employing computational methodologies, aimed to discover potential inhibitors for the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3), an intracellular sensor pivotal in inflammation and various disease processes. Despite NLRP3's critical role, there remains a research gap in the identification of novel inhibitors, making this study’s objective significant. Through statistical techniques such as principal component analysis (PCA) and K-means clustering, data refinement and division was conducted in this research, leading to a more targeted set of potential inhibitors. By employing stepwise and subset multiple linear regression, a two-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship (2D-QSAR) model was developed, revealing six essential molecular descriptors for inhibitory activity. The interpretation of these descriptors led to the proposition of five potential compounds. One of these proposed compounds demonstrated remarkable binding affinity through molecular docking studies, marking it as a promising inhibitor of NLRP3. Further verification of this compound’s potential was conducted via molecular dynamics simulations, affirming its stability and interactions within the protein–ligand system. Compliance with lipinski’s rule of five indicated the drug-like properties of the proposed compounds and their potential for oral bioavailability. This study not only underscores the power of computational techniques in drug discovery but also highlights a promising candidate for therapeutic intervention against NLRP3-mediated inflammatory conditions. The identified compounds, particularly the one with remarkable binding affinity, may pave the way for future pharmacological advancements in treating inflammation-related diseases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abchir O, Daoui O, Belaidi S, Ouassaf M, Qais FA, ElKhattabi S, Belaaouad S, Chtita S (2022) Design of novel benzimidazole derivatives as potential α-amylase inhibitors using QSAR, pharmacokinetics, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation studies. J Mol Model 28(4):106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-022-05097-9
Adelusi TI, Oyedele AQK, Boyenle ID, Ogunlana AT, Adeyemi RO, Ukachi CD, Idris MO, Olaoba OT, Adedotun IO, Kolawole OE, Xiaoxing Y, Abdul-Hammed M (2022) Molecular modeling in drug discovery. Informatics Med Unlocked 29:100880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2022.100880
Alisi IO, Uzairu A, Abechi SE, Idris SO (2018) Quantitative structure activity relationship analysis of coumarins as free radical scavengers by genetic function algorithm. Phys Chem Res 6(1):208–222. https://doi.org/10.22036/pcr.2017.95755.1409
Ambure P, Aher RB, Gajewicz A, Puzyn T, Roy K (2015) “NanoBRIDGES” software: open access tools to perform QSAR and nano-QSAR modeling. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 147:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2015.07.007
Ash J, Fourches D (2017) Characterizing the chemical space of ERK2 kinase inhibitors using descriptors computed from molecular dynamics trajectories. J Chem Inf Model 57(6):1286–1299. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.7b00048
Bhutto JA, Mubashir T, Tahir MH, Ahmad F, Sayed SRM, El-ansary HO, Ishfaq M (2023) Virtual screening and library enumeration of new hydroxycinnamates based antioxidant compounds: a complete framework. J Saudi Chem Soc 27(4):101670
Björkegren JLM, Lusis AJ (2022) Atherosclerosis: recent developments. Cell
Cardoso-Silva J, Papageorgiou LG, Tsoka S (2019) Network-based piecewise linear regression for QSAR modelling. J Comput Aided Mol Des 33(9):831–844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-019-00228-6
Chatterjee M, Banerjee A, De P, Gajewicz-Skretna A, Roy K (2022) A novel quantitative read-across tool designed purposefully to fill the existing gaps in nanosafety data. Environ Sci Nano 9(1):189–203. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1en00725d
Chatterjee M, Roy K (2022) Application of cross-validation strategies to avoid overestimation of performance of 2D-QSAR models for the prediction of aquatic toxicity of chemical mixtures. SAR QSAR Environ Res 33(6):463–484. https://doi.org/10.1080/1062936X.2022.2081255
Cherkasov A, Muratov EN, Fourches D, Varnek A, Baskin II, Cronin M, Dearden J, Gramatica P, Martin YC, Todeschini R (2014) QSAR modeling: where have you been? Where are you going to? J Med Chem 57(12):4977–5010
Chow E, Rendleman CA, Bowers KJ, Dror RO, Hughes DH, Gullingsrud J, Sacerdoti FD, Shaw DE (2008) Desmond performance on a cluster of multicore processors hardware and operating environment benchmark systems and simulation parameters. Simulation (July):14
Consonni V, Todeschini R (2009) Molecular descriptors for chemoinformatics: Volume I: Alphabetical Listing/Volume II: Appendices, References. John Wiley & Sons
Dana RD, Soilihudin D, Silalahi RH, Kurnia D., Hayati U (2021) Competency test clustering through the application of Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and the K-Means algorithm. In: IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. IOP Publishing, p 012038
Daoui O, Nour H, Abchir O, Elkhattabi S, Bakhouch M, Chtita S (2022) A computer-aided drug design approach to explore novel type II inhibitors of c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase for cancer therapy: QSAR, molecular docking ADMET and molecular dynamics simulations. J Biomol Struct Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2022.2124456
Fouedjou RT, Chtita S, Bakhouch M, Belaidi S, Ouassaf M, Djoumbissie LA, Tapondjou LA, Abul Qais F (2022) Cameroonian medicinal plants as potential candidates of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors. J Biomol Struct Dyn 40(19):8615–8629. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2021.1914170
Gilson MK, Liu T, Baitaluk M, Nicola G, Hwang L, Chong J (2016) BindingDB in 2015: a public database for medicinal chemistry, computational chemistry and systems pharmacology. Nucleic Acids Res 44(D1):D1045–D1053. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1072
Glienke J, Stelter M, Braeutigam P (2022) Influence of chemical structure of organic micropollutants on the degradability with ozonation. Water Res 222:118866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118866
Guex N, Peitsch MC (1997) SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-Pdbviewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 18(15):2714–2723. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.1150181505
Hall LH, Kier LB (1995) Electrotopological state indices for atom types: a novel combination of electronic, topological, and valence state information. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 35(6):1039–1045. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci00028a014
He Y, Hara H, Núñez G (2016) Mechanism and regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Trends Biochem Sci 41(12):1012–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2016.09.002
Huang Y, Xu W, Zhou R (2021) NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell Mol Immunol 18(9):2114–2127. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-021-00740-6
Ishfaq M, Aamir M, Ahmad F, M Mebed M, Elshahat S (2022) Machine learning-assisted prediction of the biological activity of aromatase inhibitors and data mining to explore similar compounds. ACS Omega 7(51):48139–48149
Ishfaq M, Rahman Z, Aamir M, Ali I, Guan Y, Hu Z (2023a) Insight into potent TLR2 inhibitors for the treatment of disease caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae based on machine learning approaches. Mol Divers 27(1):371–387
Ishfaq M, Shah SZA, Ahmad I, Rahman Z (2023b) Multinomial classification of NLRP3 inhibitory compounds based on large scale machine learning approaches. Mol Divers :1–20
Jansson NF, Allen RL, Skogsmo G, Tavakoli S (2022) Principal component analysis and K-means clustering as tools during exploration for Zn skarn deposits and industrial carbonates, Sala area. Sweden J Geochem Explor 233:106909. https://doi.org/10.16/j.gexplo.2021.106909
Jia L, Gao H (2022) Machine learning for in silico ADMET prediction. Methods Mol Biol 2390:447–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1787-8_20
Lakhera S, Devlal K, Ghosh A, Chowdhury P, Rana M (2022) Modelling the DFT structural and reactivity study of feverfew and evaluation of its potential antiviral activity against COVID-19 using molecular docking and MD simulations. Chem Pap 76(5):2759–2776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02067-6
Landrum G (2021) RDKit: Open-Source Cheminformatics Software. Http://www.RdkitOrg/
Lei Q, Yi T, Chen C (2018) NF-κB-gasdermin D (GSDMD) axis couples oxidative stress and NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome-mediated cardiomyocyte pyroptosis following myocardial infarction. Med Sci Monit 24:6044–6052. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.908529
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ (2012) Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:4–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.019
Martinon F, Burns K, Tschopp J (2002) The Inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-β. Mol Cell 10(2):417–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00599-3
Mouhsin M, Chtita S, Mbarki M, Oubenali M, Echajia M, Ouafy TE, Gamouh A (2022) QSAR modeling of styrylquinoline derivatives as HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. Curr Chem Biol 16(2):123–129
Nascimento IJ dos S, de Aquino TM, da Silva-Júnior EF (2022) The New Era of Drug Discovery: The Power of Computer-aided Drug Design (CADD) . Lett Drug Des Discov 19(11):951–955. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570180819666220405225817
Nour H, Daoui O, Abchir O, ElKhattabi S, Belaidi S, Chtita S (2022) Combined computational approaches for developing new anti-Alzheimer drug candidates: 3D-QSAR, molecular docking and molecular dynamics studies of liquiritigenin derivatives. Heliyon 8(12):e11991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11991
Protein Preparation Wizard | Schrödinger. https://www.schrodinger.com/science-articles/protein-preparation-wizard. Accessed 8 Aug 2023
Quadri TW, Olasunkanmi LO, Akpan ED, Fayemi OE, Lee HS, Lgaz H, Verma C, Guo L, Kaya S, Ebenso EE (2022) Development of QSAR-based (MLR/ANN) predictive models for effective design of pyridazine corrosion inhibitors. Mater Today Commun 30:103163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.103163
Rosell-Hidalgo A, Young L, Moore AL, Ghafourian T (2021) QSAR and molecular docking for the search of AOX inhibitors: a rational drug discovery approach. J Comput Aided Mol Des 35(2):245–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-020-00360-8
Roy K, Das RN, Ambure P, Aher RB (2016) Be aware of error measures. Further studies on validation of predictive QSAR models. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 152:18–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2016.01.008
Roy K, Mitra I (2012) Electrotopological state atom (E-State) index in drug design, QSAR, property prediction and toxicity assessment. Curr Comput Aided-Drug Des 8(2):135–158. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340912800492366
Schrödinger 2022. Protein Preparation Wizard. https://www.schrodinger.com/science534 articles/protein-preparation-wizard. Accessed 8 Apr 2023
Sharma B, Satija G, Madan A, Garg M, Alam MM, Shaquiquzzaman M, Khanna S, Tiwari P, Parvez S, Iqubal A, Haque SE, Khan MA (2023) Role of NLRP3 inflammasome and its inhibitors as emerging therapeutic drug candidate for Alzheimer’s disease: a review of mechanism of activation, regulation, and inhibition. Inflammation 46(1):56–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-022-01730-0
Tao H, Mo Y, Liu W, Wang H (2023) A review on gout: Looking back and looking ahead. Int Immunopharmacol 117:109977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2023.109977
Tartey S, Kanneganti TD (2019) Differential role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in infection and tumorigenesis. Immunology 156(4):329–338. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.13046
Tropsha A (2010) Best practices for QSAR model development, validation, and exploitation. Mol Inform 29(6–7):476–488. https://doi.org/10.1002/minf.201000061
Trott O, Olson AJ (2009) AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334
Vidal-Limon A, Aguilar-Toalá JE, Liceaga AM (2022) Integration of molecular docking analysis and molecular dynamics simulations for studying food proteins and bioactive peptides. J Agric Food Chem 70(4):934–943. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c06110
WHO (2021) World Health Organization.. - World Health Organization. In: Who. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/arsenic
Wenzlick M, Mamun O, Devanathan R, Rose K, Hawk J (2022) Assessment of outliers in alloy datasets using unsupervised techniques. Jom 74(7):2846–2859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05204-4
Xue Qin QN, Ming LC, Abd Wahab MS, Tan CS, Yuda A, Hermansyah A (2023) Drug-related problems among older people with dementia: a systematic review. Res Soc Adm Pharm 19(6):873–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sapharm.2023.02.015
Yamari I, Abchir O, Nour H, El Kouali M, Chtita S (2023) Identification of new dihydrophenanthrene derivatives as promising anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs through in silico investigations. Main Gr Chem (Preprint). https://doi.org/10.3233/mgc-220127
Yap CW (2011) PaDEL-descriptor: an open source software to calculate molecular descriptors and fingerprints. J Comput Chem 32(7):1466–1474. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21707
Zhu Z, Rahman Z, Aamir M, Shah SZA, Hamid S, Bilawal A, Li S, Ishfaq M (2023) Insight into TLR4 receptor inhibitory activity via QSAR for the treatment of Mycoplasma pneumonia disease. RSC Adv 13(3):2057–2069
Acknowledgements
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mouhsin, M., Abchir, O., El Otmani, F.S. et al. Identification of novel NLRP3 inhibitors: a comprehensive approach using 2D-QSAR, molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation and drug-likeness evaluation. Chem. Pap. 78, 1193–1204 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-03157-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-03157-9