Abstract
Background
The effects of rs1501299 variant of ADIPO gene on weight loss after bariatric surgery have not been evaluated. We decided to investigate the role of this genetic variant on anthropometric and biochemical outcomes such as serum adiponectin levels after biliopancreatic diversion (BPD) surgery in morbidly obese patients during 3 years.
Material and Methods
A sample of 64 patients with morbid obesity without diabetes mellitus was operated. Biochemical and anthropometric evaluation were realized at basal visit and at each visit during 3 years (1, 2, and 3 years).
Results
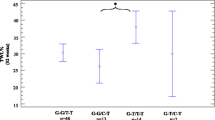
Percent excess weight loss, body mass index, weight, waist circumference, fat mass, blood pressure, fasting glucose, LDL cholesterol, total cholesterol, and triglycerides levels improved in both genotype groups. Fasting insulin levels and HOMA-IR decreased significantly only in non-T allele carriers. The decrease of fasting insulin levels at 3 years (delta −9.2 ± 3.4 vs −2.9 ± 2.2 mUI/L; p = 0.01) and HOMA-IR (delta −1.3 ± 0.3 vs −0.8 ± 0.4 units; p = 0.03) were higher in non-T allele carriers than T carriers. Adiponectin levels increased in all times after surgery in non-T allele carriers, too. The increase of adiponectin levels at 3 years (delta 12.2 ± 3.6 vs 1.8 ± 1.2 ng/mL; p = 0.01) was higher in non-T allele carriers than T carriers.
Conclusion
Non-T allele of ADIPOQ gene variant (rs1501299) is associated with increases in adiponectin levels and better improvements of insulin and HOMA-IR after BPD massive weight loss. These parameters remained unchanged in T allele carriers
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kershaw EE, Flier JS. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:2548–56.
Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, et al. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;257:79–83.
Havel PJ. Update on adipocyte hormones: regulation of energy balance and carbohydrate/lipid metabolism. Diabetes. 2004;53(Suppl 1):S143–51.
Qi Y, Takahashi N, Hileman SM, et al. Adiponectin acts in the brain to decrease body weight. Nat Med. 2004;10:524–9.
Comuzzie AG, Funahashi T, Sonnenberg G. The genetic basis of plasma variation in adiponectin, a global endophenotype for obesity and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:4321–5.
Roteau-Chonka DC, Wu Y, Li Y, et al. Population-specific coding variant underlies genome-wide association with adiponectin level. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:463–71.
Filippi E, Sentinelli F, Romeo S, et al. The adiponectin gene SNP+276G>T associates with early-onset coronary artery disease and with lower levels of adiponectin in younger coronary artery disease patients (age <or = 50 years). J Mol Med. 2005;83:711–9.
Kyriakou T, Collins LJ, Spencer-Jones NJ, et al. Adiponectin gene ADIPOQ SNP associations with serum adiponectin in two female populations and effects of SNPs on promoter activity. J Hum Genet. 2008;53:718–27.
Vasseur F, Helbecque N, Dina C, et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphism haplotypes in the both proximal promoter and exon 3 of the APM1 gene modulate adipocyte-secreted adiponectin hormone levels and contribute to the genetic risk for type 2 diabetes in French Caucasians. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:2607–14.
Salmenniemi U, Zacharova J, Ruotsalainen E, et al. Association of adiponectin level and variants in the adiponectin gene with glucose metabolism, energy expenditure, and cytokines in offspring of type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:4216–23.
Filippi E, Sentinelli F, Trischitta V, et al. Association of the human adiponectin gene and insulin resistance. Eur J Hum Genet. 2004;12:199–205.
Hara K, Boutin P, Mori Y, et al. Genetic variation in the gene encoding adiponectin is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Diabetes. 2002;51:536–40.
Szopa M, Malczewska-Malec M, Wilk B, et al. Variants of the adiponectin gene and type 2 diabetes in a Polish population. Acta Diabetol. 2009;46(4):317–22.
Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384:766–81.
Kushner RF. Weight loss strategies for treatment of obesity. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2014;56:465–72.
Abete I, Astrup A, Martinez JA, et al. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome: role of different dietary macronutrient distribution patterns and specific nutritional components on weight loss and maintenance. Nutr Rev. 2010;68:214–31.
Jaunoo SS, Southall PJ. Bariatric surgery. Int J Surg. 2010;8(2):86–9.
Kashyap SR, Gatmaitan P, Brethauer S, et al. Bariatric surgery for type 2 diabetes: weighing the impact for obese patients. Cleve Clin J Med. 2010;77:468–76.
de Luis DA, Gonzalez M, Pacheco D, et al. Effect of C358A missense polymorphism of the endocannabinoid degrading enzyme fatty acid hydrolase on weight loss and cardiovascular risk factors 1 year after biliopancreatic diversion surgery. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2010;6:516–20.
de Luis DA, Aller R, Izaola O, et al. Early clinical and surgical results of biliopancreatic diversion. Obes Surg. 2005;15:799–802.
Executive Summary of the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001;285:2486-2487.
Friedewald WT, Levy RJ, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972;18:499–502.
Duart MJ, Arroyo CO, Moreno JL. Validation of an insulin model for the reactions in RIA. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2002;40:1161–7.
Mathews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, et al. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985;28:412–4.
Suominen P. Evaluation of an enzyme immunometric assay to measure serum adiponectin concentrations. Clin Chem. 2004;50:219–21.
Lukaski H, Johnson PE. Assessment of fat-free mass using bioelectrical impedance measurements of the human body. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985;41:810–7.
Yannakoulia M, Yiannakouris N, Melistas L, et al. A dietary pattern characterized by high consumption of whole-grain cereals and low-fat dairy products and low consumption of refined cereals is positively associated with plasma adiponectin levels in healthy women. Metabolism. 2008;57:824–30.
AlSaleh A, O'Dell SD, Frost GS, et al., RISCK Study Group. Single nucleotide polymorphisms at the ADIPOQ gene locus interact with age and dietary intake of fat to determine serum adiponectin in subjects at risk of the metabolic syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;94:262–9.
Alsaleh A, Crepostnaia D, Maniou Z, et al., MARINA study team. Adiponectin gene variant interacts with fish oil supplementation to influence serum adiponectin in older individuals. J Nutr. 2013;143:1021–7.
Shin MJ, Jang Y, Koh SJ, et al. The association of SNP276G>T at adiponectin gene with circulating adiponectin and insulin resistance in response to mild weigh loss. Int J Obes. 2006;30:1702–8.
Perez-Martinez P, Lopez Miranda J, Cruz-Teno C, et al. Adiponectin gene variants are associated with insulin sensitivity in response to dietary fat consumption in Caucasian men. J Nutr. 2008;138:1609–14.
Hsiao TJ, Wu LS, Huang SY, et al. A common variant in the adiponectin gene on weight loss and body composition under sibutramine therapy in obesity. Clin Pharm. 2010;2:105–10.
Al-Suhaimi EA, Shehzad A. Leptin, resistin and visfatin: the missing link between endocrine metabolic disorders and immunity. Eur J Med Res. 2013;18:12.
Butner KL, Nickols-Richardson SM, Clark SF, et al. A review of weight loss following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass vs restrictive bariatric surgery: impact on adiponectin and insulin. Obes Surg. 2010;20(5):559–68.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
No funding source.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Luis, D.A., Pacheco, D., Primo, D. et al. The Association of SNP276G>T at Adiponectin Gene with Insulin Resistance and Circulating Adiponectin in Morbid Obese Patients After a Biliopancreatic Diversion Surgery. OBES SURG 27, 3247–3252 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-017-2766-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-017-2766-7