Abstract
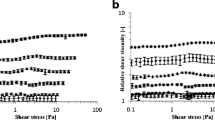
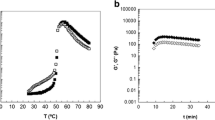
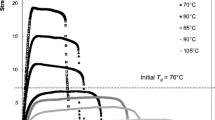
The rheology of potato starch paste (PSP) in an ultrasonic field was studied by an RS600 HAAKE rheometer. The effects of ultrasonic time on the rheological model and on shear thinning of PSP were studied. The thixotropy of PSP in the ultrasonic field and the spatial conformation of the PSP molecular chain were also investigated. From experiments under different ultrasonic times, PSP exhibited pseudoplastic fluid characteristics and conformed to the power law τ = k·γm (where k and m are constants). PSP has the characteristics of a Newtonian fluid after ultrasonic action. At the same shear rate, the apparent viscosity of PSP decreased with increasing ultrasonic time. The degree of shear thinning of PSP was greatly reduced, and the thixotropy of PSP was lower after ultrasonic action.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.Y. Chun, B. Yoo, Steady and dynamic shear rheological properties of sweet potato flour dispersions. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 223, 313–319 (2006)
C.S. Raina, S. Singh, A.S. Bawa, et al, Rheological properties of chemically modified rice starch model solu. J. Food Process Eng. 29, 134–148 (2006)
G. Zurima, P.B. Elevina, Effect of acetylation on some properties of rice starch. Starch. 54, 90–94 (2002)
B.A. David, G.C. Elodia, C.H. Eduardo et al., Chemical modification of jack bean (Canavalia ensiformis). Starch. 54, 540–546 (2002)
J.L. Willett, I.K. Jasbern, C.L. Swanson, Rheology of thermo-plastic starch: effects of temperature, moisture content, and additives on melt viscosity. Polym. Eng. Sci. 35, 202–210 (1995)
A. Walter, P. IIansGerhard, R. Stuttnart, Rheological characterization of theimplastic starch materials. Starch-Starke. 50, 77–83 (1998)
R.C. Eerlingen, H. Jacobs, K. Block, et al, Effects of hydrothermal treatments on the rheological properties of potato starch. Carbohydr. Res. 297, 347–356 (1997)
R. Hoover, T. Vasanthan, The flow properties of native, heat-moisture treated, and annealed starches from wheat, oat, potato and lentil. Food Biochem. 18, 67–82 (1994)
L. Chen, Y.S. Pang, X.X. Li et al., Effect of ball milling on the crystalline structure and paste rheological properties of mung bean starch. Food Sci. 26, 126–130 (2005)
C.S. Raina, S. Singh, A.S. Bawa et al., Rheological properties of chemically modified rice starch model solutions. J. Food Process Eng. 29, 134–148 (2006)
K. Morikawa, K. Nishinari, Effects of granule size and size distribution on rheological behavior of chemically modified potato starch. J. Food Sci. 67, 1388–1392 (2002)
E. Merica, M. Lungu, Natural polymers as rheological additives. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 37, 371–383 (2003)
M.N. Islam, M.D. Abdul. M. AzemiBin et al., Effect of temperature and starch concentration on the intrinsic viscosity and critical concentration of Sago starch. Starch. 53, 90–94 (2001)
D. Yoo, B.T. Yoo, Rheology of rice starch-sucrose composites. Starch-Starke. 57, 254–261 (2005)
A. Tarrega, E. Costell, M.A. Rao, Vane yield stress of native and cross-linked starch dispersions in skimmed milk: effect of starch concentration and lambda-carrageenan addition. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 12, 253–260 (2006)
N. Besun, B. Ozguclu, S. Peker, Shear-dependent rheological properties of starch/bentonite composite gels. Colloid Polym. Sci. 275, 567–579 (1997)
F. Hu, L. Chen, L. Li et al., Study on the rheological characteristics of micronized potato starch (a). J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 18, 61–63 (2003)
C. Andrea, Bertolini, rheological properties of acidified and UV-irradiated starch. Starch. 52, 340–344 (2000)
H. Jee-yup, T.T. Robert, Characterization of pea starches in the presence of alkali and borax. Starch. 55, 457–463 (2003)
A.M. Amini, S.M.A. Razavi, S.A. Mortazavi, Morphological, physicochemical, and viscoelastic properties of sonicated corn starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 122, 282–292 (2015)
W. Cheng, J. Chen, D. Liu, X. Ye, F. Ke, Impact of ultrasonic treatment on properties of starch film-forming dispersion and the resulting films. Carbohydr. Polym. 81, 707–711 (2010)
S. Mallakpour, L. Khodadadzadeh, Ultrasonic-assisted fabrication of starch/MWCNT glucose nanocomposites for drug delivery. Ultrason. Sonochem. 40, 402–409 (2018)
H.Y. Kim, J.A. Han, D.K. Kweon, J.D. Park et al., Effect of ultrasonic treatments on nanoparticle preparation of acid-hydrolyzed waxy maize starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 93, 582–588 (2013)
S. Manchun, J. Nunthanid, S. Limmatvapirat, P. Sriamornsak, Effect of ultrasonic treatment on physical properties of tapioca starch. Adv. Mater. Res. 506, 294–297 (2012)
G.L. Peres, D.C. Leite, N. Pesce, Ultrasound effect on molecular weight reduction of amylopectin. 67, 407–414 (2015)
S.S. Wong, S. Kasapis, D. Huang, Molecular weight and crystallinity alteration of cellulose via prolonged ultrasound fragmentation. Food Hydrocolloids. 26, 365–369 (2012)
Y. Iida, T. Tuziuti, K. Yasui, A. Towata, T. Kozuka, Control of viscosity in starch and polysaccharide solutions with ultrasound after gelatinization. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 9, 140–146 (2008)
A.R. Jambrak, Z. Herceg, D. Šubarić, J. Babić, M. Brnčić et al., Ultrasound effect on physical properties of corn starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 79, 91–100 (2010)
K.F. Chen, Food Rheology and Measurement (Light Industry Press, Beijing, 1989)
L.T. Li, F. Physics, Beijing: China Agricultural Press. (2001)
Y.F. Li, Y.G. Yin, W.H. Jin, Food Properties, Beijing: China Light Industry Press. (2005)
Y.Z. Xu, P.S. Rheology, Chengdu: Sichuan Education Publishing House. (1988)
Z.M. Wang, Preparation of anticoagulant microcrystalline cellulose sulphate and its structure-activity relationship, Guangzhou: South China University of Technology (PhD thesis). (2003)
S. Alban, J. Kraus, G. Franz, Synthesis of laminarin sulfates with anticoagulant activity. Drug Res. 42, 1005–1008 (1992)
M. Wang, X.L. Ding, Some properties of modified yeast glucan-CMG and its conformational behavior in solution. Chin. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 14, 636–640 (1998)
Z.Y. Liang, Y.S.C.Y. Zhang, Miao et al., Studies on the conformational behavior in the glycosaminoglycans CF2a solution. Biochem. Biophys. 26, 411–415 (1994)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 20864001 and 31160326), a Grant from the Key Project of the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (No. 04105934), and the Collaborative Innovation Center for Guangxi Sugar Industry, Guangxi, Nanning 530004, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YF., Li, JB., Zhang, ZY. et al. Rheological law of change and conformation of potato starch paste in an ultrasound field. Food Measure 13, 1695–1704 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00086-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-019-00086-8