Abstract
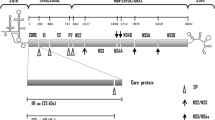
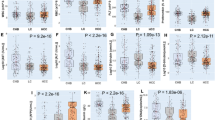
The association of viral mutations and haplotypic carriages with mutations in the preS region of hepatitis B virus (HBV) genotypes B and C with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is of great significance for the prediction of this malignancy, but it remains obscure. We analyzed the preS sequences of HBV genotypes B and C from 1172 HBV-infected subjects including 231 patients with HCC. As compared with the HBV-infected subjects without HCC, C2875T, G2946C, A3054C, C3060A, T3066C, C3116T, A3120C, G3191A, A1C, C7A, C10A, A31C, C76T, G105C, and G147C in both genotypes were significantly associated with increased risks of HCC. C2875A, G2950A, G2951A, A3054T, C3060T, T3066A, T3069G, A3120T, and G3191C were significantly associated with increased risks of HCC in genotype C, whereas these mutations were inversely associated with HCC in genotype B. Multivariate regression analyses showed that C76A/T was a novel factor independently associated with an increased risk of HCC, as compared with those without HCC. The frequencies of haplotypes 2964A-3116T-preS2 start codon wild-type-7C, 2964C-3116T-7A-76C, and 2964A-3116T-7C-76A/T were significantly higher in the patients with HCC (P<0.001), whereas a haplotypic carriage with a single mutation and another three wildtypes were inversely associated with HCC. Conclusively, the association of HBV mutations in the preS region with HCC depends on HBV genotype and haplotypic carriage with two or more mutations that are each associated with an increased risk of HCC independently.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nguyen V T, Law M G, Dore G J. Hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiological characteristics and disease burden. J Viral Hepat, 2009, 16(7): 453–463
El-Serag H B, Rudolph K L. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology, 2007, 132(7): 2557–2576
Yin J, Zhang H, Li C, Gao C, He Y, Zhai Y, Zhang P, Xu L, Tan X, Chen J, Cheng S, Schaefer S, Cao G. Role of hepatitis B virus genotype mixture, subgenotypes C2 and B2 on hepatocellular carcinoma: compared with chronic hepatitis B and asymptomatic carrier state in the same area. Carcinogenesis, 2008, 29(9): 1685–1691
Liu S, Zhang H, Gu C, Yin J, He Y, Xie J, Cao G. Associations between hepatitis B virus mutations and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2009, 101(15): 1066–1082
Cao G W. Clinical relevance and public health significance of hepatitis B virus genomic variations. World J Gastroenterol, 2009, 15(46): 5761–5769
Yin J, Zhang H, He Y, Xie J, Liu S, Chang W, Tan X, Gu C, Lu W, Wang H, Bi S, Cui F, Liang X, Schaefer S, Cao G. Distribution and hepatocellular carcinoma-related viral properties of hepatitis B virus genotypes in Mainland China: a community-based study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2010, 19(3): 777–786
Kay A, Zoulim F. Hepatitis B virus genetic variability and evolution. Virus Res, 2007, 127(2): 164–176
Chen B F, Liu C J, Jow G M, Chen P J, Kao J H, Chen D S. High prevalence and mapping of pre-S deletion in hepatitis B virus carriers with progressive liver diseases. Gastroenterology, 2006, 130(4): 1153–1168
Gao Z Y, Li T, Wang J, Du J M, Li Y J, Li J, Lu F M, Zhuang H. Mutations in preS genes of genotype C hepatitis B virus in patients with chronic hepatitis B and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol, 2007, 42(9): 761–768
Cao Z, Bai X, Guo X, Jin Y, Qian G, Tu H. High prevalence of hepatitis B virus pre-S mutation and its association with hepatocellular carcinoma in Qidong, China. Arch Virol, 2008, 153(10): 1807–1812
Fang Z L, Sabin C A, Dong B Q, Wei S C, Chen Q Y, Fang K X, Yang J Y, Huang J, Wang X Y, Harrison T J. Hepatitis B virus pre-S deletion mutations are a risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma: a matched nested case-control study. J Gen Virol, 2008, 89(Pt 11): 2882–2890
Yin J, Xie J, Zhang H, Shen Q, Han L, Lu W, Han Y, Li C, Ni W, Wang H, Cao G. Significant association of different preS mutations with hepatitis B-related cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol, 2010, 45(10): 1063–1071
Chen J, Yin J, Tan X, Zhang H, Zhang H, Chen B, Chang W, Schaefer S, Cao G. Improved multiplex-PCR to identify hepatitis B virus genotypes A-F and subgenotypes B1, B2, C1 and C2. J Clin Virol, 2007, 38(3): 238–243
Zhang H W, Yin J H, Li Y T, Li C Z, Ren H, Gu C Y, Wu H Y, Liang X S, Zhang P, Zhao J F, Tan X J, Lu W, Schaefer S, Cao G W. Risk factors for acute hepatitis B and its progression to chronic hepatitis in Shanghai, China. Gut, 2008, 57(12): 1713–1720
Shen T, Yan X M, Zou Y L, Gao J M, Dong H. Virologic characteristics of hepatitis B virus in patients infected via maternalfetal transmission. World J Gastroenterol, 2008, 14(37): 5674–5682
Bock C T, Tillmann H L, Maschek H J, Manns M P, Trautwein C. A preS mutation isolated from a patient with chronic hepatitis B infection leads to virus retention and misassembly. Gastroenterology, 1997, 113(6): 1976–1982
Hsieh Y H, Su I J, Wang H C, Chang W W, Lei H Y, Lai M D, Chang W T, Huang W. Pre-S mutant surface antigens in chronic hepatitis B virus infection induce oxidative stress and DNA damage. Carcinogenesis, 2004, 25(10): 2023–2032
Kekulé A S, Lauer U, Meyer M, Caselmann W H, Hofschneider P H, Koshy R. The preS2/S region of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA encodes a transcriptional transactivator. Nature, 1990, 343(6257): 457–461
Göbel F, Taschner S, Jurkin J, Konradi S, Vaculik C, Richter S, Kneidinger D, Mühlbacher C, Bieglmayer C, Elbe-Bürger A, Strobl H. Reciprocal role of GATA-1 and vitamin D receptor in human myeloid dendritic cell differentiation. Blood, 2009, 114(18): 3813–3821
Andrieux L O, Fautrel A, Bessard A, Guillouzo A, Baffet G, Langouët S. GATA-1 is essential in EGF-mediated induction of nucleotide excision repair activity and ERCC1 expression through ERK2 in human hepatoma cells. Cancer Res, 2007, 67(5): 2114–2123
Banerjee R, Caruccio L, Zhang Y J, McKercher S, Santella R M. Effects of carcinogen-induced transcription factors on the activation of hepatitis B virus expression in human hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells and its implication on hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology, 2000, 32(2): 367–374
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, JX., Zhao, J., Yin, JH. et al. Association of novel mutations and heplotypes in the preS region of hepatitis B virus with hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Med. China 4, 419–429 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-010-0160-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-010-0160-0