Abstract
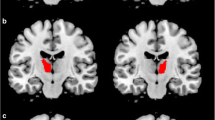
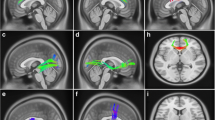
Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder (RBD) frequently occurs in Parkinson’s disease (PD), however, the exact pathophysiological mechanism is not clear. The prefrontal cortex (PFC), especially ventrolateral prefrontal cortex (VLPFC), dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), and inferior frontal gyrus (IFG) which may play roles by regulating cognitive control processes. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether there is abnormal functional connectivity (FC) maps and volume changes in PD with RBD(PD-RBD). We recruited 20 PD-RBD, 20 PD without RBD (PD-nRBD), and 20 normal controls (NC). We utilized resting-state functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (rs-MRI) to explore FC changes based on regions of interest (VLPFC, DLPFC, and IFG), and used voxel-based morphology technology to analyze whole-brain volumes by 3D-T1 structural MRI. Except the REM sleep behavioral disorders questionnaire (RBDSQ), the PD-RBD showed lower visuospatial/executive and attention scores than the NC group. The RBDSQ scores were significantly positively correlated with zFC of right DLPFC to bilateral posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) (P = 0.0362, R = 0.4708, AlphaSim corrected) and also significantly positively correlated with zFC of left VLPFC to right inferior temporal (P = 0.0157, R = 0.5323, AlphaSim corrected) in PD-RBD group. Furthermore, abnormal correlations with zFC values were also found in some cognitive subdomains in PD-RBD group. The study may suggest that in PD-RBD patients, the presence of RBD may be related to the abnormal FC of VLPFC and DLPFC, meanwhile, the abnormal FC of DLPFC and IFG may be related to the mechanisms of cognitive impairment.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Alejandra, R. L., Armony, J. L., Yolanda, R. P., et al. (2012). Enhanced emotional reactivity after selective REM sleep deprivation in humans: an fMRI study [J]. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2012.00025
B I A A. (2010). La motricité redevient-elle normale en sommeil paradoxal? Le trouble comportemental en sommeil paradoxal - ScienceDirect [J]. Revue Neurologique, 166 (10), 785–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurol.2010.07.016
Arnulf, I., Bonnet, A.-M., et al. (2000). Hallucinations, REM sleep, and Parkinson's disease: a medical hypothesis [J]. Neurology. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.57.7.1350-a
Bech, P. (2006). Rating scales in depression: limitations and pitfalls [J]. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 8(2), 207–15. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2006.8.2/pbech
Boecker, H., Ceballos-Baumann, A. O., Volk, D., et al. (2007). Metabolic alterations in patients with Parkinson disease and visual hallucinations [J]. Archives of Neurology, 64(7), 984–988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-007-0374-2
Boeve, B. F., Molano, J. R., Ferman, T. J., et al. (2011). Validation of the mayo sleep questionnaire to screen for REM sleep behavior disorder in an aging and dementia cohort [J]. Sleep Medicine, 12(5), 445–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2010.12.009
Braun, A. R., Balkin, T. J., Wesenten, N. J., et al. (1997). Regional cerebral blood flow throughout the sleep-wake cycle. An H2(15)O PET study [J]. Brain, 7, 1173–97. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/120.7.1173
Bugalho, P., & Paiva, T. (2011). Dream features in the early stages of Parkinson’s Disease [J]. Journal of Neural Transmission, 118(11), 1613–1619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-011-0679-5
Cabeza, R., Dolcos, F., Graham, R., et al. (2002). Similarities and differences in the neural correlates of episodic memory retrieval and working memory [J]. NeuroImage, 16(2), 317–330.
Cavanagh, J. F., Sanguinetti, J. L., Allen, J., et al. (2014). The subthalamic nucleus contributes to post-error slowing [J]. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 26(11), 2637–2644.
Chahine, L. M., Daley, J., Horn, S., et al. (2013). Questionnaire-based diagnosis of REM sleep behavior disorder in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Movement Disorders Official Journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 28(8), 1146–1149.
Chen, Y., Fan, C., Yang, W., et al. (2019). Cortical hypoperfusion in patients with idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder detected with arterial spin-labeled perfusion MRI [J]. Neurological Sciences, 41(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-04118-5
Cools, R., Miyakawa, A., Sheridan, M., et al. (2010). Enhanced frontal function in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Brain, 133(Pt 1), 225–233.
Diwadkar, V. A., Carpenter, P. A., & Just, M. A. (2000). Collaborative activity between parietal and dorso - lateral prefrontal cortex in dynamic spatial working memory revealed by fMRI [J]. NeuroImage, 12(1), 85–99.
Dolcos, F., la Ba, R. K. S., & Cabeza, R. (2004). Dissociable effects of arousal and valence on prefrontal activity indexing emotional evaluation and subsequent memory: An event-related fMRI study [J]. NeuroImage, 23(1), 64–74.
Doruk, D., Gray, Z., Bravo, G. L., et al. (2014). Effects of tDCS on executive function in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Neuroscience Letters, 582, 27–31.
Fantini, M. L., Macedo, L., Zibetti, M., et al. (2015). Increased risk of impulse control symptoms in Parkinson’s disease with REM sleep behaviour disorder [J]. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 86(2), 174–179.
Fantini, M. L., Figorilli, M., Arnulf, I., et al. (2018). Sleep and REM sleep behaviour disorder in Parkinson’s disease with impulse control disorder [J]. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2017-316576
Ford, A. H., Duncan, G. W., Firbank, M. J., et al. (2013). Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder in Parkinson"s disease: Magnetic resonance imaging study [J]. Movement Disorders, 28(6), 832–836.
Fox, K., Nijeboer, S., Solomonova, E., et al. (2013). Dreaming as mind wandering: evidence from functional neuroimaging and first-person content reports [J]. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00412
Gagnon, J. F., Postuma, R. B., Mazza, S., et al. (2006). Rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder and neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Lancet Neurology, 5(5), 424–432.
Gallagher, D. A., Parkkinen, L., O’Sullivan, S. S., et al. (2011). Testing an aetiological model of visual hallucinations in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Brain A Journal of Neurology, 134(11), 3299–3309.
Garcia-Diaz, A. I., Segura, B., Baggio, H. C., et al. (2014). Structural MRI correlates of the MMSE and pentagon copying test in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 20(12), 1405–1410.
García-Lorenzo, D., Santos, L. D., Ewenczyk, C., et al. (2013). The coeruleus/subcoeruleus complex in rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorders in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Brain, 136(Pt 7), 2120–9.
Geng, J., Yan, R., et al. (2018). Altered regional homogeneity in patients with somatic depression: A resting-state fMRI study [J]. Journal of Affective Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2018.12.066
Gilbert, C. D., & Li, W. (2013). Top-down influences on visual processing [J]. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 14(5), 350–363.
Goetz, C. G., Fahn, S., Martinez-Martin, P., et al. (2007). Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): Process, format, and clinimetric testing plan [J]. Movement Disorders, 22(1), 41–47.
Han, X. H., Li, X. M., et al. (2019). Assessing gray matter volume in patients with idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder [J]. Neural Regeneration Research, 14(5), 868–875
Heinrichs-Graham, E., Wiesman, A., Embury, C. M., et al. (2022). Differential impact of movement on the alpha and gamma dynamics serving visual processing[J]. Journal of Neurophysiology. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00380.2021
Ibarretxe-Bilbao, N., Ramirez-Ruiz, B., Junque, C., et al. (2010). Differential progression of brain atrophy in Parkinson’s disease with and without visual hallucinations [J]. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(6), 650.
Ide, J. S., & Li, C. (2011). A cerebellar thalamic cortical circuit for error-related cognitive control [J]. NeuroImage, 54(1), 455–464.
Ioannides, A. A., Kostopoulos, G. K., Liu, L., et al. (2009). MEG identifies dorsal medial brain activations during sleep [J]. NeuroImage, 44(2), 455–468.
Jaromír, H., Jan, R., Ondrej, B., et al. (2018). Eye movements in idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder: High antisaccade error rate reflects prefrontal cortex dysfunction [J]. Journal of Sleep Research, 28, e12742.
Ji, I. K., Sunwoo, M. K., Sohn, Y. H., et al. (2016). The MMSE and MoCA for screening cognitive impairment in less educated patients with Parkinson's disease [J]. Journal of Movement Disorders, 9(3). https://doi.org/10.14802/jmd.16020
Jia, X., Fan, W., Wang, Z., et al. (2022). Progressive prefrontal cortex dysfunction in Parkinson's disease with probable REM sleep behavior disorder: A 3-year longitudinal study [J]. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, (13). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.750767
Kim, H. J., Im, H. K., Kim, J., et al. (2015) Brain atrophy of secondary REM-sleep behavior disorder in neurodegenerative disease [J]. Journal of Alzheimers Disease Jad, 52(3). https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-151197
Lerche, S., & Brockmann, K. (2018). REM sleep behaviour disorder (RBD): Risk for Parkinsonism and executive dysfunction in elderly [J]. Oncotarget, 9(95), 36732–36733.
Li, Z. (2014). Dynamic functional connectivity pattern analysis based on resting state magnetic resonance imaging of brain[D]. National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, Hunan, China. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CDFDLAST2016&filename=1015959199.nh
Li, D., Huang, P., Zang, Y., Lou, Y., Cen, Z., Gu, Q., Xuan, M., Xie, F., Ouyang, Z., Wang, B., Zhang, M., & Luo, W. (2017). Abnormal baseline brain activity in Parkinson's disease with and without REM sleep behavior disorder: A resting‐state functional MRI study [J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 46(3). https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25571
Lim, J. S., Shin, S. A., Lee, J. Y., et al. (2016). Neural substrates of rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 23, 31–6.
Maquet, P., Aerts, J., Delfiore, G., et al. (1996). Functional neuroanatomy of human rapid-eye-movement sleep and dreaming [J]. Nature, 383(6596), 163–166.
Meppelink, A. M., Jong, B. M. D., Teune, L. K., et al. (2015). Regional cortical grey matter loss in Parkinson’s disease without dementia is independent from visual hallucinations [J]. Movement Disorders, 26(1), 142–147.
Meppelink, A. M., De Jong, B. M., et al. (2009). Impaired visual processing preceding image recognition in Parkinson's disease patients with visual hallucinations [J]. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awp223
Mihaescu, A. S., Mario, M., Ariel, G. G., et al. (2018). Brain degeneration in Parkinson's disease patients with cognitive decline: a coordinate-based meta-analysis [J]. Brain Imaging & Behavior, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9922-0
Modi, H. N., Singh, H., Darzi, A., et al. (2020). Multitasking and time pressure in the operating room: impact on surgeons’ brain function [J]. Annals of Surgery, (272). https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000004208
Muzur, A., Pace-Schott, E. F., & Hobson, J. A. (2002). The prefrontal cortex in sleep [J]. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 6(11), 475–481.
Nagano-Saito, A., Washimi, Y., Arahata, Y., et al. (2004). Visual hallucination in Parkinson’s disease with FDG PET [J]. Movement Disorders, 19(7), 801–806.
Naumann, A., Bellebaum, C., & Daum, I. (2010). Cognitive deficits in narcolepsy [J]. Journal of Sleep Research, 15(3), 329–338.
Nomura, T., Inoue, Y., Kagimura, T., et al. (2011). Utility of the REM sleep behavior disorder screening questionnaire (RBDSQ) in Parkinson’s disease patients [J]. Sleep Medicine, 12(7), 711–713.
Olson, E. J., Boeve, B. F., & Silber, M. H. (2000). Rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder: demographic, clinical and laboratory findings in 93 cases [J]. Brain, (2), 331–339. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/123.2.331
Pan, P. L., Song, W., et al. (2012). Voxel-wise meta-analysis of gray matter abnormalities in idiopathic Parkinson's disease [J]. European Journal of Neurology: The Official Journal of the European Federation of Neurological Societies. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03474
Pappert, E. J., Goetz, C. G., Niederman, F. G., et al. (1999). Hallucinations, sleep fragmentation, and altered dream phenomena in Parkinson's disease [J]. Movement Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1002/1531-8257(199901)14:1<117::AID-MDS1019>3.0.CO;2-0
Plomhause, L., Dujardin, K., Boucart, M., et al. (2014). Impaired visual perception in rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder [J]. Neuropsychology, 28(3), 388.
Postuma, R. B., Bertrand, J. A., Montplaisir, J., et al. (2012). Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder and risk of dementia in Parkinson’s disease: A prospective study [J]. Movement Disorders, 27(6), 720–726.
Rahayel, S., Montplaisir, J., Monchi, O., et al. (2013). Patterns of cortical thinning in idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder [J]. Sleep Medicine, 14(supp S1), e239.
Rahayel, S., Postuma, R. B., et al. (2017). Abnormal gray matter shape, thickness, and volume in the motor cortico-subcortical loop in idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder: association with clinical and motor features [J]. Cerebral Cortex. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhx137
Ramírez‐Ruiz, B., Martí, M. J., Tolosa, E., et al. (2010). Brain response to complex visual stimuli in Parkinson's patients with hallucinations: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study [J]. Movement Disorders, 23(16). https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22258
Salehinejad, A., Ghanavati, E., Rashid, M. H. A., et al. (2021). Hot and cold executive functions in the brain: A prefrontal- cingular network [J]. Brain and Neuroscience Advances, 5, 1–19.
Saletu, M., et al. (2008). Event-related-potential low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (ERP-LORETA) suggests decreased energetic resources for cognitive processing in narcolepsy [J]. Clinical Neurophysiology, 119(8), 1782–94.
Salsone, M., Cerasa, A., Arabia, G., et al. (2014). Reduced thalamic volume in Parkinson disease with REM sleep behavior disorder: Volumetric study [J]. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 20(9), 1004–1008.
Santangelo, G., Trojano, L., Vitale, C., et al. (2007). A neuropsychological longitudinal study in Parkinson’s patients with and without hallucinations [J]. Movement Disorders, 22(16), 2418–2425.
Shady, R., Malo, G., Postuma, R. B., et al. (2019). Brain atrophy in Parkinson’s disease with polysomnography-confirmed REM sleep behavior disorder [J]. Sleep, 6, 6.
Sinforiani E, Zangaglia R, Manni R, et al. (2006) REM sleep behavior disorder, hallucinations, and cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease [J]. Movement Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20719
Sixel-Doring, F., Trautmann, E., Mollenhauer, B., et al. (2011). Associated factors for REM sleep behavior disorder in Parkinson disease [J]. Neurology, 77(11), 1048–1054.
Soehner, A. M., Bertocci, M. A., Manelis, A., et al. (2016). Preliminary investigation of the relationships between sleep duration, reward circuitry function, and mood dysregulation in youth offspring of parents with bipolar disorder [J]. Journal of Affective Disorders, 144–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2016.03.074
Sorensen, G. L., Kempfner, J., Zoetmulder, M., et al. (2012). Attenuated heart rate response in REM sleep behavior disorder and Parkinson’s disease [J]. Movement Disorders, 27(7), 888–894.
Stephenson, R., Houghton, D., Sundarararjan, S., et al. (2010). Odor identification deficits are associated with increased risk of neuropsychiatric complications in patients with Parkinson's disease [J]. Movement Disorders, (25). https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23234
Takahashi, E., Ohki, K., & Kim, D. S. (2007). Diffusion tensor studies dissociated two fronto-temporal pathways in the human memory system [J]. NeuroImage, 34(2), 827–838.
Tessitore, A., Micco, R. D., Giordano, A., et al. (2017). Intrinsic brain connectivity predicts impulse control disorders in patients with Parkinson's disease [J]. Movement Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27139
Tirapu-Ustarroz, J. (2012). Neuropsychology of dreams [J]. Revista De Neurologia, 55(2), 101–110.
Valli, M. et al. (2021). Extra‐striatal dopamine in Parkinson's disease with rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder [J]. Journal of Neuroscience Research. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24779
Vendette, M., Gagnon, J. F. O., Soucy, J. P., et al. (2011). Brain perfusion and markers of neurodegeneration in rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder [J]. Movement Disorders, 26(9), 1717–1724.
Vendette, M., Montplaisir, J., Gosselin, N., et al. (2012). Brain perfusion anomalies in rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder with mild cognitive impairment [J]. Movement Disorders, 27(10), 1255–1261.
Vijayraghavan, S., Wang, M., Birnbaum, S. G., et al. (2007). Inverted-U dopamine D1 receptor actions on prefrontal neurons engaged in working memory [J]. Nature Neuroscience, 10(3), 376–384.
Wakasugi, N., Togo, H., Mukai, Y., et al. (2021). Prefrontal network dysfunctions in rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder [J]. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, (10). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2021.03.005
Wang, Y., Zhang, S., Yang, H., et al. (2021). Altered cerebellum functional network on newly diagnosed drug-naive Parkinson’s disease patients with anxiety [J]. Translational Neuroscience, 12(1), 415–424.
Weintraub, D., Oehlberg, K. A., Katz, I. R., et al. (2006). Test characteristics of the 15-item geriatric depression scale and Hamilton depression rating scale in Parkinson disease [J]. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 14(2), 169–175.
Williams-Gray, C. H., Hampshire, A., Robbins, T. W., Owen, A. M., & Barker, R. A. (2007).Catechol O-Methyltransferase val158 met genotype influences frontoparietal activity during planning in patients with Parkinson's disease [J]. Journal of Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0774-07.2007
Woolrich, M. W., Ripley, B. D., Brady, M., et al. (2001). Temporal autocorrelation in univariate linear modeling of FMRI data [J]. NeuroImage, 14(6), 1370–1386.
Ye, G., Li, Y., Zhou, L., et al. (2020). Predictors of conversion to α-synucleinopathy diseases in idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder [J]. Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, 10(4). https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-202243
Zhan, Z. W., Lin, L. Z., Yu, E. H., et al. (2018) Abnormal resting-state functional connectivity in posterior cingulate cortex of Parkinson's disease with mild cognitive impairment and dementia [J]. Cns Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 24(10). https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12838
Zhao, Y. J., Wee, H. L., Chan, Y. H., et al. (2010). Progression of Parkinson’s disease as evaluated by Hoehn and Yahr stage transition times [J]. Movement Disorders, 25(6), 710–716.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81871002, 81471334, 81100981) and the National Key Clinical Specialties Construction Program of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and study design (Oumei Cheng, Juan Peng and Jinjing Liu), data collection or acquisition (Jinjing Liu, Xiaoya Zou, Jinming Gu, Qian Yu, Zhaoying Dong, Hongzhou Zuo, Xiaocui Chen, Xinyi Du, Dezhi Zou and Yu Han), statistical analysis (Jinjing Liu and Jinming Gu), interpretation of results (Jinjing Liu and Xiaoya Zou), drafting the manuscript work or revising it critically for important intellectual content (Oumei Cheng, Juan Peng and Jinjing Liu) and approval of final version to be published and agreement to be accountable for the integrity and accuracy of all aspects of the work (All authors).
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
All subjects recruited into the study provided written informed consent, and the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital, Chongqing Medical University in China, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Xiaoya Zou and Jinming Gu are co-first author.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Zou, X., Gu, J. et al. Altered connectivity in the cognitive control-related prefrontal cortex in Parkinson’s disease with rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. Brain Imaging and Behavior 17, 702–714 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-023-00796-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-023-00796-0