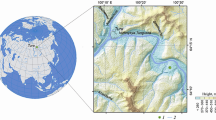
Abstract
Evapotranspiration is an important parameter used to characterize the water cycle of ecosystems. To understand the properties of the evapotranspiration and energy balance of a subalpine forest in the southeastern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, an open-path eddy covariance system was set up to monitor the forest from November 2020 to October 2021 in a core area of the Three Parallel Rivers in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. The results show that the evapotranspiration peaked daily, the maximum occurring between 11:00 and 15:00. Environmental factors had significant effects on evapotranspiration, among them, net radiation the greatest (R2 = 0.487), and relative humidity the least (R2 = 0.001). The energy flux varied considerably in different seasons and sensible heat flux accounted for the main part of turbulent energy. The energy balance ratio in the dormant season was less than that in the growing season, and there is an energy imbalance at the site on an annual time scale.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiro B (2009) Measuring boreal forest evapotranspiration using the energy balance residual. J Hydrol X 366(1–4):112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.12.021
Aubinet M, Grelle A, Ibrom A, Rannik Ü, Moncrieff J, Foken T, Vesala T (2000) Estimates of the annual net carbon and water exchange of forests: the EUROFLUX methodology. Adv Ecol Res 30:113–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60018-5
Baldocchi D, Falge E, Gu L, Olson R, Hollinger D, Running S, Anthoni P, Bernhofer C, Davis K, Evans R, Fuentes J, Goldstein A, Katul G, Law B, Lee X, Malhi Y, Meyers T, Munger W, Oechel W, Paw KT, Pilegaard K, Schmid HP, Valentini R, Verma S, Vesala T, Wilson K, Wofsy S (2001) FLUXNET: a new tool to study the temporal and spatial variability of ecosystem-scale carbon dioxide, water vapor, and energy flux densities. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 82(11):2415–2434. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(2001)082%3c2415:fantts%3e2.3.co;2
Baldocchi D, Finnigan J, Wilson K, Falge E (2000) On measuring net ecosystem carbon exchange over tall vegetation on complex terrain. Boundary Layer Meteorol 96:257–291. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1002497616547
Berryman EM, Vanderhoof MK, Bradford JB, Hawbaker TJ, Henne PD, Burns SP, Frank JM, Birdsey RA, Ryan MG (2018) Estimating soil respiration in a subalpine landscape using point, terrain, climate, and greenness data. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 123(10):3231–3249. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018jg004613
Bowen IS (1926) The ratio of heat losses by conduction and by evaporation from any water surface. Phys Rev 27(6):779–787. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.27.779
Cao SK, Cao GC, Chen KL, Han G, Liu Y, Yang YF, Li XD (2019) Characteristics of CO2, water vapor, and energy exchanges at a headwater wetland ecosystem of the Qinghai Lake. Can J Soil Sci 99(3):227–243. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjss-2018-0104
Chen YM, Xue YJ, Hu YM (2018) How multiple factors control evapotranspiration in North America evergreen needleleaf forests. Sci Total Environ 622–623:1217–1224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.038
Cheng GW, Yu XX, Zhao YT, Zhou YM, Luo J (2003) Evapotranspiration simulation of subalpine forest area in Gongga Mountain. J Beijing for Univ 25(1):23–27 ((in Chinese))
Feng XY, Liu HJ, Feng DX, Tang XP, Li L, Chang J, Tanny J, Liu RH (2023) Quantifying winter wheat evapotranspiration and crop coefficients under sprinkler irrigation using eddy covariance technology in the North China Plain. Agric Water Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2022.108131
Gao GL, Feng Q, Liu XD, Zhao YH (2021) Measuring and modeling evapotranspiration of a Populus euphratica forest in northwestern China. J Forestry Res 32(5):1963–1977. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-020-01228-1
Gao GL, Zhang XY, Yu TF, Liu BH (2015) Comparison of three evapotranspiration models with eddy covariance measurements for a Populus euphratica Oliv. forest in an arid region of northwestern China. J Arid Land 8(1):146–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-015-0017-0
Gao X, Du ZY, Yang QS, Zhang JS, Li YT, Wang XJ, Gu FX, Hao WP, Yang ZK, Liu DX, Chu JM (2022) Energy partitioning and evapotranspiration in a black locust plantation on the Yellow River Delta, China. J Forestry Res 33(4):1219–1232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-021-01376-y
Garratt JR (1993) Sensitivity of climate simulations to land-surface and atmospheric boundary-layer treatments—a review. J Clim 6(3):419–448. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1993)006%3c0419:socstl%3e2.0.co;2
Gonzalez G, Ley RE, Schmidt SK, Zou X, Seastedt TR (2001) Soil ecological interactions: comparisons between tropical and subalpine forests. Oecologia 128(4):549–556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420100685
Heijmans MMPD, Arp WJ, Chapin FS (2004) Controls on moss evaporation in a boreal black spruce forest. Glob Biogeochem Cycles. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003gb002128
Hertzberg M, Schreuder H (2016) Role of atmospheric carbon dioxide in climate change. Energy Environ 27(6–7):785–797. https://doi.org/10.1177/0958305x16674637
Javadian M, Behrangi A, Smith WK, Fisher JB (2020) Global trends in evapotranspiration dominated by increases across large cropland regions. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071221
Jia X, Mu Y, Zha TS, Wang B, Qin SG, Tian Y (2020) Seasonal and interannual variations in ecosystem respiration in relation to temperature, moisture, and productivity in a temperate semi-arid shrubland. Sci Total Environ 709:136–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136210
Knowles JF, Blanken PD, Williams MW, Chowanski KM (2012) Energy and surface moisture seasonally limit evaporation and sublimation from snow-free alpine tundra. Agric for Meteorol 157:106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2012.01.017
Knowles JF, Burns SP, Blanken PD, Monson RK (2015) Fluxes of energy, water, and carbon dioxide from mountain ecosystems at Niwot Ridge, Colorado. Plant Ecol Divers 8(5–6):663–676. https://doi.org/10.1080/17550874.2014.904950
Kuang X, Jiao JJ (2016) Review on climate change on the Tibetan Plateau during the last half century. J Geophys Res Atmos 121(8):3979–4007. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015jd024728
Langs LE, Petrone RM, Pomeroy JW (2021) Subalpine forest water use behaviour and evapotranspiration during two hydrologically contrasting growing seasons in the Canadian Rockies. Hydrol Process. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.14158
Leuning R, King KM (1992) Comparison of eddy-covariance measurements of CO2 fluxes by open- and closed-path CO2 analysers. Boundary Layer Meteorol 59(3):297–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00119818
Li J, Jiang S, Wang B, Jiang WW, Tang YH, Du MY, Gu S (2013) Evapotranspiration and its energy exchange in alpine meadow ecosystem on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. J Integr Agric 12(8):1396–1401. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(13)60546-8
Li XW, Zhou JL, Jin MG, Liu YF, Li Q (2012) Experiments on evaporation of high-tds phreatic water in an arid area. Adv Mat Res 446–449:2815–2823. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.446-449.2815
Liao QW, Li XY, Shi FZ, Deng YH, Wang P, Wu TY, Wei JQ, Zuo FL (2022) Diurnal evapotranspiration and its controlling factors of alpine ecosystems during the growing season in northeast Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Water. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14050700
Lin Y, Wang GX, Guo JY, Sun XY (2012) Quantifying evapotranspiration and its components in a coniferous subalpine forest in Southwest China. Hydrol Process 26(20):3032–3040. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.8321
Lin YX, Zhang YP, Fei XH, Song QH, Xu K, Deng Y, Liu WW, Chen AG, Li PG, Huang H, Jin YQ (2019) Comparative study of evapotranspiration characteristics over different forest ecosystems in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. J Yunnan Univ Nat Sci Ed 41(1):205–218. https://doi.org/10.7540/j.ynu.20170568. (in Chinese)
Liu XD, Dong BW (2013) Influence of the Tibetan Plateau uplift on the Asian monsoon-arid environment evolution. Sci Bull 58(34):4277–4291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-013-5987-8(inChinese)
Liu YB, Qiu GY, Zhang HS, Yang YH, Zhang YS, Wang Q, Zhao WZ, Jia L, Ji XB, Xiong YJ, Yan CH, Ma N, Han SM, Cui YF (2022) Shifting from homogeneous to heterogeneous surfaces in estimating terrestrial evapotranspiration: review and perspectives. Sci China Earth Sci 65(2):197–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-020-9834-y
Ma JY, Wang MJ (2023) The pathway for implementing sustainable livelihood capital among community residents within the “Three Parallel Rivers” World Natural Heritage Site. IJGP 11(3):527–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgeop.2023.08.004
Ma N, Zhang YS, Guo YH, Gao HF, Zhang HB, Wang YF (2015) Environmental and biophysical controls on the evapotranspiration over the highest alpine steppe. J Hydrol 529:980–992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.09.013
Mackay DS, Ahl DE, Ewers BE, Gower ST, Burrows SN, Samanta S, Davis KJ (2002) Effects of aggregated classifications of forest composition on estimates of evapotranspiration in a northern Wisconsin forest. Glob Chang Biol 8:1253–1265. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2002.00554.x
Mao KS, Wang Y, Liu JQ (2021) Evolutionary origin of species diversity on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. J Syst Evol 59(6):1142–1158. https://doi.org/10.1111/jse.12809
Mayr S, Schmid P, Rosner S (2019) Winter embolism and recovery in the conifer shrub Pinus mugo L. Forests 10:941. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10110941
Mészároš I, Miklánek P (2009) Influence of vegetation cover on evapotranspiration patterns in mountainous areas. Biologia 64(3):610–614. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-009-0098-3
Moncrieff JB, Massheder JM, de Bruin H, Elbers J, Friborg T, Heusinkveld B, Kabat P, Scott S, Soegaard H, Verhoef A (1997) A system to measure surface fluxes of momentum, sensible heat, water vapour and carbon dioxide. J Hydrol 188–189:589–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(96)03194-0
Monson RK, Turnipseed AA, Sparks JP, Harley PC, Scott-Denton LE, Sparks K, Huxman TE (2002) Carbon sequestration in a high-elevation, subalpine forest. Glob Chang Biol 8:459–478. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2002.00480.x
Monteith J (1965) Evaporation and environment. Symp Soc Exp Biol 19:205–234
Nakai T, Kim Y, Busey RC, Suzuki R, Nagai S, Kobayashi H, Park H, Sugiura K, Ito A (2013) Characteristics of evapotranspiration from a permafrost black spruce forest in interior Alaska. Polar Sci 7(2):136–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polar.2013.03.003
Ohta T, Hiyama T, Tanaka H, Kuwada T, Maximov TC, Ohata T, Fukushima Y (2001) Seasonal variation in the energy and water exchanges above and below a larch forest in eastern Siberia. Hydrol Process 15:1459–1476. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.219
Oki T, Kanae S (2006) Global hydrological cycles and world water resources. Science 313(5790):1068–1072. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1128845
Sarangi C, Chakraborty TC, Tripathi S, Krishnan M, Morrison R, Evans J, Mercado LM (2022) Observations of aerosol-vapor pressure deficit-evaporative fraction coupling over India. Atmos Chem Phys 22(5):3615–3629. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-22-3615-2022
Scheidl C, Heiser M, Vospernik S, Lauss E, Perzl F, Kofler A, Kleemayr K, Bettella F, Lingua E, Garbarino M, Skudnik M, Trappmann D, Berger F (2020) Assessing the protective role of alpine forests against rockfall at regional scale. Eur J for Res 139(6):969–980. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-020-01299-z
Schotanus P, Nieuwstadt FTM, De Bruin HAR (1983) Temperature measurement with a sonic anemometer and its application to heat and moisture fluxes. Boundary Layer Meteorol 26(1):81–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00164332
Scott St G (2019) The aberrant global synchrony of present-day warming. Nature 571:483–484. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-02179-2
Sofo A, Mininni AN, Ricciuti P (2020) Soil macrofauna: a key factor for increasing soil fertility and promoting sustainable soil use in fruit orchard agrosystems. Agronomy. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10040456
Sun J, Desjardins R, Mahrt L, MacPherson I (1998) Transport of carbon dioxide, water vapor, and ozone by turbulence and local circulations. J Geophys Res 103(D20):25873–25885. https://doi.org/10.1029/98JD02439
Swinbank WC (1951) The measurement of vertical transfer of heat and water vapor by eddies in the lower atmosphere. J Meteorol 8(3):135–145. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1951)008%3c0135:tmovto%3e2.0.co;2
Teskey RO, Hinckley TM, Grier CC (1984) Temperature-Induced change in the water relations of Abies amabilis (Dougl.) Forbes. Plant Physiol 74:77–80. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.74.1.77
Thornthwaite CW, Holzman B (1943) Measurement of evaporation from land and water surfaces. Geogr Rev 33(2):343–344. https://doi.org/10.2307/209794
Wang CY, Wang JN, Naudiyal N, Wu N, Cui X, Wei YQ, Chen QT (2021a) Multiple effects of topographic factors on spatio-temporal variations of vegetation patterns in the three parallel rivers region, southeast Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens 14(1):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010151
Wang KX, Ma N, Zhang YH, Qiang YH, Guo YH (2022) Evapotranspiration and energy partitioning of a typical alpine wetland in the central Tibetan Plateau. Atmos Res 267:105931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2021.105931
Wang KC, Wang PC, Li ZQ, Cribb M, Sparrow M (2007) A simple method to estimate actual evapotranspiration from a combination of net radiation, vegetation index, and temperature. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JD008351
Wang SR, Guo LL, He B, Lyu YLY, Li TW (2020) The stability of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau ecosystem to climate change. Phys Chem Earth, Parts a/b/c. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2019.102827
Wang TX, Zhang HY, Zhao JJ, Guo XY, Xiong T, Wu RH (2021b) Shifting contribution of climatic constraints on evapotranspiration in the boreal forest. Earths Future 9(8):e2021EF002104. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021EF002104
Widmoser P, Wohlfahrt G (2018) Attributing the energy imbalance by concurrent lysimeter and eddy covariance evapotranspiration measurements. Agric for Meteorol 263:287–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2018.09.003
Xu XD, Lu CG, Shi XH, Gao ST (2008) World water tower: an atmospheric perspective. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008gl035867
Yang LS, Feng Q, Adamowski JF, Alizadeh MR, Yin ZL, Wen XH, Zhu M (2021) The role of climate change and vegetation greening on the variation of terrestrial evapotranspiration in northwest China’s Qilian Mountains. Sci Total Environ 759:143532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143532
Zhang FW, Li HQ, Wang WY, Li YK, Lin L, Guo XW, Du YG, Li Q, Yang YS, Cao G, Li YN (2018a) Net radiation rather than surface moisture limits evapotranspiration over a humid alpine meadow on the northeastern Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Ecohydrology 11(2):e1925. https://doi.org/10.1002/eco.1925
Zhang H, Dou RY (2020) Interannual and seasonal variability in evapotranspiration of alpine meadow in the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Arab J Geosci 13(18):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06022-1
Zhang K, Kimball JS, Running SW (2016) A review of remote sensing based actual evapotranspiration estimation. Wires Water 3(6):834–853. https://doi.org/10.1002/wat2.1168
Zhang SY, Li XY, Ma YJ, Zhao GQ, Li L, Chen J, Jiang ZY, Huang YM (2014) Interannual and seasonal variability in evapotranspiration and energy partitioning over the alpine riparian shrub Myricaria squamosa Desv. on Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Cold Reg Sci Technol 102:8–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2014.02.001
Zhang XT, Wang L, Chen DL (2018b) How does temporal trend of reference evapotranspiration over the Tibetan Plateau change with elevation? Int J Clim. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5951
Zhao J, Xu ZX, Singh VP, Zuo DP, Li M (2016) Sensitivity of potential evapotranspiration to climate and vegetation in a water-limited basin at the northern edge of Tibetan Plateau. Water Resour Manag 30(13):4667–4680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1446-z
Zhu GF, Lu L, Su YH, Wang XF, Cui X, Ma JZ, He JH, Zhang K, Li CB (2014) Energy flux partitioning and evapotranspiration in a sub-alpine spruce forest ecosystem. Hydrol Process 28(19):5093–5104. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9995
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Neha Bisht for her substantial comments and language revision on improving the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Project funding: This research was supported by the CAS “Light of West China” Program (2021XBZG-XBQNXZ-A-007), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31971436), and the State Key Laboratory of Cryospheric Science, Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy Sciences (SKLCS-OP-2021-06).
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com.
Corresponding editor: Tao Xu.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, N., Wang, J., Luo, D. et al. Unveiling evapotranspiration patterns and energy balance in a subalpine forest of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: observations and analysis from an eddy covariance system. J. For. Res. 35, 53 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-024-01708-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-024-01708-8