Abstract
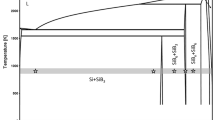
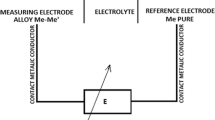
The paper addresses the measurement of the partial molar Gibbs energy (\(\Delta {\stackrel{-}{G}}_{Bi},\Delta {\stackrel{-}{G}}_{Sn}\)), thermodynamic activity (\({a}_{Bi},{a}_{Sn}\)) and the activity coefficient (\({\gamma }_{Bi ,}{\gamma }_{Sn}\)) of the Bi-Sn binary system at 600 and 903 K. The experiments were carried out in an H-shaped electrochemical cell based on the measurement of electromotive force with the reversible electrode–solid electrolyte. The measuring electrode was made of Bix-Sn1−x alloys with x ranging from 0.1 to 0.9, step 0.1. The reference electrode was manufactured from pure bismuth, while the electrolyte was a mixture of 17% moles KCl and 83% moles SnCl2 (selected because it contains free ions Sn and the melting temperature of the electrolyte (563 K). To obtain reliable experimental data, each measurement was repeated five times and the standard deviation/error was calculated. Based on error propagation law, the mathematical expression of the compound uncertainty for each quantity addressed in the paper was derived. An innovative derivation is presented for the compound uncertainty (uc) of γSn. The values of the \(\Delta {\stackrel{-}{G}}_{Bi},\Delta {\stackrel{-}{G}}_{Sn}\), aBi, aSn, γBi and γSn are accompanied by their expanded uncertainty having a 95% confidence level. The novelties addressed in the paper are the values of ΔGBi, ΔGSn, aBi, aSn, γBi and γSn in the Bi-Sn binary system at 600 and 903 K.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
References
A. Roshanghias, A. Yakymovych, J. Bernardi, and H. Ipser, Synthesis and Thermal Behavior of Tin-Based Alloy (Sn-Ag-Cu) Nanoparticles, Nanoscale, 2015, 13(7), p 5843–5851
M. Abtew, and G. Selvaduray, Lead-Free Solders in Microelectronics, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2000, 27, p 95–141
F. Frongia, M. Pilloni, A. Scano, A. Ardu, C. Cannas, A. Musinu, G. Borzone, S. Delsante, R. Novakovic, and G. Ennas, Synthesis and Melting Behaviour of Bi, Sn and Sn-Bi Nanostructured Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 623, p 7–14
J. Vizdal, M.H. Braga, A. Kroupa, K.W. Richter, D. Soares, L.F. Malheiros, and J. Ferreira, Thermodynamic Assessment of the Bi-Sn-Zn System, Calphad, 2007, 31, p 438–448
L. Wani, A. Ara, and A. Usmani, Lead Toxicity: A Review, Interdiscipl. Toxicol., 2015, 8(2), p 55–64
Eur-Lex-32002L0095, Directive 2002/95/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 January 2003 on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, Official Journal L 037, (2003) 0019–0023.
S.I. Bogatyrenko, A.A. Minenkov, and A.P. Kryshtal, Supercooling Under Crystallization of Bi-Sn Eutectic Alloy in Contact with Bi, Sn and Amorphous C, Vacuum, 2018, 152, p 1–7
T.T. Issa, F.N. Jasim, H.J. Mohammed, and Z.K. Abbas, Improvement of the Microstructure of Sn-Bi Lead Free Solder Alloy, AIP Conf. Proc., 2017, 1809(020024), p 1–5
I. Plotog, G. Varzaru, B. Mihailescu, M. Branzei, A. Bibis, I. Cristea, Lead/Lead Free Solder Joints Comparative Shear Tests Function of Working Temperature and Soldering Thermal Profile, IEEE SIITME, (2013) 283–286.
M. Branzei, F. Miculescu, A. Bibis, I. Cristea, I. Plotog, G. Varzaru, B. Mihailescu, Lead/Lead Free Solder Joints Comparative Electrical Tests as Function of Microstructure and Soldering Thermal Profile, IEEE SIITME (2013) 255–258.
Eur-Lex-32011L0065, Directive 2011/65/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 8 June 2011 on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment Text with EEA relevance, Official Journal L 174 (2011) 88–110.
M. Branzei, B. Mihailescu, I. Pencea, Lead/Lead–Free Solder Alloys Shear Tests Correlations with Structure at Different Temperatures IEEE ISSET (2014) 252–255.
A.M. Erer, S. Oguz, Y. Türen, Influence of Bismuth (Bi) Addition on Wetting Characteristics of Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu Solder Alloy on Cu Substrate, Eng. Sci. Technol. Int J. 21 (2018) 1159–1163.
M.I.I. Ramli, M.S.S. Yusof, M.A.A.M. Salleh, R.M. Said, K. Nogita, Influence of Bi Addition on Wettability and Mechanical Properties of Sn-0.7 Cu Solder Alloy, Solid State Phenom. 273 (2018) 27–33.
I. Plotog, G. Dumitru, N.D. Codreanu, A. Vasile, M. Branzei , I. Pencea, M. Tarcolea, Microstructure Comparative Analysis of the Solder Joints Based on SAC/SN100 Soldering Alloy Type Depending on the Cooling Rate, IEEE SIITME (2012) 167–172.
Th. Heckmann, Th. Souvignet, S. Lepeer, and D. Naccache, Low-Temperature Low-Cost 58 Bismuth—42 Tin Alloy Forensic Chip Re-balling and Re-soldering, Digit. Invest., 2016, 19, p 60–68
P. Suksongkarm, S. Rojananan, and S. Rojananan, Using Recycled Bismuth-Tin Solder in Novel Machinable Lead-Free Brass, Mater. Trans., 2017, 58(12), p 1754–1760
O.G. Shpyrko, AYu. Grigoriev, R. Streitel, D. Pontoni, P.S. Pershan, M. Deutsch, B. Ocko, M. Meron, and B. Lin, Atomic-Scale Surface Demixing in a Eutectic Liquid BiSn Alloy, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2005, 95(10), p 1–4
S.H. Chen, C.C. Chen, and C.G. Chao, Novel Morphology and Solidification Behavior of Eutectic Bismuth-Tin (Bi-Sn) Nanowires, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 481, p 270–273
I. Manasijević, L. Balanović, T.H. Grgurić, D. Minić, and M. Gorgievski, Study of Microstructure and Thermal Properties of the Low Melting Bi-In-Sn Eutectic Alloys, Mat. Res., 2018, 21(6), p 1–8
D.R. Frear, and P.T. Vianco, Intermetallic Growth and Mechanical Behavior of Low and High Melting Temperature Solder Alloys, Metall Mater Trans A, 1994, 25, p 1509–1523
F. Niculescu, D. Marcu, Ş Burciu, M. Buzatu, M.I. Petrescu, N. Şerban, and G. Iacob, Experimental Researches Regarding the Thermodynamic Activities in the Binary Pb-Sb Alloy System, J. Phase Equilib. Diff., 2017, 38(5), p 700–706
F. Niculescu, I. Constantin, M. Buzatu, D.F. Marcu, I. Csaki, The Thermodynamic Properties of the Pb-Sb System, U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series B 78 (4) (2016), 167–174.
Z. Moser, W. Gasior, and J. Pstrus, Surface Tension Measurements of the Bi-Sn and Sn-Bi-Ag Liquid Alloys, J. Electron. Mater., 2001, 30(9), p 1104–1111
Z. Guo, W. Yuan, M. Hindler, and A. Mikula, Thermodynamic Properties of Liquid Au-Bi-Sn Alloys, J. Chem. Thermodyn., 2012, 48(6), p 201–206
Z. Guo, M. Hindler, W. Yuan, and A. Mikula, Thermodynamic Properties of Liquid Au–Cu–Sn Alloys Determined From Electromotive Force Measurements, Thermochim. Acta, 2011, 525(1–2), p 183–189
C.A. Popescu, D. Taloi, Thermodynamic Calculations in Liquid Al-Sn Alloys Systems, U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series B 69 (3) (2007) 77–84.
R. Hultgen, Ed., Selected values of the thermodynamic properties of binary alloys ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1973
M.A. Imam, J.S. Young, and R.G. Reddy, Determination of Thermodynamic Properties of Si-B Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2019, 50, p 981–990
T. Lichtenstein, J. Gesualdi, Yu. Chen-Ta, and H. Kim, Thermochemical Properties and Phase Transitions of Ba-Sn Alloys from Thermal Characterization and Emf Measurements, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 811, p 151531
M.A. Imam, and R.G. Reddy, Thermodynamic Properties of Magnesium-Boron Binary Alloys Determined Using Solid-State Electrochemical Measurements, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2018, 49, p 3504–3512
G. Kaptay, On the Tendency of Solutions to Tend Toward Ideal Solutions at High Temperatures, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, 43, p 531–543
R.I. Gayley, E.A. Lynton, and B. Serin, Specific Heats of Tin Alloys and Their Relation to the Superconducting Transition Temperature, Phys. Rev., 1962, 126, p 43–49
H.O. von Samson-Himmelstjerna, Heat Capacity and Heat of Formation of Molten Alloys, Z. Metallk., 1936, 28, p 197–201
S. Nagasaki, and E. Fujita, A Study of the Phase Diagrams by the Specific Heat Measurements (II), J. Jpn. I. Met., 1952, 16(6), p 317–321
Y. Tiba, T. Matsushima, and K. Ono, Thermodynamics of Fused Bismuth-Tin Alloy and Fused Bismuth-Arsenic Alloy, Bull. Res. Inst. Miner. Dressing Metall., 1964, 20(1), p 41–49
A. Podgornik, and R. Bhargava, Meritve Energetskih Sprememb Pri Tvorbi Zmesnih Kristalov, Rudarsko-Met. Zbornik, 1960, 4, p 357–362
H. Seltz, and F.J. Dunkerley, A Thermodynamic Study of the Tin—Bismuth System, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1942, 64, p 1392–1395
C. Wagner, and G. Englehardt, Beitrag zur Kenntniss der Thermodynamischen Aktivitaten in binaren Legierungen, Z. Physik. Chem., 1932, 159A, p 241–267
S.A. Cho, R. Camisotti, M.H., Velez, Detailed Assessment of Partial Thermodynamic Quantities of Tin In Molten Bi-Sn Alloys from Electromotive Force Measurements, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 21B (1990) 87–96.
N. Asryan, and A. Mikula, Thermodynamic Properties of Liquid Bi-Sn Alloys, Int. J. Mater. Res., 2004, 95(3), p 132–135
N. Asryan, and A. Mikula, Thermodynamic Properties of Bi–Sn Melts, Inorg. Mater., 2004, 40, p 386–390
A. Yazawa, and K. Koike, Activity Measurement in Sn-Pb, Sn-Bi, Sn-Tl and Sn-Pb-Bi Alloys at 110 °C, J. Min. Met. Inst. Japan, 1968, 184, p 1593–1596
A. Yazawa, T. Kawashima, and K. Itagaki, Measurements of Heats of Mixing in Molten Alloys with the Adiabatic Calorimeter, J. Japan Inst. Metals, 1968, 32, p 1281–1287
F.E. Witting, F. Huber, The energetics of metallic systems. VII. Heats of Mixing in the Liquid Binary Systems Bismuth-Tin and Bismuth-Lead at 475 Degree, Z. Physik. Chem. Frankfurt, 18 (1958) 330–347.
M. Kawakami, The Heat of Mixing of Metals, Sci. Rep. Tohoku. Imp. Univ., 1927, 16, p 915–935
M.R. Kumar, S. Mohan, and C.K. Behera, Thermodynamic Accessment Experimentally on Bi-Sn System by Calorimeter, Mater. Today Proc., 2018, 5, p 27777–27785
A. Kroupa, A.T. Dinsdale, A. Watson, J. Vrestal, and A. Zemanova, Study of the Advanced Materials for Lead Free Soldering, Journal of Mining and Metallurgy B., 2007, 43, p 113–123
A. Kroupa, A.T. Dinsdale, A. Watson, J. Vrestal, J. Vizdal, and A. Zemanova, The Development of the COST 531 Lead-Free Solders Thermodynamic Database (Review), JOM, 2007, 59, p 20–25
P.W. Atkins, and J. de Paula, Physical Chemistry, 7th edn. W.H. Freeman and Co., NY, 2001.
A. Magnus, and M. Mannheimer, The Measurements of the Enthalpy of Mixing of Liquid Metals, Z. Physik. Chem., 1926, 121, p 267–278
ISO/IEC Guide 98-3:2008 (JCGM/WG1/100) Uncertainty of measurement—Part 3: Guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement (GUM:1995), http://www.iso.org/sites/JCGM/JCGM-introduction.htm (2008).
P.V. Clark, SC-R-65-930, V1, Physical Properties of Fused Salt Mixtures, NSA-19-042460, Sandia Laboratory, Albuquerque, (1965) 10.
P.W. Watkins, Physical Chemistry, 5th edn. W.H. Freeman and Co., NY, 1994.
I. Pencea, Metallurgy—Advances in Materials and Processes, Chapter 6. IntechOpen Limited, London, 2012.
S.L.R. Ellison, A. Williams, Eds., EURACHEM/CITAC Guide Quantifying Uncertainty in Analytical Measurement, Third Edition, 2012). http://www.eurachem.org.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niculescu, E., Iacob, G., Niculescu, F. et al. Experimental Determination of the Activities of Liquid Bi-Sn Alloys. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 42, 278–289 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-021-00880-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-021-00880-2