Abstract
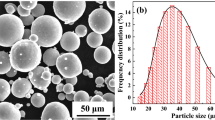
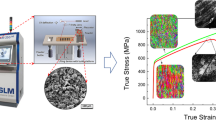
In this study, we printed high layer thickness Ti-6Al-4V parts using a stable keyhole melt pool mode. Firstly, we performed the single tracks experiments to obtain the size of the melt pool at different scanning speeds. Results demonstrated that the depths of the molten pools are high which makes it possible to improve the building rate by increasing layer thickness. Under the conditions of 170 W laser power, 60 μm layer thickness, and a scanning speed of 900 mm/s, the building rate, relative density, microhardness, ultimate tensile strength (UTS), yield strength (YS), and elongations are 424 HV, 3.78 mm3/s, 99.4%, 1283 MPa, and 1202 MPa, 7.8%, respectively. The results showed that employing a stable keyhole mode enables the formation of high layer thickness samples which had the advantage of both high relative density and exceptional mechanical properties.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
A.Y. Alfaify, J. Hughes, and K. Ridgway, Critical Evaluation of the Pulsed Selective Laser Melting Process When Fabricating Ti64 Parts Using a Range of Particle Size Distributions, Addit. Manuf., 2018, 19, p 197–204.
H. Azizi, H. Zurob, B. Bose, S. Reza Ghiaasiaan, X. Wang, S. Coulson, V. Duz, and A.B. Phillion, Additive Manufacturing of a Novel Ti-Al-V-Fe Alloy Using Selective Laser Melting, Addit. Manuf., 2018, 21, p 529–535.
A. Khorasani, I. Gibson, U.S. Awan, and A. Ghaderi, The Effect of SLM Process Parameters on Density, Hardness, Tensile Strength and Surface Quality of Ti-6Al-4V, Addit. Manuf., 2019, 25, p 176–186.
J.J. Lin, Y.H. Lv, Y.X. Liu, B.S. Xu, Z. Sun, Z.G. Li, and Y.X. Wu, Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Wall Deposited by Pulsed Plasma Arc Additive Manufacturing, Mater. Des., 2016, 102, p 30–40.
H. Hassanin, L. Finet, S.C. Cox, P. Jamshidi, L.M. Grover, D.E.T. Shepherd, O. Addison, and M.M. Attallah, Tailoring Selective Laser Melting Process for Titanium Drug-Delivering Implants with Releasing Micro-Channels, Addit. Manuf., 2018, 20, p 144–155.
D. Gu, X. Shi, R. Poprawe, D.L. Bourell, R. Setchi, and J. Zhu, Material-Structure-Performance Integrated Laser-Metal Additive Manufacturing, Science, 2021, 372(6545), p eabg1487.
Z. Hu, L. Xue, Y. Yang, X. Zhang, D. Lu, Y. Liu, and M. Wu, Improved Fatigue Life of SLM-Produced TC4 Alloy Treated by a Pulsed Magnetic Field, Mater. Today Commun., 2023, 37, 107160.
P. Sun, Z.Z. Fang, Y. Zhang, and Y. Xia, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting of Powder Produced by Granulation-Sintering-Deoxygenation Method, JOM, 2017, 69(12), p 2731–2737.
M. Ma, Z. Wang, M. Gao, and X. Zeng, Layer Thickness Dependence of Performance in High-Power Selective Laser Melting of 1Cr18Ni9Ti Stainless Steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2015, 215, p 142–150.
H. Schleifenbaum, W. Meiners, K. Wissenbach, and C. Hinke, Individualized Production by Means of High Power Selective Laser Melting, CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol., 2010, 2(3), p 161–169.
X. Shi, S. Ma, C. Liu, C. Chen, Q. Wu, X. Chen, and J. Lu, Performance of High Layer Thickness in Selective Laser Melting of Ti6Al4V, Materials, 2016, 9(12), p 975.
W. Zhang, W. Hou, L. Deike, and C.B. Arnold, Using a Dual-Laser System to Create Periodic Coalescence in Laser Powder Bed Fusion, Acta Mater., 2020, 201, p 14–22.
P. Promoppatum, Dual-Laser Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing: Computational Study of the Effect of Process Strategies on Thermal and Residual Stress Formations, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2022, 121(1–2), p 1337–1351.
M. Guo, D. Gu, L. Xi, L. Du, H. Zhang, and J. Zhang, Formation of Scanning Tracks during Selective Laser Melting (SLM) of Pure Tungsten Powder: Morphology, Geometric Features and Forming Mechanisms, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2019, 79, p 37–46.
W.E. King, H.D. Barth, V.M. Castillo, G.F. Gallegos, J.W. Gibbs, D.E. Hahn, C. Kamath, and A.M. Rubenchik, Observation of Keyhole-Mode Laser Melting in Laser Powder-Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2014, 214(12), p 2915–2925.
C. Tang, J.L. Tan, and C.H. Wong, A Numerical Investigation on the Physical Mechanisms of Single Track Defects in Selective Laser Melting, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 2018, 126, p 957–968.
N.T. Aboulkhair, I. Maskery, C. Tuck, I. Ashcroft, and N.M. Everitt, On the Formation of AlSi10Mg Single Tracks and Layers in Selective Laser Melting: Microstructure and Nano-Mechanical Properties, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2016, 230, p 88–98.
Y. Huang, T.G. Fleming, S.J. Clark, S. Marussi, K. Fezzaa, J. Thiyagalingam, C.L.A. Leung, and P.D. Lee, Keyhole Fluctuation and Pore Formation Mechanisms during Laser Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(1), p 1170.
E. Soylemez, High Deposition Rate Approach of Selective Laser Melting through Defocused Single Bead Experiments and Thermal Finite Element Analysis for Ti-6Al-4V, Addit. Manuf., 2020, 31, 100984.
C. Tenbrock, Influence of Keyhole and Conduction Mode Melting for Top-Hat Shaped Beam Profiles in Laser Powder Bed Fusion, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116514
J. Metelkova, Y. Kinds, K. Kempen, C. De Formanoir, A. Witvrouw, and B. Van Hooreweder, On the Influence of Laser Defocusing in Selective Laser Melting of 316L, Addit. Manuf., 2018, 23, p 161–169.
R. Rai, J.W. Elmer, T.A. Palmer, and T. DebRoy, Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow during Keyhole Mode Laser Welding of Tantalum, Ti-6Al-4V, 304L Stainless Steel and Vanadium, J. Phys. Appl. Phys., 2007, 40(18), p 5753.
S. Liu and H. Guo, Balling Behavior of Selective Laser Melting (SLM) Magnesium Alloy, Materials, 2020, 13(16), p 3632.
K.C. Mills, Recommended Values of Thermophysical Properties for Selected Commercial Alloys, Vol 74, Aircraft Engineering and Aerospace Technology, Emerald Group Publishing Limited, 2002.
Z. Gan, Universal Scaling Laws of Keyhole Stability and Porosity in 3D Printing of Metals, Nat. Commun., 2021 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22704-0
V. Juechter, T. Scharowsky, R.F. Singer, and C. Körner, Processing Window and Evaporation Phenomena for Ti-6Al-4V Produced by Selective Electron Beam Melting, Acta Mater., 2014, 76, p 252–258.
L. Thijs, F. Verhaeghe, T. Craeghs, J.V. Humbeeck, and J.-P. Kruth, A Study of the Microstructural Evolution during Selective Laser Melting of Ti-6Al-4V, Acta Mater., 2010, 58(9), p 3303–3312.
S.M. Kelly and S.L. Kampe, Microstructural Evolution in Laser-Deposited Multilayer Ti-6Al-4V Builds: Part II. Thermal Modeling, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, 35(6), p 1869–1879.
X. Shi, S. Ma, C. Liu, Q. Wu, J. Lu, Y. Liu, and W. Shi, Selective Laser Melting-Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Hybrid Fabrication of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 684, p 196–204.
M. Simonelli, Y.Y. Tse, and C. Tuck, Effect of the Build Orientation on the Mechanical Properties and Fracture Modes of SLM Ti-6Al-4V, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 616, p 1–11.
D. Gu, K. Lin, J. Ma, W. Chen, J. Huang, X. Sun, and M. Chu, Selective Laser Melting of Titanium Parts: Influence of Laser Process Parameters on Macro- and Microstructures and Tensile Property, Powder Technol., 2019, 342, p 371–379.
J.J.S. Dilip, S. Zhang, C. Teng, K. Zeng, C. Robinson, D. Pal, and B. Stucker, Influence of Processing Parameters on the Evolution of Melt Pool, Porosity, and Microstructures in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Parts Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting, Prog. Addit. Manuf., 2017, 2(3), p 157–167.
H. Gong, K. Rafi, H. Gu, T. Starr, and B. Stucker, Analysis of Defect Generation in Ti-6Al-4V Parts Made Using Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing Processes, Addit. Manuf., 2014, 1–4, p 87–98.
S.M. Kelly and S.L. Kampe, Microstructural Evolution in Laser-Deposited Multilayer Ti-6Al-4V Builds: Part I. Microstructural Characterization, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, 35(6), p 1861–1867.
E. Chlebus, B. Kuźnicka, T. Kurzynowski, and B. Dybała, Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviour of Ti-6Al-7Nb Alloy Produced by Selective Laser Melting, Mater Charact, 2011, 62(5), p 488–495.
T. Sercombe, N. Jones, R. Day, and A. Kop, Heat Treatment of Ti-6Al-7Nb Components Produced by Selective Laser Melting, Rapid Prototyp. J., 2008, 14(5), p 300–304.
R. Trivedi, V. Seetharaman, and M.A. Eshelman, The Effects of Interface Kinetics Anisotropy on the Growth Direction of Cellular Microstructures, Metall. Trans. A, 1991, 22(2), p 585–593.
Y. Zhu, J. Li, X. Tian, H. Wang, and D. Liu, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Fabricated Ti-6.5Al-3.5Mo-1.5Zr-0.3Si Titanium Alloy by Laser Additive Manufacturing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 607, p 427–434.
J. Fu, H. Li, X. Song, and M.W. Fu, Multi-Scale Defects in Powder-Based Additively Manufactured Metals and Alloys, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2022, 122, p 165–199.
F1472 Standard Specification for Wrought Titanium-6Aluminum-4Vanadium Alloy for Surgical Implant Applications (UNS R56400), n.d., https://www.astm.org/f1472-20a.html. Accessed 5 June 2023
B. Vrancken, L. Thijs, J.-P. Kruth, and J. Van Humbeeck, Heat Treatment of Ti6Al4V Produced by Selective Laser Melting: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties, J. Alloys Compd., 2012, 541, p 177–185.
X. Yan, S. Yin, C. Chen, C. Huang, R. Bolot, R. Lupoi, M. Kuang, W. Ma, C. Coddet, H. Liao, and M. Liu, Effect of Heat Treatment on the Phase Transformation and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting, J. Alloys Compd., 2018, 764, p 1056–1071.
Z. Liang, Z. Sun, W. Zhang, S. Wu, and H. Chang, The Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure Evolution and Tensile Properties of Selective Laser Melted Ti6Al4V Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 782, p 1041–1048.
W. Shi, Y. Liu, X. Shi, Y. Hou, P. Wang, and G. Song, Beam Diameter Dependence of Performance in Thick-Layer and High-Power Selective Laser Melting of Ti-6Al-4V, Materials, 2018, 11(7), p 1237.
J.D. Madison and L.K. Aagesen, Quantitative Characterization of Porosity in Laser Welds of Stainless Steel, Scr. Mater., 2012, 67(9), p 783–786.
B. Sagbas, G. Gencelli, and A. Sever, Effect of Process Parameters on Tribological Properties of Ti6Al4V Surfaces Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2021, 30(7), p 4966–4973.
A. Gupta, R.K. Khatirkar, A. Kumar, and M.S. Parihar, Investigations on the Effect of Heating Temperature and Cooling Rate on Evolution of Microstructure in an α + β Titanium Alloy, J. Mater. Res., 2018, 33(8), p 946–957.
M. Simonelli, Y.Y. Tse, and C. Tuck, Further Understanding on Ti-6Al-4V Selective Laser Melting Using Texture Analysis, Univ. Texas Austin, 2012 https://doi.org/10.26153/tsw/15367
B. Zhou, J. Zhou, H. Li, and F. Lin, A Study of the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Fabricated by SLM under Vacuum, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 724, p 1–10.
J. Airao, H. Kishore, and C.K. Nirala, Measurement and Analysis of Tool Wear and Surface Characteristics in Micro Turning of SLM Ti6Al4V and Wrought Ti6Al4V, Measurement, 2023, 206, 112281.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Major Project (202202AG050007), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51961017), and the Yunnan Provincial Key Project of Basic Research (202101AS070017). Special thanks to the Center for Analysis and Testing of Kunming University of Science and Technology for instrumental analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Li, Z., Zhang, Z. et al. Role of Stable Keyhole Mode in the Formability, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties of High Layer Thickness in Laser Powder Bed Fusion of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09377-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09377-8