Abstract
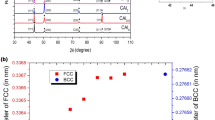
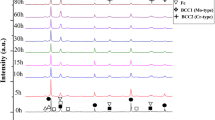
In recent years, multicomponent alloy systems such as high entropy alloys (HEA) have been synthesized by the conventional alloying strategy where all the elements are mixed in equiatomic or near-equiatomic proportions and processed mostly by mechanical alloying, vacuum arc melting or vacuum induction melting and selective laser melting. In this article, we have explored the possibility of sequential alloying strategy where a binary equiatomic mixture is chosen to start the alloy preparation which is followed by mixing of other elements sequentially in subsequent steps maintaining the equiatomic proportions throughout the process using mechanical alloying and vacuum arc melting. Equiatomic CoCrFeMnNiTi alloy has been synthesized in this study using initial equiatomic Fe and Cr and subsequent addition of Co, Ni, Mn and Ti by mechanical alloying as well as vacuum arc melting. During sequential alloying by mechanical alloying, there is the formation of initially FeCr body-centered cubic (BCC) phase, and by subsequent addition of other elements, the phases evolved were FeCrCo-BCC, FeCrCoNi-face-centered cubic (FCC), FeCrCoNiMn-BCC + FCC and FeCrCoNiMnTi-BCC + FCC. Due to vacuum arc melting, there is a marginal change in the evolved phase when sequential alloying was conducted by the addition of Mn (FeCrCoNiMn) and additional NiTi-rich phase for FeCrCoNiMnTi. Sequential alloying has been proven to be a superior technique for the development of multicomponent alloys as the formation of Laves and R phase may be avoided as was observed in equiatomic multicomponent alloy with similar composition (FeCrMnTi and CoCrFeMn) developed by melting and casting.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.P. George, D. Raabe, and R.O. Ritchie, High Entropy Materials, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2019, 4(8), p 515–534.
Y.F. Ye, Q. Wang, J. Lu, C.T. Liu, and Y. Yang, High-Entropy Alloy: Challenges and Prospects, Mater. Today, 2016, 19(6), p 349–362.
P. Sharma, V.K. Dwivedi, and S.K. Dwivedi, Development of High Entropy Alloys: A Review, Mater. Today Proc., 2021, 43(1), p 502–509.
D.B. Miracle and O.N. Senkov, A Critical Review of High Entropy Alloys and Related Concepts, Acta Mater., 2017, 122, p 448–511.
J. Chen, X. Zhou, W. Wang, B. Liu, Y. Lv, W. Yang, D. Xu, and Y. Li, A Review on Fundamental of High Entropy Alloys with Promising High-Temperature Properties, J. Alloys Compd., 2018, 760, p 15–30.
Y. Zhang, T.T. Juo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Damen, P.K. Liaw, and Z.P. Lu, Microstructure and Properties of High Entropy Alloys, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2014, 61, p 1–93.
A. Kumar, A. Singh, and A. Suhane, Mechanically Alloyed High Entropy Alloys: Existing Challenges and Opportunities, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2022, 17, p 2431–2456.
X.J. Fan, R.T. Qu, and Z.F. Zhang, Remarkably High Fracture Toughness of HfNbTaTiZr Refractory High-Entropy Alloy, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2022, 123, p 70–77.
C. Zhang, H. Wang, X. Wang, Y.T. Tang, Q. Yu, C. Zhu, M. Xu, S. Zhao, R. Kou, X. Wang, B.E. Macdonald, R.C. Reed, K.S. Vecchio, P. Cao, T.J. Rupert, and E.J. Lavernia, Strong and Ductile Refractory High-Entropy Alloys with Super Formability, Acta Mater., 2023, 245, p 118602.
J. Shittu, M. Pole, I. Cockerill, M. Sadeghilaridjani, L.V.K. Reddy, G. Manivasagam, H. Singh, H.S. Grewal, H.S. Arora, and S. Mukherjee, Biocompatible High Entropy Alloys with Excellent Degradation Resistance in a Simulated Physiological Environment, ACS Appl. Bio Mater., 2020, 3, p 8890–8900.
S. Gonzalez, A.K. Sfikas, S. Kamnis, C.G. Garay-Reyes, A. Hurtado-Macias, and R. Martinez-Sanchez, Wear Resistant CoCrFeMnNi0.8V High Entropy Alloy With Multi Length-Scale Hierarchical Microstructure, Mater. Lett., 2023, 331, p 133504.
P. Shi, Y. Zhong, Y. Li, W. Ren, T. Zheng, Z. Shen, B. Yang, J. Peng, P. Hu, Y. Zhang, P.K. Liaw, and Y. Zhu, Multistage Work Hardening Assisted by Multi-Type Twinning in Ultrafine-Grained Heterostructural Eutectic High-Entropy Alloys, Mater. Today, 2020, 41, p 62–71.
J. Ren, Y. Zhang, D. Zhao, Y. Chen, S. Guan, Y. Liu, L. Liu, S. Peng, F. Kong, J.D. Poplawsky, G. Gao, T. Voisin, K. An, Y. Morris Wang, K.Y. Xie, T. Zhu, and W. Chen, Strong Yet Ductile Nanolamallar High-Entropy Alloys by Additive Manufacturing, Nature, 2022, 608, p 62–68.
M. Garg, H.S. Grewal, R.K. Sharma, and H.S. Arora, Enhanced Oxidation Resistance of Ultrafine-Grain Microstructure AlCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy, ACS Omega, 2022, 7, p 12589–12600.
W.R. Zhang, W.B. Liao, P.K. Liaw, J.L. Ren, J. Brechtl, and Y. Zhang, Effect of Transient Thermal Shock on the Microstructures and Corrosion Properties of a Reduced Activation High Entropy Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2022, 918, p 165762.
J. Moon, E. Tabachnikova, S. Shumilin, T. Hryhorova, Y. Estrin, J. Brechtl, P.K. Liaw, W. Wang, K.A. Damen, A. Zargaran, J.W. Bae, H.S. Do, B.J. Lee, and H.S. Kim, Deformation Behavior of a Co-Cr-Fe-Ni-Mo Medium-Entropy Alloy a Extremely Low Temperatures, Mater. Today, 2021, 50, p 55–68.
Y. Zong, N. Hashimoto, and H. Oka, Study on Irradiation Effects of Refractory bcc High Entropy Alloys, Nucl. Mater. Energy, 2022, 31, p 101158.
S.K. Dewangan, A. Mangish, S. Kumar, A. Sharma, B. Ahn, and V. Kumar, A Review on High-Temperature Applicability: A Milestone for High-Entropy Alloys, Eng. Sci. Technol., 2022, 35, p 101211.
M. Vaidya, A. Prasad, A. Parakh, and B.S. Murty, Influence of Sequence of Elemental Addition on Phase Evolution in Nanocrystalline AlCoCrFeNi: Novel Approach to Alloy Synthesis Using Mechanical Alloying, Mater. Des., 2017, 126, p 37–46.
S. Praveen, B.S. Murty, and R.S. Kottada, Phase Evolution and Densification Behavior of Nanocrystalline Multicomponent High Entropy Alloys During Spark Plasma Sintering, J. Mater., 2003, 65, p 1797–1804.
K.A. Christofidou, E.J. Pickering, P. Orsatti, P.M. Mignanelli, T.J.A. Slater, H.J. Stone, and N.G. Jones, On the Influence of Mn on the Phase Stability of the CrMnxFeCoNi High Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2018, 92, p 84–92.
Z. Chen, W. Chen, B. Wu, X. Cao, L. Liu, and Z. Fu, Effects of Co and Ti on Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of Al0.75FeNiCrCo High Entropy Alloy Prepared by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 648, p 217–224.
B.D. Cullity and S.R. Stock, Elements of x-ray Diffraction, Pearson Education, 1978.
C. Lee, G. Song, M.C. Gao, R. Feng, P. Chen, J. Brechtl, Y. Chen, K. An, W. Guo, J.D. Poplawsky, S. Li, A.T. Samaei, W. Chen, A. Hu, H. Choo, and P.K. Liaw, Lattice Distortion in a Strong and Ductile Refractory High-Entropy Alloy, Acta Mater., 2018, 160, p 158–172.
Z. Zeng, M. Xiang, D. Zhang, J. Shi, W. Wang, X. Tang, W. Tang, Y. Wang, X. Ma, Z. Chen, W. Ma, and K. Morita, Mechanical Properties of Cantor Alloys Driven by Additional Elements: A Review, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2021, 15, p 1920–1934.
X. Zhang, Solidification Modes and Microstructure of Solidified Fe-Cr Alloys at Different Undercoolings, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, 247(1–2), p 214–221.
A.C. Yeh, Y.J. Chang, C.W. Tsai, Y.C. Wang, J.W. Yeh, and C.M. Kuo, On the Solidification and Phase Stability of a Co-Cr-Fe-Ni-Ti High Entropy Alloy, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, 45(1), p 184–190.
N. Yazdani, M.R. Toroghinejad, A. Shabani, and P. Cavaliere, Effects of Process Control Amount Milling Time, and Annealing Heat Treatment on the Microstructure of AlCrCuFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Synthesized through Mechanical Alloying, Metals, 2021, 1, p 1493.
C. Suryanarayana, Mechanical Alloying: A Novel Technique to Synthesize Advanced Materials, Research, 2019.
A. Asabre, A. Kostka, O. Stryzhyboroda, J. Pfetzing-Micklich, U. Hetcht, and G. Laplanche, Effect of Al, Ti and C Additions on Windmanstatten Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Cast Al0.6CoCrFeNi Compositionally Complex Alloys, Mater. Des., 2019, 184, p 108201.
A.C. Fan, J.H. Li, and M.H. Tsai, On the Phase Constituents of Four CoCrFeNix(X= Y, Ti, Zr, Hf) HEA After Prolonged Annealing, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2020, 9(5), p 11231–11240.
Y. Chen, W. Liu, H. Wang, J. Xie, T. Zhang, L. Yin, and Y. Huang, Effect of Ti Content on the Microstructure and Properties of CoCrFeNiMnTix High Entropy Alloy, Entropy (Basel), 2022, 24(2), p 241.
X. Chen, Q. Lu, Y. Gao, W. Tian, H. Wang, and H. Zhou, Bidirectional Improvement of Strength and Ductility of CoCrFeNiTi (Co40Cr16Fe35Ni8Ti1) High Entropy Alloys Suitable for Coronary Stents, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2022, 18, p 1934–1946.
A. Takeuchi and A. Inoue, Classification of Bulk Metallic Glasses by Atomic Size Difference, Heat of Mixing and Period of Constituent Elements and its Application to Characterization of the Main Alloying Element, Mater. Trans., 2005, 46(12), p 2817–2829.
F. Otto, Y. Bang, H. Bei, and E.P. George, Relative Effects of Enthalpy and Entropy on the Phase Stability of Equiatomic High Entropy Alloys, Acta Mater., 2013, 61(7), p 2628–2638.
M.H. Tsai, A.C. Fan, and H.A. Wang, Effect of Atomic Size Difference on the Type of Major Intermetallic Phase in Arc-Melted CoCrFeNiX High-Entropy Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2017, 695, p 1479–1487.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Central Research Facility (CRF), IIT, Kharagpur, for assistance in carrying out the experimental work. TD would like to thank MHRD, Govt. of India, for financial support. Partial financial grants from Alexander von Humboldt (AvH) (Friedrich Wlhelm Bessel Award), Department of Science and Technology (POWER Fellowship) to JDM and Department of Science and Technology (J. C. Bose Fellowship) to IM are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is an invited submission to the Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance selected from presentations at the 4th International Conference on Processing & Characterization of Materials (ICPCM 2022) held December 9-11, 2022, at the National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, Odisha, India. It has been expanded from the original presentation. The issue was organized by Prof. Joao Pedro Oliveira, Universidade NOVA de Lisboa, Portugal; Prof. B. Venkata Manoj Kumar, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, India; Dr. D. Arvindha Babu, DMRL, DRDO, Hyderabad, India; Prof. Kumud Kant Mehta and Prof. Anshuman Patra, National Institute of Technology Rourkela, Odisha, India and Prof. Manab Mallik, National Institute of Technology Durgapur, India.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Datta, T., Manna, I. & Majumdar, J.D. Synthesis of Equiatomic CoCrFeMnTiNi Multicomponent Alloy by Sequential Alloying Using Mechanical Alloying and Vacuum Arc Melting. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09193-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09193-0