Abstract
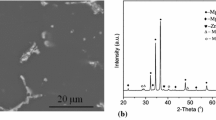
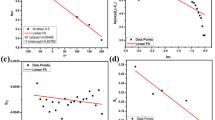
The Laves phase NbCr2/Nb two-phase alloy has received significant research interest as a potential high-temperature structural material. Based on isothermal and constant strain rate compression experiments conducted on the alloy within a temperature range of 1000 -1200 °C and strain rate range of 0.001-0.1 s−1, the flow stress constitutive relationship of the alloy was established using the J-C model and BP artificial neural network model, respectively. It was found that the conventional J-C model fails to describe the flow stress softening behavior of the alloy. In contrast, the modified J-C model provides a better prediction of the flow stress softening phenomenon and accurately characterizes the flow stress behavior of the alloy, it exhibits high prediction accuracy as indicated by the correlation coefficient (R) of 0.9902, average absolute relative error (AARE) of 8.773% and mean relative error (MRE) of 7.389%. The flow stress behavior of the alloy can be more accurately characterized using the constitutive relationship built by the BP neural network model. The model exhibits higher prediction accuracy with R of 0.9998, AARE of 2.232% and MRE of 0.870%. The results demonstrate that the BP neural network model has superior capability in predicting the flow stress behavior of the alloy. The established flow stress constitutive relationship can provide more accurate and reliable fundamental data with respect to flow stress for finite element simulations of forging deformation process of the Laves phase NbCr2/Nb two-phase alloy. In addition, it serves as theoretical basis for rational design of forging process and accurate calculation of the deformation force of the alloy.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.S. Zhang, Y.J. Chen, and J.L. Hu, Recent Advances in the Development of Aerospace Materials, Prog. Aerosp. Sci., 2018, 97, p 22–34.
M. Takeyama and C.T. Liu, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laves-Phase Alloys Based on Cr2Nb, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1991, 132, p 61–66.
T. Takasugi, M. Yoshida, and S. Hanada, Deformability Improvement in C15 NbCr2 Intermetallics by Addition of Ternary Elements, Acta Mater., 1996, 44, p 669–674.
T. Takasugi, M. Yoshida, and S. Hanada, Microstructure and High-Temperature Deformation of the C15 NbCr2-Based Laves Intermetallics in Nb-Cr-V Alloy System, J. Mater. Res., 1995, 10, p 2463–2470.
F. Gao, S.M. Li, and K.W. Li, Formation of Non-Equilibrium Ductile Solid Solutions and Textures in NbCr2 Bulks Produced by Mechanical Milling and Spark Plasma Sintering, J. Alloys Compd., 2020, 826, p 154130.
X. Xiao, S.Q. Lu, P. Hu, M.G. Huang, and M.W. Fu, Effect of Ball Milling Time on Microstructure and Properties of Laves Phase NbCr2 Alloys Synthesized by Hot Pressing, Trans. Nonferr. Metals Soc. China, 2009, 19, p 545–551.
X. Xiao, S.Q. Lu, P. Hu, M.G. Huang, X.W. Nie, and M.W. Fu, The Effect of Hot Pressing Time on the Microstructure and Properties of Laves Phase NbCr2 Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 485, p 80–85.
P. Li, T. Satoshi, I. Ken-ichi, H. Toshiaki, and M. Seiji, Effect of Si on the Stability of NbCr2 Laves Phase in Cr-Mo-Nb System, Intermetallics, 2019, 110, p 106457.
H.T. Huang, G.F. Li, X. Xiao, S.Q. Lu, and P. Peng, First-Principles Investigations of the Fracture Toughness of NbCr2 Alloyed by X (V, Mo, Ti, Fe), Solid State Commun., 2022, 344, p 114664.
H.Z. Zheng, S.Q. Lu, J.Y. Zhu, and G.M. Liu, Effect of Al Additions on the Oxidation Behavior of Laves Phase NbCr2 Alloys at 1373 K and 1473 K, Int. J. Refract Metal Hard Mater., 2009, 27, p 659–663.
C.T. Liu, J.H. Zhu, M.P. Brady, C.G. McKamey, and L.M. Pike, Physical Metallurgy and Mechanical Properties of Transition-Metal Laves Phase Alloys, Intermetallics, 2000, 8, p 1119–1129.
P. Berthod and M. Ritouet-Léglise, Microstructures and Hardness of Model Niobium-Based Chromium-Rich Cast Alloys, Adv. Mater. Res., 2018, 7, p 17–28.
L.P. Deng, S.Q. Lu, B.B. Tang, and W. Yu, Thermal Stability of Nb-Cr-Mo, Int. J. Mater. Res., 2018, 109(4), p 301–307.
L.P. Deng, S.Q. Lu, B.B. Tang, and Y. Lin, Effect of Si on Thermal Stability of Nb-22.5 Cr Alloy, Vacuum, 2018, 152, p 312–318.
Y.Q. Qiao, M.Y. Li, and X.P. Guo, Development of Silicide Coatings Over Nb-NbCr2 Alloy and their Oxidation Behavior at 1250° C, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2014, 258, p 921–930.
X. Xiao, S.Q. Lu, Y.Q. Ma, P. Hu, and X.W. Nie, Microstructure and Properties of Nb/NbCr2 Composites Prepared by Mechanical Alloying Followed by Hot Pressing, Chin. J. Nonferr. Metals, 2007, 17, p 1761–1766. (in Chinese)
Y.C. Lin and X.M. Chen, A Critical Review of Experimental Results and Constitutive Descriptions for Metals and Alloys in Hot Working, Mater. Des., 2011, 32, p 1733–1759.
Y.C. Lin, L.T. Li, Y.X. Fu, and Y.Q. Jiang, Hot Compressive Deformation Behavior of 7075 Al Alloy Under Elevated Temperature, J. Mater. Sci., 2012, 47, p 1306–1318.
Y.C. Lin, L.T. Li, and Y.Q. Jiang, A Phenomenological Constitutive Model for Describing Thermo-Viscoplastic Behavior of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy Under Hot Working Condition, Exp. Mech., 2012, 52, p 993–1002.
J.K. Wu, S.Q. Lu, L.P. Deng, T.X. Wang, and K.L. Wang, Thermal Deformation Behavior and Constitutive Relationship of Laves Phase NbCr2/Nb Dual-phase Alloy, Rare Metal Mater. Eng., 2021, 50, p 2541–2551. (in Chinese)
A. Saxena, A. Kumaraswamy, N. Kotkunde, and S. Kurra, Constitutive Modeling of High-Temperature Flow Stress of Armor Steel in Ballistic Applications a Comparative Study, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2019, 28, p 6505–6513.
Y.C. Lin, X.M. Chen, and G. Liu, A Modified Johnson-Cook Model for Tensile Behaviors of Typical High-Strength Alloy Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 6980–6986.
Q.Y. Hou and J.T. Wang, A Modified Johnson-Cook Constitutive Model for Mg-Gd-Y Alloy Extended to a Wide Range of Temperatures, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2010, 50, p 147–152.
A. Iturbe, E. Giraud, E. Hormaetxe, A. Garay, G. Germain, K. Ostolaza, and P.J. Arrazola, Mechanical Characterization and Modelling of Inconel 718 Material Behavior for Machining Process Assessment, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 682, p 441–453.
X.R. Chen, Q.Y. Liao, Y.X. Niu, W.T. Jia, Q.C. Le, C.L. Cheng, F.X. Yu, and J.Z. Cui, A Constitutive Relation of AZ80 Magnesium Alloy During Hot Deformation Based on Arrhenius and Johnson-Cook Model, J. Market. Res., 2019, 8, p 1859–1869.
S. Deb, A. Muraleedharan, R.J. Immanuel, S.K. Panigrahi, G. Racineux, and S. Marya, Establishing Flow Stress Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy and Development of Constitutive Models Using Johnson-Cook Method and Artificial Neural Network for Quasi-Static and Dynamic Loading, Theoret. Appl. Fract. Mech., 2022, 119, p 103338.
Y. Han, G.J. Qiao, J.P. Sun, and D.N. Zou, A Comparative Study on Constitutive Relationship of As-Cast 904L Austenitic Stainless Steel During Hot Deformation Based on Arrhenius-Type and Artificial Neural Network Models, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2013, 67, p 93–103.
L.P. Deng, Study on thermal stability and high temperature mechanical properties of two-phase NbCr2/Nb and NbCr2/Cr alloy. Nanjing Univ. Aeronau. Astronaut. 2018 (in Chinese)
L.P. Deng, S.Q. Lu, B.B. Tang, and Z.L. Lei, High Temperature Creep Behavior of NbCr2/Nb Alloy, J. Plast. Eng., 2019, 26(2), p 194–198. (in Chinese)
Y.W. Xiao, Y.C. Lin, Y.Q. Jiang, X.Y. Zhang, G.D. Pang, D. Wang, and K.C. Zhou, A Dislocation Density-Based Model and Processing Maps of Ti-55511 Alloy with Bimodal Microstructures During Hot Compression in α+ β Region, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 790, p 139692.
R. Amitava, A. Mohammad, K.T. Jitendar, D. Satyabrata, and D. Rupa, Study of Processing Map and Effect of Hot Rolling on Mechanical Properties of Aluminum 5083 Alloy, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2020, 73(7), p 1809–1826.
R. Amitava, A. Mohammad, D. Satyabrata, and D. Rupa, Constitutive Modeling for Predicting High-Temperature Flow Behavior in Aluminum 5083+10wt Pct SiCp Composite, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2019, 50, p 1061–1076.
Y.C. Lin, Y.W. Xiao, Y.Q. Jiang, G.D. Pang, H.B. Li, X.Y. Zhang, and K.C. Zhou, Spheroidization and Dynamic Recrystallization Mechanisms of Ti-55511 Alloy with Bimodal Microstructures During Hot Compression in α+ β Region, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 782, p 139282.
T. Takasugi, S. Hanada, and M. Yoshida, High Temperature Mechanical Properties of C15 Laves Phase Cr2Nb Intermetallics, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1995, 192, p 805–881.
C.Y. Lu, J. Wang, and P.Z. Zhang, Flow Behavior Analysis and Flow Stress Modeling of Ti17 Alloy in β Forging Process, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2021, 30(10), p 7668–7681.
A.V. Kazantzis, M. Aindow, I.P. Jones, G.K. Triantafyllidis, and JTh.M. De Hosson, The mechanical properties and the deformation microstructures of the C15 Laves phase Cr2Nb at high temperatures, Acta Mater., 2007, 55, p 1873–1884.
A.N. Behera, A. Chaudhuri, R. Kapoor, J.K. Chakravartty, and S. Suwas, High Temperature Deformation Behavior of Nb-1 wt.% Zr alloy, Mater. Design, 2016, 92, p 750–759.
M. Yoshida and T. Takasugi, TEM Observation for Deformation Microstructure of Laves Phase NbCr2 Containing V, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 345, p 350–356.
D.P. Pope and F. Chu, Grain Boundary Faceting and Twinning in Complex Intermetallic Compounds, Philos. Mag. A, 1994, 69(3), p 409–420.
D.V. Luzzi, Analysis of Stacking Faults in the Hf-V-Nb Cubic Laves Phase, Scripta Mater., 1997, 37(6), p 713–720.
K.S. Kumar and P.M. Hazzledine, Polytypic Transformations in Laves phases, Intermetallics, 2004, 12(7–9), p 763–770.
G.R. Johnson, A Constitutive Model and Data for Materials Subjected to Large Strains, High Strain Rates, and High Temperatures, Proc 7th Inf. Symp. Ballist., 1983, 19, p 541–547.
A. Abbasi-Bani, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, M.H. Pishbin, and N. Haghdadi, A Comparative Study on the Capability of Johnson-Cook and Arrhenius-Type Constitutive Equations to Describe the Flow Behavior of Mg-6Al-1Zn Alloy, Mech. Mater., 2014, 71, p 52–61.
L.Q. Niu, M. Cao, Z.L. Liang, B. Han, and Q. Zhang, A Modified Johnson-Cook Model Considering Strain Softening of A356 Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 789, p 139612.
C.Y. Lu, J. Shi and J. Wang, Physically Based Constitutive Modeling for Ti17 Alloy with Original Basketweave Microstructure in β Forging A Comparison of Three Approaches, Mater Charact, 2021, 181, p 111455.
N. Fiorentini, D. Pellegrini, and M. Losa, Overfitting Prevention in Accident Prediction Models: Bayesian Regularization of Artificial Neural Networks, Transport. Res. Record: J. Transport. Res. Board, 2023, 2677(2), p 1455–1470.
D.Q. Yan, Q. Zhou, J.Z. Wang, and N. Zhang, Bayesian Regularization Neural Network Based on Artificial Intelligence Optimization, Int. J. Prod. Res., 2017, 55(8), p 2266–2287.
C.Y. Lu, J. Shi, and V. Maitra, Modelling and Process Optimization for Relative Density of Ti6Al4V Produced by Selective Laser Melting A Data-driven Study, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2022, 121, p 1973–1988.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51964034, 52161021) and the fund of the National Defense Key Discipline Laboratory of Light Alloy Processing Science and Technology (EG202201333).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
JiangFeng, J., Lu, S., Xiao, X. et al. Constitutive Relationship Study of Laves Phase NbCr2/Nb Two-Phase Alloy Using Modified J-C Model and Back Propagation Neural Network Model. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08941-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08941-y