Abstract
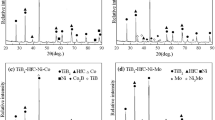
A TiB2-based cermet tool material with excellent mechanical performance was rapidly prepared by microwave hybrid sintering. Microwave hybrid sintering is based on pure microwave sintering with the addition of high microwave absorbing materials (e.g., SiC coating and SiC powder) to assist in the heating of the sample, which has the characteristics of hybrid heating. The effects of two different microwave hybrid sintering methods and nano-HfC content on mechanical properties and microstructure of cermets were investigated. The experimental results indicated that different sintering methods changed the distribution of microwave electric field in the furnace, which affected the sample heating mechanism. SiC-buried powder hybrid sintering was more efficient than SiC coating hybrid sintering, so the sintered material had higher densities and mechanical properties. The fracture toughness and flexural strength of cermets containing 20 wt.% HfC were 36.7% and 45.4%, respectively, higher than those without HfC, and the fracture toughness reached 10.68 MPa·m1/2. With the increase of nano-HfC content, the TiB2 grains changed from coarse irregular shape to fine rectangular shape, and the average grain size can be reduced by 2.6 times. The toughening and strengthening mechanisms of the nano-HfC added phase were mainly fine-grain strengthening, particle dispersion strengthening, solid solution strengthening, crack deflection, and pinning effect.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Nekahi, F.S. Moghanlou, M. Vajdi, Z. Ahmadi, A. Motallebzadeh, and M.S. Asl, Microstructural, Thermal and Mechanical Characterization of TiB2-SiC Composites Doped with Short Carbon Fibers, Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater., 2019, 82, p 129–135.
S.D. Oguntuyi, O.T. Johnson, and M.B. Shongwe, Spark Plasma Sintering of Ceramic Matrix Composite of ZrB2 and TiB2: Microstructure, Densification, and Mechanical Properties-A Review, Met. Matre. Int., 2020, 27, p 2146–2159.
S. Mondal, S. Chakraborty, and S. Das, Mechanical and Tribological Behavior of ZrB2-TiB2 System Prepared by Mechanical Activation Spark Plasma Sintering Technique, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2018, 27, p 6040–6048.
J. Song, S. Liu, R. Ahmad, J. Gao, and M. Lv, Tribological Behaviour of TiB2-HfC Ceramic Tool Material under Dry Sliding Condition, Ceram. Int., 2020, 46, p 20320–20327.
Y. Deng, H. Chen, X. Chen, and Y. Yao, Dynamic Failure Behaviour Analysis of TiB2-B4C Ceramic Composites by Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar Testing, Ceram. Int., 2021, 47, p 22096–22107.
G. Zhao, C. Huang, H. Liu, B. Zou, H. Zhu, and J. Wang, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiB2-SiC Ceramic Composites by Reactive Hot Pressing, Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater., 2014, 42, p 36–41.
W. Wang, Effects of TiN Content on the Properties of Hot Pressed TiB2-SiC Ceramics, Ceram. Int., 2021, 47, p 16762–16769.
J. Sun, J. Zhao, Z. Huang, K. Yan, Y. Jian, and H. Yang, Hybrid Multilayer Graphene and SiC Whisker Reinforced TiB2 Based Nano-Composites by Two-Step Sintering, J. Alloy. Compd., 2021, 856, p 157283.
M. Gu, C. Huang, B. Zou, and B. Liu, Effect of (Ni, Mo) and TiN on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiB2 Ceramic Tool Materials, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 433, p 39–44.
N. Wu, F. Xue, J. Wang, H. Yang, F. Luo, and J. Ruan, Effect of TiN Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiB2-FeNi Based Cermets, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2019, 743, p 546–557.
M. Hu, N. Bi, M. Liu, G. Gao, S. Li, and T. Su, Rapid Sintering of TiB2 Ceramics Using Co as Sintering Aid under High Pressure Condition, Mater. Sci. Poland., 2020, 38, p 502–507.
M. Vajdi, F.S. Moghanlou, Z. Ahmadi, Z. Ahmadia, A. Motallebzadeh, and M.S. Asl, Thermal Diffusivity and Microstructure of Spark Plasma Sintered TiB2-SiC-Ti Composite, Ceram. Int., 2019, 45, p 8333–8344.
S.R. Yan, L.K. Foong, and Z. Lyu, Technical Performance of Co-addition of SiC Particulates and SiC Whiskers in Hot-Pressed TiB2-Based Ultrahigh Temperature Ceramics, Ceram. Int., 2020, 46, p 19443–19451.
B. Liu, W. Wei, Y. Gan, C. Duan, and H. Cui, Preparation, Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of TiB2 Based Ceramic Cutting Tool Material Toughened by TiC Whisker, Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater., 2020, 93, p 105327.
M. Yao, L. Chen, Z. Liu, S. Huo, S. Wang, Y. Wang, J. Ouyang, and Y. Zhou, Two-Step Sintering of TiB2-40 wt.% TiN Composites, Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater., 2019, 84, p 105037.
J. Song, C. Huang, B. Zou, H. Liu, L. Liu, and J. Wang, Effects of Sintering Additives on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiB2-WC Ceramic-Metal Composite Tool Materials, Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater., 2012, 30, p 91–95.
AYu. Popov, A.A. Sivak, HYu. Borodianska, HYu. Borodianska, and I.L. Shabalin, High Toughness TiB2-Al2O3 Composite Ceramics Produced by Reactive Hot Pressing with Fusible Components, Adv. Appl. Ceram., 2015, 114, p 178–182.
T.P. Nguyen, M.D. Germi, Z.H. Mahaseni, S.A. Delbari, Q.V. Le, Z. Ahmadi, M. Shokouhimehr, A.S. Namini, and M.S. Asl, Enhanced Densification of Spark Plasma Sintered TiB2 Ceramics with Low Content AlN Additive, Ceram. Int., 2020, 46, p 22127–22133.
N. Wu, F. Xue, Q. Yang, H. Yang, and J. Ruan, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiB2-Based Composites with High Volume Fraction of Fe-Ni Additives Prepared by Vacuum Pressureless Sintering, Ceram. Int., 2017, 43, p 1394–1401.
M. Yao, Y. Wang, L. Chen, J. Ouyang, H. Li, H. Gu, and Y. Zhou, Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Evolution of Pressureless Sintered Ceramics Obtained from High-Energy Ball-Milled TiB2-TiC Powders, Mat. Sci. Eng. A., 2021, 819, p 141510.
B. Song, W. Yang, X. Liu, H. Chen, and M. Akhlaghi, Microstructural Characterization of TiB2-SiC-BN Ceramics Prepared by Hot Pressing, Ceram. Int., 2021, 47, p 29174–29182.
Y. Yuan, W. Ji, S. Dai, Z. Zhang, H. Zhang, and L. Xu, Effects of Ultrafine Refractory Carbides on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hot-Pressing Sintered TiB2-ZrC Cermet Composites at Different Temperatures, Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater., 2019, 84, p 105002.
S. Ramesh, N. Zulkifli, C.Y. Tan, Y.H. Wong, F. Tarlochan, S. Ramesh, W.D. Teng, I. Sopyan, L.T. Bang, and A.A.D. Sarhan, Comparison Between Microwave and Conventional Sintering on the Properties and Microstructural Evolution of Tetragonal Zirconia, Ceram. Int., 2018, 44, p 8922–8927.
Z. Yin, S. Yan, W. Xu, and J. Yuan, Microwave Sintering of Ti(C, N)-Based Cermet Cutting Tool Material, Ceram. Int., 2018, 44, p 1034–1040.
J. Liu, B. Zhou, L. Xu, Z. Hun, and J. Zhou, Fabrication of SiC Reinforced Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites Through Microwave Sintering, Mater. Res. Express, 2020, 7, p 125101.
K.V.V. Nagaraju, S. Kumaran, and T.S. Rao, Microwave-Assisted Hybrid Sintering of 316L Powder Compacts: Microstructure, Mechanical, and Electrochemical Properties, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2022, 31, p 9555–9572.
G. Zhao, L. Xin, L. Li, Y. Zhang, N. He, and H.N. Hansen, Cutting Force Model and Damage Formation Mechanism in Milling of 70 wt.% Si/Al Composite, Chin. J. Aeronaut., 2022 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2022.07.018
R.K. Chadha, K.L. Singh, C. Sharma, A.P. Singh, and V. Naithani, Effect of Microwave and Conventional Processing Techniques on Mechanical Properties of Strontium Substituted Hydroxyapatite, Ceram. Int., 2020, 46, p 1091–1098.
N. Vasudevan, N.N.N. Ahamed, P.B.A. Aravindhan, and B.P. Shanmugavel, Effect of Ni Addition on the Densification of TiC: A Comparative Study of Conventional and Microwave Sintering, Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater., 2020, 87, p 105165.
D. Demirskyi, J. Cheng, D. Agrawal, and A. Ragulya, Densification and Grain Growth During Microwave Sintering of Titanium Diboride, Scripta Mater., 2013, 69, p 610–613.
D. Demirskyi, D. Agrawal, and A. Ragulya, Tough Ceramics by Microwave Sintering of Nanocrystalline Titanium Diboride Ceramics, Ceram. Int., 2014, 40, p 1303–1310.
H. Wang, J. Liu, G. Li, F. Tang, Y. Yan, L. Gao, and Y. Zhao, Effect of TiB2 Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of (TiB2p+B4Cp)/Al Composites Fabricated by Microwave Sintering, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2021, 13, p 1509–1520.
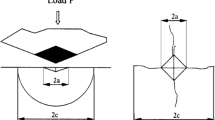
A.G. EVans and E.A. Charles, Fracture Toughness Determinations by Indentation, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1976, 59, p 371–372.
J.M. Chaix, Microwave Sintering of Ceramics, Encyclop. Mater. Tech. Ceram. Glasses, 2021, 1, p 327–341.
N. Moelans, B. Blanpain, and P. Wollants, Pinning Effect of Second-Phase Particles on Grain Growth in Polycrystalline Films Studied by 3-D Phase Field Simulations, Acta Mater., 2007, 55, p 2173–2182.
H. Ryou, J.W. Drazin, K.J. Wahl, S.B. Qadri, E.P. Gorzkowski, B.N. Feigelson, and J.A. Wollmershauser, Below the Hall-Petch Limit in Nanocrystalline Ceramics, ACS Nano, 2018, 12, p 3083–3094.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52005154) and Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (E2020202035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, W., Wu, X., Dai, S. et al. Effects of Microwave Hybrid Sintering Methods and Nano-HfC Content on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of TiB2-Based Cermets. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08440-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08440-0