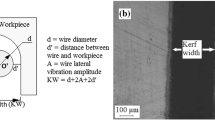
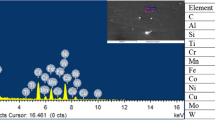
Abstract
The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of cutting parameters such as pulse-on time (Ton), servo-voltage (U), feed rate (S) and flushing pressure (P) on surface roughness (Ra) when machining Ti-6242 super alloy by WEDM process. The cutting was performed using a brass tool electrode and deionized water as a dielectric fluid. To optimize cutting parameters for surface roughness improvement, Taguchi’s signal‐to‐noise ratio (S/N) approach was applied using L9 (3^4) orthogonal array and Lower-The-Better (LTB) criteria. Substantially, the findings from current investigation suggest the application of the values 0.9 µs, 100 V, 29 mm/min, and 60 bar for the cutting parameters Ton, U, S and p, respectively, for producing a good surface finish quality. Electron microscope scanning (SEM) observations have been performed on machined surface for a wide range of cutting parameters to characterize wire EDMed surface of Ti-6242. SEM micrographs indicated that white layer and machining-induced damage characteristics are highly dependent on cutting parameters. For high servo-voltage, decreasing the pulse-on time Ton and feed rate S leads to a strong decrease in the overall machining-induced surface damage. Furthermore, for high levels of servo-voltage and feed rate, it was observed that pulse-on time could play a role in controlling the density of surface microcracks. In fact, the use of low cutting pulse-on time combined with high servo-voltage and feed rate was found to inhibit surface microcracks formation, giving the material surface better resistance to cracking than with high pulse on-time.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Metals Handbook TENTH EDITION Volume 2 Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials (1990). ASM International the Materials Information Society. ISBN: 978-0-87170-378-1.
R.R. Boyer, An Overview on the Use of Titanium in the Aerospace Industry, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1996, 213, p 103–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(96)10233-1
A. Kramer, D. Lung, and F. Klocke, High Performance Cutting of Aerospace Materials, Adv. Mater. Res., 2012, 498, p 127–132. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.498.127
D.K. Aspinwall, S.L. Soo, A.E. Berrisford, and G. Walder, Workpiece Surface Roughness and Integrity After WEDM of Ti6Al-4V and Inconel 718 Using Minimum Damage Generator Technology, Ann. CIRP, 2008, 57, p 187–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2008.03.054
D.T. Curtis, S.L. Soo, Aspinwall, D.K. Huber C, J. Fuhlendorf, and A. Grimm, Production of complex blade mounting slots in turbine disks using novel machining techniques. in Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on High Performance Cutting - CIRP HPC. (Dublin, Ireland, 2008) pp 219–228
F. Boud, C. Carpenter, J. Folkes, and P.H. Shipway, Abrasive Waterjet Cutting of a Titanium Alloy: The Influence of Abrasive Morphology and Mechanical Properties on Workpiece Grit Embedment and Cut Quality, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2010, 210, p 2197–2205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.08.006
D.T. Curtis, S.L. Soo, D.K. Aspinwall, and C. Sage, Electrochemical Superabrasive Machining of a Nickel-Based Aeroengine Alloy Using Mounted Grinding Points, Ann. CIRP, 2009, 58, p 173–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2009.03.074
G. Kappmeyer, C. Hubig, M. Hardly, M. Witty, and M. Brusch, Modern Machining of Advanced Aerospace Alloys - Enabler for Quality and Performance, Procedia CIRP, 2012, 1, p 28–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2012.04.005
T. Meurig, T. Sam, and J. Martin, Microstructural Damage During High-Speed Milling of Titanium Alloys, Scripta Mater., 2010, 62, p 250–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2009.11.009
S. Ezeddini, G. Zambelis, E. Bayraktar, I. Miskioglu, and D. Katundi, Experimental Study of Laser Cutting Process of Titanium Aluminium (Ti-Al) Based Composites Designed Through Combined Method of Powder Metallurgy and Thixoforming, Mech. Compos. Multi-funct. Mater., 2018, 6, p 21–27.
D. Evarasiddappa, M. Chandrasekaran, and R. Arunachalam, Experimental Investigation and Parametric Optimization for Minimizing Surface Roughness During WEDM of Ti6Al4V Alloy Using Modified TLBO Algorithm, J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng., 2020, 42, p 128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-2224-7
H. Sidhom, G. Farhat, A. Tidiane, G. Gonzalo, and B. Chedly, Effect of Electro Discharge Machining (EDM) on the AISI316L SS White Layer Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2013, 65, p 141–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4156-6
W. Rajhi, I. Alatawi, T. Subhani, B. Ayadi, A. Al-Ghamdi, and A. Khaliq, A Contribution to Numerical Prediction of Surface Damage and Residual Stresses on die-Sinking EDM of Ti6Al4V, J. Manuf. Process., 2021, 68, p 1458–1484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.06.056
O.A. Zeid, On the Effect of Electro Discharge Machining Parameters on the Fatigue Life on AISID6 Tool Steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1997, 68, p 27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(96)02523-X
L. Li, X.T. Wei, Y.B. Guo, W. Li, and J.F. Liu, Surface Integrity of Inconel 718 by Wire-EDM at Different Energy Modes, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2014, 23, p 3051–3057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1048-y
A. Hasçalık and U. Çaydaş, Electrical Discharge Machining of Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V), Appl. Surf. Sci., 2007, 253, p 9007–9016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.05.031
F. Nourbakhsh, K.P. Rajurkar, A.P. Malshe, and J. Cao, Wire Electro-Discharge Machining of Titanium Alloy, Procedia CIRP, 2013, 5, p 13–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2013.01.003
A. Perumal, A. Azhagurajan, S. Baskaran, R. Prithivirajan, and P. Narayansamy, Statistical Evaluation and Performance Analysis of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) Characteristics of Hard Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo Alloy, Mater. Res. Exp., 2019 https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab06da
S. Ben Salem, W. Tebni, and E. Bayraktar, Prediction of Surface Roughness by Experimental Design Methodology in Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), J. Achieve. Mater. Manuf. Eng., 2011, 49, p 150–157.
M. Boujelbene, E. Bayraktar, W. Tebni, and S. Ben Salem, Influence of Machining Parameters on the Surface Integrity in Electrical Discharge Machining, Arch. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2009, 37(2), p 110–116.
S.S. Mahapatra and A. Patnaik, Optimization of Wire Electrical Discharge Machining (WEDM) Process Parameters Using Taguchi Method, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2007, 34, p 911–925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0672-6
Y.I. Yun, I.Y. Park, and S.J. Song, Performance Degradation due to Blade Surface Roughness in a Single-Stage Axial Turbine, ASME. J. Turbomach., 2005, 127, p 137–143. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1811097
A. Perumal, A. Azhagurajan, R. Prithivirajan, and S. Suresh Kumar, Experimental Investigation and Optimization of Process Parameters in Ti—(6242) Alpha-Beta Alloy Using Electrical Discharge Machining, J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater., 2021, 31, p 1787–1800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01786-1
S.K. Shather, A. Bin Sapit, and F. Nehad, Performance of Ti-6242 Production Using Nano Powder Mixed with Different Dielectrics, Mater. Today Proc., 2021, 45, p 4490–4497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.997
R. Prasanna, V. Kavimani, P.M. Gopal, and D. Simson, Multi-Response Optimization and Surface Integrity Characteristics of Wire Electric Discharge Machining α-Phase Ti-6242 Alloy, Process. Integrat. Opt. Sustain., 2021 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41660-021-00179-2
A. Perumal, A. Azhagurajan, S.S. Kumar et al., Influence of Optimization Techniques on Wire Electrical Discharge Machining of Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo Alloy using Modeling Approach, J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym., 2021, 31, p 3272–3289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-01953-y
K. Mandeep and S. Hari, Multi Response Optimization in Wire Electrical Discharge Machining of Inconel X-750 Using Taguchi’s Technique and Grey Relational Analysis, Cogent Eng., 2016, 3, p 1. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2016.1266123
R.V. Rao and R. Venkata Rao, Modeling and optimization of machining processes, Adv. Modell. Opt. Manuf. Process. Int. Res. Develop., 2011 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-85729-015-1_2
R. Chalisgaonkar and J. Kumar, Multi-Response Optimization and Modeling of Trim Cut WEDM Operation of Commercially Pure Titanium (CPTi) Considering Multiple User’s Performance, Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J., 2015, 18, p 125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2014.10.006
F.J. Ridgeon, M.J. Raine, D.P. Halliday, M. Lakrimi, A. Thomas, and D.P. Hampshire, Superconducting Properties of Titanium Alloys (Ti-64 and Ti-6242) for Critical Current Barrels, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond., 2017, 27, p 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASC.2016.2645378
A. Boulila, M. Boujelbene, C. Fekiri, and A. Hammami, Optimization of Manufacturing Complex-Shaped Gas Turbine Blades, Measurement, 2019, 135, p 768–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.12.040
G.S. Peace, Taguchi Methods: A Hands-on Approach, Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of present manuscript declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ezeddini, S., Rajhi, W., Boujelbene, M. et al. An Investigation to Achieve Good Surface Integrity in Wire Electrical Discharge Machining of Ti-6242 Super Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 33, 4523–4537 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08270-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08270-0