Abstract
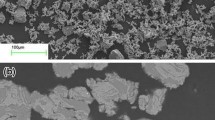
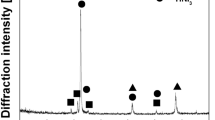
Porous NiTi alloys exhibit excellent properties for biomedical applications, but the existing processing techniques are expensive and difficult. In this study, gel-casting, a near-net-shape technique, is used to prepare porous NiTi from a slurry containing MAM as a monomer, Ni and TiH2 powders as raw materials. The properties of the slurries and the sintered samples were characterized. The porous NiTi alloys with a porosity of 40-46% were fabricated by gel-casting a slurry with an ammonium citrate content of 1 wt.%, MAM concentration of 15-20 wt.%, and a solid loading of 42-45 vol.%, followed by sintering at temperatures from 1000-1050 °C for 2 h. The resulting alloys had compressive strengths of 100-200 MPa and elastic moduli of 13-17 GPa. The use of TiH2 powder in the aqueous gel system prevented the formation of TiO2 and TiC phases and helped to form the NiTi phase. This indicates that gel-casting is a promising technology for the fabrication of porous implants with complex shapes at low cost.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Bansiddhi, T.D. Sargeant, S.I. Stupp et al., Porous NiTi for Bone Implants: A Review, Acta. Biomater., 2008, 4(4), p 773–782
Y.H. Li, G.B. Rao, L.J. Rong et al., The Influence of Porosity on Corrosion Characteristics of Porous NiTi Alloy in Simulated Body Fluid, Mater. Lett., 2002, 57(2), p 448–451
V. Karageorgiou and D. Kaplan, Porosity of 3D Biomaterial Scaffolds and Osteogenesis, Biomaterials, 2005, 26(27), p 5474–5491
G. Chen, P. Cao, and N. Edmonds, Porous NiTi Alloys Produced by Press-and-Sinter from Ni/Ti and Ni/TiH2 Mixtures, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 582(2), p 117–125
C.L. Chu, C.Y. Chung, P.H. Lin et al., Fabrication of Porous NiTi Shape Memory Alloy for Hard Tissue Implants by Combustion Synthesis, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 366(1), p 114–119
B. Yuan, C.Y. Chung, X.P. Zhang et al., Control of Porosity and Superelasticity of Porous NiTi Shape Memory Alloys Prepared by Hot Isostatic Pressing, Smart Mater. Struct., 2005, 14(14), p 201–206
G. Tosun, L. Ozler, M. Kaya et al., A Study on Microstructure and Porosity of NiTi Alloy Implants Produced by SHS, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 487(1–2), p 605–611
G. Chen, P. Cao, G. Wen et al., Using an Agar-Based Binder to Produce Porous NiTi Alloys by Metal Injection Moulding, Intermetallics, 2013, 37(3), p 92–99
K. Manuel, H. Tim, B. Martin et al., Powder Metallurgical Near-Net-Shape Fabrication of Porous NiTi Shape Memory Alloys for Use as Long-Term Implants by the Combination of the Metal Injection Molding Process with the Space-Holder Technique, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2009, 11(12), p 959–968
M. Bram, M. Bitzer, H.P. Buchkremer et al., Reproducibility Study of NiTi Parts Made by Metal Injection Molding, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2012, 21(21), p 2701–2712
H.I. Muhammad, G. Russell, A.D. Hywel et al., Porous NiTi Alloy by Metal Injection Moulding Sintering of Elemental Powders: Effect of Sintering Temperature, Mater. Lett., 2012, 70(3), p 142–145
H. Christoph, E. Mohammad, M.W. Jason et al., On the Development of High Quality NiTi Shape Memory and Pseudoelastic Parts by Additive Manufacturing, Smart. Mater. Struct., 2014, 23(10), p 64–75
B. Therese, S. Ralf, M. Bert et al., Tailoring Selective Laser Melting Process Parameters for NiTi Implants, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2012, 21(12), p 2519–2524
Y. Li and Z. Guo, Gelcasting of wc-8wt% Co Tungsten Cemented Carbide, Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater., 2008, 26(5), p 472–477
R. Gilissen, J.P. Erauw, A. Smolders et al., Gelcasting, a Near Net Shape Technique, Mater. Design., 2000, 21(4), p 251–257
M. Bengisu and E. Yilmaz, Gelcasting of Alumina and Zirconia Using Chitosan Gels, Ceram. Int., 2002, 28(4), p 431–438
J. Yu, H. Wang, H. Zeng et al., Effect of Monomer Content on Physical Properties of Silicon Nitride Ceramic Green Body Prepared by Gelcasting, Ceram. Int., 2009, 35(3), p 1039–1044
W. Liu, C.C. Jia, Y. Shi et al., Copper Base Materials Prepared by Gel-Casting Process, Rare Metals, 2008, 27(1), p 78–82
L. Yan, Z. Guo, J.J. Hao et al., Porosity and Mechanical Properties of Porous Titanium Fabricated by Gelcasting, Rare Matels, 2008, 27(7), p 282–286
Q. Ye, Z. Guo, Q. Duan et al., Preparation of TiAl Intermetallic Alloy by Gelcasting, Mater. Sci. Forum., 2012, 747, p 101–104
B.H. Duan, H.X. Hong, D.Z. Wang et al., Porous Nickel-Titanium Alloy Prepared by Gel-Casting, Rare Metals, 2013, 33(4), p 394–399
V. Bhosle, E.G. Baburaj, M. Miranova et al., Dehydrogenation of TiH2, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 356(1–2), p 190–199
R. Buscall, J.W. Goodwin, and R.H. Ottewill, The Setting of Particles Through Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Media, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1982, 85(1), p 78–86
Acknowledgments
This project was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (No. 2015JJ2170) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51274246).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bohua, D., Yasong, Z., Dezhi, W. et al. Fabrication and Properties of Porous NiTi Alloy by Gel-Casting with TiH2 Powders. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 26, 5118–5125 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2957-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2957-3