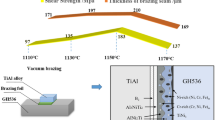
Abstract
Electric vehicles are becoming increasingly popular as environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional fossil fuel-based vehicles. The need to improve their performance demands design of materials that can withstand high current density without adversely affecting their durability. In this study, the influence of high-density current on the structure of a Ni-Sn solid–liquid interdiffusion joint with an Al interlayer was examined. The temperature at the joint region increased to 240°C without external heating under energization of 20 kA/cm2. After 100 h of energization, several structural evolutions from the initial state were observed in the joint region, including precipitation of Al3Ni at the cathode-side Al/Ni interface and enrichment of Ni concentration on both sides of the Ni-Sn intermetallic compound (IMC) layer. Electromigration influenced the precipitation position of the Al3Ni grains. However, there was only a trace of electromigration in the Ni enrichment behavior of the Ni-Sn IMC layer, because thermal and stress migration were very active there. The degree of Ni enrichment in the energized Ni-Sn IMC layer was much higher than that in the Ni-Sn IMC layer annealed at 300°C for 100 h. This result implies that a high-density current activates the thermal migration and stress migration. The influence on the reliability of the joint is a concern because the high degree of Ni enrichment in the energized Ni-Sn IMC layer generates many Kirkendall voids.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.J. Wellman, Power electronic semiconductor materials for automotive and energy saving applications – SiC, GaN, Ga2O3, and diamond. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 643, 1312 (2017).
K.N. Tu, Recent advances on electromigration in very-large-scale-integration of interconnects. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 5451 (2003).
J.-Q. Chen, J.-D. Guo, K.-L. Liu, and J.-K. Shang, Dependence of electromigration damage on Sn grain orientation in Sn–Ag–Cu solder joints. J. Appl. Phys. 114, 153509 (2013).
T. Kadoguchi, T. Sakai, T. Sei, N. Take, K. Yamanaka, S. Nagao, and K. Suganuma, Effect of Sn crystallographic orientation on solder electromigration and Ni diffusion in Cu/Ni plating/Sn–0.7Cu joint at low current density. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 12630 (2017).
A. Tasooji, L. Lara, and K. Lee, Effect of grain boundary misorientation on electromigration in lead-free solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 43, 4386 (2014).
H.-C. Huang, K.-L. Lin, and A.T. Wu, Disruption of crystalline structure of Sn3.5Ag induced by electric current. J. Appl. Phys. 119, 115102 (2016).
C.-M. Chen and S.-W. Chen, Electromigration effect upon the Sn–0.7 wt% Cu/Ni and Sn–3.5 wt% Ag/Ni interfacial reactions. J. Appl. Phys. 90, 1208 (2001).
L. Ma, G. Xu, J. Sun, F. Guo, and X. Wang, Effects of Co additions on electromigration behaviors in Sn–3.0 Ag–0.5 Cu-based solder joint. J. Mater. Sci. 46, 4896 (2011).
M. Lu, D.-Y. Shih, S.K. Kang, C. Goldsmith, and P. Flaitz, Effect of Zn doping on SnAg solder microstructure and electromigration stability. J. Appl. Phys. 106, 053509 (2009).
P. Zhang, S. Xue, and J. Wang, New challenges of miniaturization of electronic devices: electromigration and thermomigration in lead-free solder joints. Mater. Des. 192, 108726 (2020).
L.-D. Chen, M.-L. Huang, and S.-M. Zhou, Effect of electromigration on intermetallic compound formation in line-type Cu/Sn/Cu interconnect. J. Alloys Compd. 504, 535 (2010).
C.-H. Wang, H.-T. Shen, and W.-H. Lai, Effective suppression of electromigration-induced Cu dissolution by using Ag as a barrier layer in lead-free solder joints. J. Alloys Compd. 564, 35 (2013).
S.A. Paknejad and S.H. Mannan, Review of silver nanoparticle based die attach materials for high power/temperature applications. Microelectron. Reliab. 70, 1 (2017).
K.S. Siow, Are sintered silver joints ready for use as interconnect material in microelectronic packaging? J Electron. Mater. 43, 947 (2014).
C. Chen, C. Choe, D. Kim, and K. Suganuma, Lifetime prediction of a SiC power module by micron/submicron Ag sinter joining based on fatigue, creep and thermal properties from room temperature to high temperature. J. Electron. Mater. 50, 687 (2021).
T. Ishizaki and R. Watanabe, A new one-pot method for the synthesis of Cu nanoparticles for low temperature bonding. J. Mater Chem. 22, 25198 (2012).
T. Satoh and T. Ishizaki, Enhanced pressure-free bonding using mixture of Cu and NiO nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 629, 118 (2015).
M.-S. Kim and H. Nishikawa, Silver nanoporous sheet for solid-state die attach in power device packaging. Scripta Mater. 92, 43 (2014).
S. Sakamoto, T. Sugahara, and K. Suganuma, Microstructural stability of Ag sinter joining in thermal cycling. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 1332 (2013).
S.-W. Yoon, M.D. Glover, and K. Shiozaki, Nickel–tin transient liquid phase bonding toward high-temperature operational power electronics in electrified vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 28, 2448 (2013).
H. Ito, M. Kuwahara, H. Kadoura, and M. Usui, Highly reliable joining for high-temperature power modules: Ni-Sn DSLID with an Al sheet. IET Power Electron. 12, 492 (2019).
H. Ito, H. Kadoura, M. Kuwahara, and M. Usui, Effect of purity of Al interlayer on stress and thermal cycling durability of die-attach Ni-Sn joints. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 21389 (2020).
C.-T. Ma and Z.-H. Gu, Review on driving circuits for wide-bandgap semiconductor switching devices for mid- to high-power applications. Micromachines 12, 65 (2021).
T. Kimoto, Material science and device physics in SiC technology for high-voltage power devices. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 54, 040103 (2015).
A. Lis and C. Leinenbach, Effect of process and service conditions on TLP-bonded components with (Ag, Ni–)Sn interlayer combinations. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 4576 (2015).
I. Ansara, N. Dupin, H.L. Lukas, and B. Sundman, Thermodynamic assessment of the Al-Ni system. J. Alloys Compd. 247, 20 (1997).
P. Nash and A. Nash, The Ni-Sn (nickel-tin) system. Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams 6, 350 (1985).
A. Lis, S. Kicin, F. Brem, and C. Leinenbach, Thermal stress assessment for transient liquid-phase bonded Si chips in high-power modules using experimental and numerical methods. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 729 (2017).
M. Zoli and V. Bortolani, Thermodynamic properties of FCC metals: Cu and Al. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2, 525 (1990).
J.-W. Xian, G. Zeng, S.A. Belyakov, Q. Gu, K. Nogita, and C.M. Gourlay, Anisotropic thermal expansion of Ni3Sn4, Ag3Sn, Cu3Sn, Cu6Sn5 and βSn. Intermetallics 90, 50 (2017).
G.-Y. Jang, J.-W. Lee, and J.-G. Duh, The nanoindentation characteristics of Cu6Sn5, Cu3Sn, and Ni3Sn4 intermetallic compounds in the solder bump. J. Electron. Mater. 33, 1103 (2004).
H.P.R. Frederikse, R.J. Fields, and A. Feldman, Thermal and electrical properties of copper-tin and nickel-tin intermetallics. J. Appl. Phys. 72, 2879 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Satoh, T., Wakasugi, M. & Usui, M. Effects of High-Density Current on the Reliability of Ni-Sn Solid–Liquid Interdiffusion Joints with Al Interlayer. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 1132–1144 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10059-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10059-1