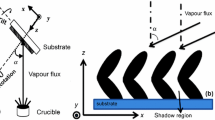
Abstract
Zinc oxide films were prepared using oblique angle deposition of Zn at four deposition angles of 0°, 30°, 45°, and 60° and subsequent annealing with the flow of oxygen. Structural characteristics of the films were obtained using atomic force microscopy and field emission scanning electron microscopy while their crystallography was investigated by x-ray diffraction analysis. The largest value of void fraction and the highest preferred orientation were obtained for the ZnO(101) diffraction line for the Zn film deposited at 45°. The former is explained in the published literature on the basis of rearrangement of atoms resulting from the diffusion or thermal vibration and the available crystallographic sites and surface energy on the substrate/growing film surface for relaxation of an adatom. Zn film anisotropy due to the bundling effect resulting from oblique angle deposition was examined by sheet resistivity measurements along x and y directions of the samples. Optical spectra of the samples were measured using both polarized light and unpolarized light from which optical constants were deduced. Both direct and indirect band gap energies were obtained and compared with the reported theoretical calculations. Our results are consistent with the experimental data in the literature; while they are larger than the theoretical reported values.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Toledano, R.E. Galindo, M. Yuste, J.M. Albella, and O.S. Anchez, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 46, 045306 (2013).
A.K. Singh, Adv. Powder Technol. 21, 609 (2010).
S.H. Mousavi, H. Haratizadeh, and H. Minaee, Opt. Commun. 284, 3558 (2011).
Z.L. Wang, J. Phys. Condens. Matt. 16, R 289 (2004).
Y. Liu, A. Liu, W. Liu, Z. Hu, and Y. Sang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 1263 (2010).
R. Shi, P. Yang, S. Zhang, and X. Dong, Ceram. Int. 40, 3637 (2014).
U. Ozgur, Y.I. Alivov, C. Liu, A. Teke, M.A. Reshchikov, S. Dogan, V. Avrutin, S.J. Cho, and H. Morkoc, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 041301 (2005).
E. Monroy, F. Omnes, and F. Calle, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 18, R33 (2003).
S.D. Škapin, G. Dražič, and Z.O. Crnjak, Mater. Lett. 61, 2783 (2007).
J.R. Anderso and G. Myers, J. Dent. Res. 45, 379 (1966).
H.U. Lee, S.Y. Park, S.C. Lee, J.H. Seo, B. Son, H. Kim, H.J. Yun, G.W. Lee, S.M. Lee, B. Nam, J.W. Lee, Y.S. Huh, C. Jeon, H.J. Kim, and J. Lee, Appl. Catal B: Environ. 144, 83 (2014).
S. Talam, S.R. Karumuri, and N. Gunnam, ISRN Nanotechnology, 372505 (2012). doi:10.5402/2012/372505.
H. Morkoç and U. Ozgur, Zinc Oxide: Fundamentals, Materials and Device Technology (Weinheim, Germany: Wiley, 2008).
C. Jagadish and S. Pearton, eds., Zinc Oxide Bulk, Thin Films and Nanostructures (Netherland: Elsevier, 2011).
P.X. Gao, Y. Ding, W.J. Mai, L.H. William, and Z.L. Wang, Science 309, 1700 (2005).
X.Y. Kong, Y. Ding, R. Yang, and Z.L. Wang, Science 303, 1348 (2004).
Z.L. Wang, Mater. Today 7, 26 (2004).
K. Khojier, H. Savaloni, and E. Amani, Appl. Surf. Sci. 289, 564 (2014).
K. Khojier and H. Savaloni, J. Elect. Mater. (2015). doi:10.1007/s11664-015-3833-2.
S. Mukhtar, A. Asadov, and W. Gao, Thin Solid Films 520, 3453 (2012).
J.P. Singh, T. Karabacak, D.-X. Ye, and D.-L. Liup, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 23, 2114–2121 (2005). doi:10.1116/1.2052747.
L. Abelmann and C. Lodder, Thin Solid Films 305, 1 (1997).
J. Takadoum, ed., Nanomaterials and Surface Engineering (Wiley, 2013). doi:10.1002/9781118618523.ch11.
A. Siabi-Garjan, H. Savaloni, J. Beik-Mohammadi, and A.R. Grayeli-Korpi, Philos. Magn. 93, 3527 (2013).
F.M. Smits, Bell Syst. Technol. J. 37, 711 (1958).
J.R. Taylor, An Introduction to Error Analysis, 2nd ed. (Sausalito: University Science Books, 1997).
H. Savaloni, F. Babaei, S. Song, and F. Placido, Vacuum 85, 776 (2011).
Y. Ueda, W. Takakura, and A. Yamada, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 239, 45 (2002).
W. Takakura, S. Ikeda, and Y. Ueda, Mater. Trans. 42, 881 (2001).
H. Savaloni, M. Gholipour-Shahraki, and M.A. Player, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39, 2231 (2006).
F.H. Chung and D.K. Smith, Industrial Applications of X-ray Diffraction (New York: Marcel Dekker, 1999), p. 798.
H. Savaloni and R. Babaei, Appl. Surf. Sci. 280, 439 (2013).
S. Mukherjee and D. Gall, Thin Solid Films 527, 158 (2013).
H. Savaloni and M. Gholipour-Shahraki, Nanotechnology 15, 311 (2004).
I.S. Yahia, A.A.M. Farag, M. Cavas, and F. Yakuphanoglu, Superlattices Microstruct. 53, 63 (2013).
A. Sinaoui, I. Trabelsi, F. Chaffar-Akkar, F. Aousgi, and M. Kanzari, Int. J. Thin Film Sci. Technol. 3, 19 (2014).
H. Kangarlou, M.M. Aghagonbad, and Z. Barjisi, Optick 124, 107 (2013).
A. Schleife, F. Fuchs, J. Furthmuller, and F. Bechstedt, Phys. Rev. B 73, 245212 (2006).
Ü. ÖzgÜr, Y.I. Alivov, C. Liu, A. Teke, M.A. Reshchikov, S. Doğan, V. Avrutin, S.-J. Cho, and H. Morkoç, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 041301 (2005). doi:10.1063/1.1992666.
D.A.G. Bruggeman, Ann. Phys. 24, 636 (1935).
H. Savaloni, F. Babaei, S. Song, and F. Placido, Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 8041 (2009).
R. Rosi and D.W. Lynch, Phys. Rev. B 5, 3883 (1972).
A. Siabi-Garjan, H. Savaloni, F. Abdi, A. Ghaffal, and F. Placido, Phys. Scr. 87, 055705 (2013).
A. Lakhtakia and R. Messier, Sculptured Thin Films, Nanoengineered Morphology and Optics (Bellingham, WA: SPIE, 2005).
F. Babaei and H. Savaloni, Opt. Commun. 278, 221 (2007).
F. Babaei and H. Savaloni, Opt. Commun. 278, 321 (2007).
A. Lakhtakia, Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 24, 239 (2000).
J.A. Sherwin, A. Lakhtakia, and B. Michel, Opt. Commun. 178, 267 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savaloni, H., Abbaszadeh, N. Influence of Oblique Angle Deposition on the Nano-structure and Characteristics of ZnO Thin Films Produced by Annealing of Zn Films. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 3343–3355 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4510-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4510-9