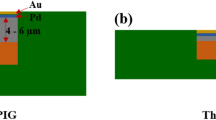Abstract
In the present study, several under bump metallization (UBM) schemes using either electroplated Ni or electroless Ni (EN) as the solderable layer are investigated. The EN and electroplated Ni are first deposited on Cu/Al2O3 substrates, followed by electroplating of thin gold coatings. Joints of 42Sn-58Bi/Au/EN/Cu/Al2O3 and 42Sn-58Bi/Au/Ni/Cu/Al2O3 are annealed at 145 C and 185CC for 30–180 minutes to investigate the interfacial reaction between the solder and metallized substrates. For 42Sn-58Bi/Au/Ni-5.5wt.%P/Cu/Al2O3, 42Sn-58Bi/Au/Ni-12.1wt.%P/Cu/Al2O3, and 42Sn-58Bi/Au/Ni/CU/Al2O3 joints annealed at 145 C, only Ni3Sn4 intermetallic compound (IMC) formed at the solder/EN interace. When annealed at an elevated temperature of 185 C, plate-like Ni3Sn4 IMC forms at the solder/Ni-5.5wt.%P interface, while a trace of (Ni, Cu)3Sn4 IMC is observed at the solder/Ni-12.1wt.%P interface and within the solder region. For the electroplated Ni-based multi-metallization substrate, the Ni3Sn4 IMC is present at the solder/Ni interface during annealing at 185 C for a short period of time. In the 42Sn-58Bi/Au/EN/Cu/Al2O3 joint, the EN spalls off the EN layer and migrates into the solder region when annealed at 185 C. The interface of the solder/electroplating Ni becomes saw-toothed as the annealing temperature is raised to 185 C. In addition, an enrichment of phosphorus is observed at the interface of the Ni-Sn IMC and EN.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.A. Powers, T.J. Singler, and J.A. Clum, J. Electron. Mater. 23, 773 (1994)
R.B. Cinque and J.W. Morris, Jr., J. Electron. Mater. 23, 533 (1994).
D.R. Frear, F.M. Hosking, and P.T. Vianco, Proc. Materials Developments in Microelectronic Packaging Conf. (Materials Park, OH: ASM, 1991), p. 229.
H.D. Blair, T.Y. Pan, and J.M. Nicholson, Proc. Electronic Component and Technol. Conf. (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 1998), p. 259.
C.Y. Lee and K.L. Lin, Thin Solid Films 249, 201 (1994).
J. Glazer, Int. Mater. Rev. 40, 65 (1995).
B.L. Young, J.G. Duh, and B.S. Chiou, J. Electron. Mater. 30, 543 (2001).
T. Massalski, Binary Alloy Phase Diagram (Materials Park, OH; ASM, 1986), p. 540.
J.W. Jang, P.G. Kim, K.N. Tu, D.R. Frear, and P. Thompson, J. Appl. Phys. 85, 8546 (1999).
K.C. Hung, Y.C. Chan, C.W. Tang, and H.C. Ong, J. Mater. Res. Soc. 15, 2534 (2000).
K.C. Hung and Y.C. Chan, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 19, 1755 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Young, BL., Duh, JG. Interfacial reaction and microstructural evolution for electroplated Ni and electroless Ni in the under bump metallurgy with 42Sn58Bi solder during annealing. J. Electron. Mater. 30, 878–884 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-001-0075-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-001-0075-2