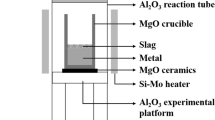
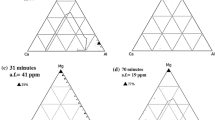
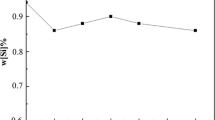
Abstract
Calcium treatment of Fe-13 pct Cr stainless steel, with inclusion modification as its main purpose, was evaluated on a laboratory scale. The stability diagram of Ca-Al was obtained using the FactSage software and could be divided into three parts based on the [Al] content: the ultra-low-Al region, the low-Al region, and the medium-high-Al region. Each of these regions required different amounts of calcium for inclusion modification. The ferrosilicon deoxidation product could be modified into low melting temperature inclusions by a CaO-SiO2 top slag in the ultra-low-Al region ([Al] content less than 40 ppm). Calcium treatment was necessary to modify the ferrosilicon deoxidation product into low melting temperature inclusions in the low-Al region ([Al] content from 40 to 100 ppm) for the CaO-SiO2-Al2O3 top slag. Calcium addition has a “liquid window” where adding calcium can accelerate inclusion modification. Adding calcium for 15 and 30 minutes resulted in complete modification times of 45 and 60 minutes, respectively, which indicates that early calcium treatment can produce plastic inclusions sooner. The relationship between the steel and inclusion content was determined by fitting the experimental data in the low-Al region. An appropriate range of T.Ca/T.O (total calcium content/total oxygen content) for inclusion modification is 0.99 to 1.44.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q. Wang, L. Wang, J. Zhai, J. Li and K. Chou: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, vol. 48(1), pp.564-72.
K.Suzuki, S.Banya and M.Hino: ISIJ int., 2001,vol41,pp. 813-17.
J.H.Park and Y.Kang. Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2006, vol. 37B, pp.791-97.
Y. Ren, L. Zhang, H. Ling, Y. Wang, D. Pan, Q. Ren and X. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, vol. 48(3), pp. 1433-38.
G. Xu, Z. Jiang, Y. Li: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47(4), pp. 2411-20.
YT. Guo, SP. He, GJ Chen and Q. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol.47(4), pp.2549-57.
J. Xu, F. Huang, X. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol.47(2),pp.1217-27.
K. Taguchi, ON. Hideki, T. Usui, K. Marukawa, K. Katogi: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol.45(11), pp.1572-76.
Y. Higuchi, M.Numata, S. Fukagawa, K Shinme:ISIJ Int., 1996, vol.36,pp.S151-S154.
JH. Park, SB. Lee, SK. Dong: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2005, vol.36(1), pp.67-73.
JMA Geldenhuis, PC Pistorius :Ironmaking Steelmaking, 2000, vol. 27(6), pp. 442-449.
Y. Ren, Y. Zhang, L. Zhang: Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2016, 44: 497-504
L. Holappa, M. Hämäläinen, M. Liukkonen, M. Lind and K. Tshilombo: Ironmaking &Steelmaking, 2003,vol.30, pp.111-15.
G. Yang and X. Wang: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol.55, pp.126-33.
D. Zhao, H. Li, Y. Cui and J Yang: ISIJ International, 2016, vol.56(7),pp. 1181-87.
Steelmaking Data Sourcebook: The Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. The 19th Committee on Steelmaking, Goldon Breach Science Pub, New York, 1988.
MP. Howard and B. Debanshu: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1984, vol.15, pp. 547-62.
H. Itoh and M. Hino: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1997, vol. 28, pp. 953-56.
H. Ohta and H. Suito: ISIJ int., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 1293-300.
MH Zayan, OM Jamjoom, NA Razik: Oxide Metall., 1990, vol. 34, pp. 323–33.
A. Löfgren. Internal report, Avesta Research Centre, Sweden. 1986.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their appreciation to the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFB0300204) and the National Nature Science Foundation of China (51374020, 51774027, and 51734002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted May 17, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Wang, L., Zhai, J. et al. Calcium Treatment for FeSi-killed Fe-13 Pct Cr Stainless Steel with Various Top Slag Compositions. Metall Mater Trans B 49, 325–333 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-1156-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-1156-9