Abstract
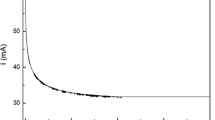
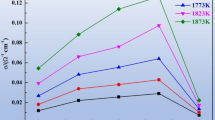
The electrical conductivity of molten slag has many important and practical effects in modeling and operating the electric smelting furnace. In the present study, the electrical conductivities (total and electronic/ionic properties) of MnO-CaO-SiO2 slags were measured by a four-electrode method at different oxygen potentials and temperatures. Experimental results show that the effects of temperature on the total, electronic, and ionic conductivities obey the Arrhenius law, and all conductivities increase when increasing the temperature. The stepped potential chronoamperometry method was used to measure the electronic transference number, which is affected strongly by oxygen potential but is unaffected by temperature. The total electrical, electronic, and ionic conductivities present similar increasing trends when increasing the CO/CO2 ratio, which resulted from increasing Mn2+.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Gruener, D. De Sousa Meneses, P. Odier, and J.P. Loup: J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2001, vol. 281, pp. 117–24.
M.T. Simnad, G. Derge, and I. George: Trans. AIME, 1954, vol. 6, pp. 1386–90.
J.O.M. Bockris, I.A. Kitchener, and S.A. Ignatowicz: Disc. Faraday Soc., 1948, vol. 4, pp. 265–81.
J.O.M. Bockris, I.A. Kitchener, and S.A. Ignatowicz: Trans. Faraday Soc., 1952, vol. 48, pp. 75–91.
L. Segers, A. Fontana, and R. Winand: Can. Metall. Q., 1983, vol. 22, pp. 429–35.
A. Fontana, L. Segers, and R. Winand: Can. Metall. Q., 1980, vol. 20, pp. 209–14.
J. W. Tomlinson and H. Inouye: J. Chem. Phys., 1952, vol. 20, p. 193.
M.T. Simnad and G. Derge: J. Chem. Phys., 1953, vol. 21, pp. 933–34.
H. Inouye, J.W. Tomlinson, and J. Chipman: Trans. Faraday Soc., 1953, vol. 49, pp. 796–801.
N.A. Fried, K.G. Rhoads, and D.R. Sadoway: Electrochim. Acta, 2001, vol. 46, pp. 3351–58.
G.M. Haarberg, K.S. Osen, R.J. Heus, and J.J. Egan: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1990, vol. 137, pp. 2777–81.
J.H. Park: ISIJ Int., 2012, vol. 52, pp. 1627–36.
D. Wang, A.J. Gmitter, and D.R. Sadoway: J. Electrochem. Soc., 2011, vol. 158, pp. E51–E54.
D.R. Sadoway: J. Mater. Res., 1995, vol. 10, pp. 487–92.
S.L. Schiefelbein, N.A. Fried, K.G. Rhoads, and D.R. Sadoway: Rev. Sci. Instrum., 1998, vol. 69, pp. 3308–13.
J.H. Liu, G.H. Zhang, and K.C. Chou: J. Electrochem. Soc., 2015, vol. 162, pp. E314–E318.
K. Narita, T. Onoye, T. Ishll, and K. Uemura: ISIJ Int., 1975, vol. 61, pp. 2943–51.
M. Barati and K.S. Coley: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2006, vol. 37B, pp. 41–49.
L. Bobok, L. Bodnar, and J. Schmiedl: Hutnicke Listy, 1982, vol. 37, pp. 419–24.
S.N. Shin, S.A. Lyamkin, R.I. Gulyaeva, and V.M. Chumarev: Rasplavy, 1998, vol. 5, pp. 20–24.
J.H. Liu, G.H. Zhang, Y.D. Wu, and K.C. Chou: Can. Metall. Q., 2016, vol. 55, pp. 221–25.
M. Kawahara, K.J. Morinaga, and T. Yanagase: Can. Metall. Q., 1983, vol. 22, pp. 143–47.
J.H. Liu, G.H. Zhang, Y.D. Wu, and K.C. Chou: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 47B, pp. 798–803.
J.H. Liu, G.H. Zhang, and K.C. Chou: Can. Metall. Q., 2015, vol. 54, pp. 170–76.
J.H. Liu, G.H. Zhang, and K.C. Chou: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55, pp. 2325–31.
W.R. Dickson and E.B. Dismukes: Trans. AIME, 1962, vol. 224, pp. 505–11.
M. Barati and K.S. Coley: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2006, vol. 37B, pp. 51–60.
Acknowledgment
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51422405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted March 28, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, JH., Zhang, GH. & Wang, Z. Experimental Study on Electrical Conductivity of MnO-CaO-SiO2 Slags at 1723 K to 1823 K (1450 °C to 1550 °C) and Various Oxygen Potentials. Metall Mater Trans B 48, 3359–3363 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-1072-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-1072-z