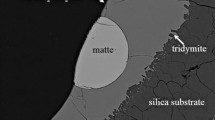
Abstract
Copper concentrates and fluxes can contain variable levels of SiO2, CaO, and MgO in addition to main components Cu, Fe, and S. Metal recovery, slag tapping, and furnace wall integrity all are dependent on phase equilibria and other properties of the phases and are functions of slag composition and operational temperature. Optimal control of the slag chemistry in the copper smelting, therefore, is essential for high recovery and productivity; this, in turn, requires detailed knowledge of the slag phase equilibria. The present work provides new phase equilibrium experimental data in the FeO-Fe2O3-SiO2-CaO-MgO-Al2O3 system at oxygen partial pressure of 10−8 atm within the range of temperatures and compositions directly relevant to copper smelting. For the range of conditions relevant to the Kennecott Utah Copper (South Magna, UT) smelting furnace, it was confirmed experimentally that increasing concentrations of MgO or CaO resulted in significant decreases of the tridymite liquidus temperature and in changes in the position of the tridymite liquidus in the direction of higher silica concentration; in contrast, the spinel liquidus temperatures increase significantly with the increase of MgO or CaO. Olivine and clinopyroxene precipitates appeared at high MgO concentrations in the liquid slag. The liquidus temperature in the spinel primary phase field was expressed as a linear function of 1/(wt pctFe/wt pctSiO2), wt pctCaO, wt pctMgO, and wt pctAl2O3. The positions of each of the liquidus points (wt pctFe)/(wt pctSiO2) at a fixed temperatures in the tridymite primary phase field were expressed as linear functions of wt pctCaO, wt pctMgO, and wt pctAl2O3.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.M. Henao and K. Itagaki: Mater. Trans., JIM., 2005, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 812–19.
H.M. Henao, H. Ohono, and K. Itagaki: Sohn Intl. Symp., San Diego, CA, TMS, Warrandale, PA, 2006, pp. 731–39.
B. Zhao, E. Jak, and P.C. Hayes: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1999, vol. 30B, pp. 597–605.
B. Zhao, E. Jak, and P.C. Hayes: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1999, vol. 30B, pp. 597–605.
J.A. Imlach and F.P. Glasser: Trans. J. Br. Ceram. Soc., 1971, vol. 70, pp. 227.
J.A. Imlach and F.P. Glasser: Trans. J. Br. Ceram. Soc., 1973, vol. 72, pp. 221.
A. Muan and E.F. Osborn: J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 1956, vol. 39, pp. 121–40.
S. Nikolic, P.C. Hayes, and E. Jak: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39B, pp. 179–88.
S. Nikolic, H.M. Henao, P.C. Hayes, and E. Jak: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39B, pp. 189–99.
P. Wu, G. Eriksson, and A.D. Pelton: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1993, vol. 76 no. 8, pp. 2065–75.
P. Wu, G. Eriksson, A.D. Pelton, and M. Blander: Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1993, vol. 33, pp. 26–35.
G. Eriksson, W. Ping, A.D. Pelton, and M. Blander: Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn, 1993, vol. 33, pp. 25–34.
S.A. Degterov and A.D. Pelton: Metall. Mater. Trans., 1999, vol. 30B, pp. 661–69.
E. Jak and P. Hayes: VIII Intl. Conf. on Molten Slags, Fluxes and Salts, Santiago, Chile, 2009, pp. 473–90.
E. Jak, Zhao B. Zhao, and P. Hayes: 6th Intl. Conf. on Slags, Fluxes and Molten Salts, Stockholm, Sweden, 2000.
M. Selleby and B. Sundman: Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. Computer Software in Chemical and Extractive Metallurgy, Quebec, Canada, 1993, pp. 113–26.
M. Selleby: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1997, vol. 28B, pp. 563–76.
E. Jak, B. Zhao, S. Nikolic, and P.C. Hayes: European Metallurgy Conference, Düsseldorf, Germany, 2007.
E. Jak and P.C. Hayes: VIII Intl. Conf. on Molten Slags, Fluxes, and Salts, Santiago, Chile, 2009, pp. 473–90.
S. Nikolic, P.C. Hayes, and E. Jak: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39B, pp. 210–17.
C.W. Bale, P. Chartrand, S.A. Decterov, E. Eriksson, K. Hack, R.B. Mahfoud, J. Mclancon, A.D. Pelton, and S. Petersen: CALPHAD, 2002, vol. 26, pp. 189–228.
S. Decterov, I.H. Jung, E. Jak, P.C. Hayes, and D. Pelton: VII Intl. Conf. on Molten Slags, Fluxes and Salts, Capetown, South Africa, SAIMM, Johannesburg, South Africa, 2004, pp. 839–50.
Acknowledgments
The research has been founded by Rio Tinto—Kennecott Utah Copper LLC. The authors would like to thank the following individuals for their assistance in this project: Ms. Jie Yu and Dr. Baojun Zhao from the Pyrometallurgy Research Centre (PYROSEARCH) within the University of Queensland; Mr. Ron Rasch and Mr. Ying Yu from the Centre of Microscopy and Microanalysis (CMM) within the University of Queensland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted December 2, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henao, H.M., Nexhip, C., George-Kennedy, D.P. et al. Investigation of Liquidus Temperatures and Phase Equilibria of Copper Smelting Slags in the FeO-Fe2O3-SiO2-CaO-MgO-Al2O3 System at PO2 10−8 atm. Metall Mater Trans B 41, 767–779 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-010-9369-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-010-9369-1