Abstract
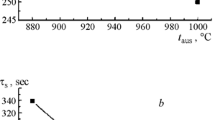
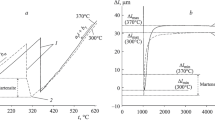
The bainite transformation temperatures of eight high-silicon steels were determined metallographically. The bainite start (B s ) temperatures, which define the highest temperature at which bainite can form, all lay below the T 0 loci, where ferrite and austenite of the same chemical compositions have identical free energy. The established method of calculating B s temperatures gave reasonable agreement with the experimental results. Careful study of the isothermally reacted samples revealed that Widmanstätten ferrite and bainite could both be observed, even at the beginning of the transformation, at around the B s temperature. On the other hand, the lower bainite start (LB s ) temperatures of these steels were found to be very close to the martensite start (M s ) temperatures. Silicon is considered to be responsible for depressing the LB s temperature by retarding the formation of cementite. The coformation of upper and lower bainite near the LB s temperature is also confirmed. The results indicate that the displacive formation mechanism of bainite is sustainable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.F. Hehemann, K.R. Kinsman, and H.I. Aaronson: Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 1077–93.
H.I. Aaronson: The Mechanism of Phase Transformations in Crystalline Solids, Institute of Metals Monograph 33, Institute of Metals, London, 1986, pp. 270–81.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia and D.V. Edmonds: Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 895–907.
W.T. Reynolds, Jr., H.I. Aaronson, and G. Spanos: Mater. Trans. JIM, 1991, vol. 32, pp. 737–46.
G.J. Shiflet and H.I. Aaronson: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1413–32.
W.T. Reynolds, Jr., F.Z. Li, C.K. Shui, and H.I. Aaronson: Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1433–63.
H.I. Aaronson, W.T. Reynolds, Jr., G.J. Shiflet, and G. Spanos: Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1343–80.
Y. Ohmori and T. Maki: Mater. Trans. JIM, 1991, vol. 32, pp. 631–41.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Bainite in Steels, The Institute of Materials, London, 1992, pp. 117–21.
M. Takahashi and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1990, vol. 6, pp. 592–603.
N.F. Kennon and N.A. Kaye: Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 975–78.
J.M. Oblak and R.F. Hehemann: Transformation and Hardenability in Steels, Climax Molybdenum Co., Ann Arbor, MI, 1967, pp. 15–30.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Acta Metall., 1981, vol. 29, pp. 1117–30.
Y.C.J. Jung, K. Nakai, H. Ohtsubo, and Y. Ohmori: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1994, vol. 34 (1), pp. 43–50.
W.S. Owen: ASM Trans., 1954, vol. 11, pp. 812–28.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: J. Phys., 1982, vol. 43, pp. C4-437–C4-441.
R.F. Hehemann: Phase Transformation, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1970, pp. 397–432.
H.I. Aaronson and C. Wells: Trans. AIME, 1956, vol. 256, pp. 1216–23.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia and J.W. Christian: Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 21A, pp. 767–97.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1985, vol. 1, pp. 497–504.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia and D.V. Edmonds: Acta Metall., 1980, vol. 28, pp. 1265–73.
C. Zener: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1946, vol. 167, pp. 550–59.
H.I. Aaronson, H.A. Domian, and G.M. Pound: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1966, vol. 236, pp. 753–67.
H.I. Aaronson, H.A. Domian, and G.M. Pound: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1966, vol. 236, pp. 768–80.
A. Ali and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1989, vol. 5, pp. 398–402.
K. Tsuzaki, C. Fujiwara, and T. Maki: Mater. Trans. JIM, 1991, vol. 32, pp. 658–66.
V.T.T. Miihkinen and D.V. Edmonds: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1987, vol. 3, pp. 422–31.
A.M. Llopis: Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, 1977.
F.B. Pickering: Transformation and Hardenability in Steels, Climax Molybdenum Co., Ann Arbor, MI, 1967, pp. 109–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, L.C. Bainite transformation temperatures in high-silicon steels. Metall Mater Trans A 30, 909–916 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-999-0144-3
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-999-0144-3