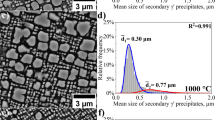
Abstract
The effects of grain boundary serration on boron segregation and liquation cracking behavior in a simulated weld heat-affected zone (HAZ) of a wrought nickel-based superalloy 263 have been investigated. The serrated grain boundaries formed by the developed heat treatment were highly resistant to boron segregation; the serrated sample contained 41.6 pct grain boundaries resistant to boron enrichment as compared with 14.6 pct in the unserrated sample. During weld thermal cycle simulation, liquated grain boundaries enriched with boron were observed at the peak temperature higher than 1333 K (1060 °C) in both unserrated and serrated samples; however, serrated grain boundaries exhibited a higher resistance to liquation. The primary cause of liquation in this alloy was associated with the segregation of the melting point depressing element boron at grain boundaries. The hot ductility testing result indicated that the serrated grain boundaries showed a lower susceptibility to liquation cracking; the grain boundary serration led to an approximate 15 K decrease in the brittle temperature range. These results reflect closely a significant decrease in interfacial energy as well as a grain boundary configuration change by the serration.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.J. Pepe and W.F. Savage: Weld. J., 1967, vol. 46, pp. 411s-422s.
R. Nakkalil, N.L. Richards, and M.C. Chaturvedi: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1992, vol. 26, pp. 1599-1604.
R. Vincent: Acta Metall., 1985, vol. 33, pp. 1205-16.
O.A. Ojo and M.C. Chaturvedi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2007, vol. 38A, pp. 356-69.
H. Guo, M.C. Chaturvedi, N.L. Richards, and G.S. McMahon: Scripta Mater., 1999, vol. 40, pp. 383-88.
K.R. Vishwakarma, N.L. Richards, and M.C. Chaturvedi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 480, pp. 517-28.
H. Kokawa, C.H. Lee, and T.H. North: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 1627-31.
M. Qian and J.C. Lippold: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 3351-61.
P. Lin, G. Palumbo, U. Erb, and K.T. Aust: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1995, vol. 33, pp. 1387-92.
N. Souaï, N. Bozzolo, L. Nazé, Y. Chastel, and R. Logé: Scripta Mater., 2010, vol. 62, pp. 851-54.
J.M. Larson and S. Floreen: Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 51-55.
A.K. Koul and G.H. Gessinger: Acta Metall., 1983, vol. 31, pp. 1061-69.
A.K. Koul and R. Thamburaj: Metall. Trans. A, 1985, vol. 16A, pp. 17-26.
A.K. Koul, P. Au, N. Bellinger, R. Thamburaj, W. Wallace, and J-P. Immarigeon: Superalloys 1988, Eds. S. Reichman, D.N. Duhl, G. Maurer, S. Antolovich, and C. Lund, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1988, pp. 3–12.
H. Loyer Danflou, M. Marty, and A. Walder: Superalloys 1992, Eds. S.D. Antolovich, R.W. Stusrud, R.A. MacKay, D.L. Anton, T. Khan, R.D. Kissinger, and D.L. Klarstrom, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1992, pp. 63–72.
H.U. Hong, I.S. Kim, B.G. Choi, M.Y. Kim, and C.Y. Jo: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 517, pp. 125-31.
H.U. Hong, H.W. Jeong, I.S. Kim, B.G. Choi, Y.S. Yoo, and C.Y. Jo: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2010, vols. 638–642, pp. 2245–50.
H.U. Hong, I.S. Kim, B.G. Choi, C.Y. Jo, Y.S. Yoo, H.W. Jeong, and S.M. Seo: US Patent Application Serial No. 12/484,597.
J.C. Zhao, V. Ravikumar, and A.M. Beltran: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 1271-82.
V. Randle: Scripta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 1011-15.
G.S. Rohrer, V. Randle, C.S. Kim, and Y. Hu: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 4489-4502.
B. Hu and H. Li: Superalloys 1980, Eds. J.K. Tien, S.T. Wlodek, H. Morrow III, M. Gell, and G.E. Maurer, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1980, pp. 423–29.
R.M. Kruger and G.S. Was: Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 2555-66.
W. Chen, M.C. Chaturvedi, N.L. Richards, and G. McMahon: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 1947-54.
D. McLean: Grain Boundaries in Metals, Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK, 1957.
L. Karlsson, H. Nordén, and H. Odelius: Acta Metall., 1988, vol. 36, pp. 1-12.
L. Karlsson and H. Nordén: Acta Metall., 1988, vol. 36, pp. 13-24.
W. Chen, M.C. Chaturvedi, and N.L. Richards: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 931-39.
R.W. Balluffi: Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 2069-95.
M. Kurban, U. Erb, and K.T. Aust: Scripta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 1053-58.
H.U. Hong, I.S. Kim, B.G. Choi, H.W. Jeong, S.M. Seo, Y.S. Yoo, and C.Y. Jo: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2010, vols. 654–656, pp. 488-91.
W.A. Owczarski: Welding Research Council Bulletin, New York, NY, 1969, pp. 6-9.
C.S. Smith: Trans. AIME, 1948, vol. 175, pp.15-51.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support from MKE (Ministry of Knowledge Economy), Account No. UCN215-2848.C and 615-2848.C, which made this work possible. The authors also would like to thank Dr. Hong at KBSI, Busan for his sincere assistance with the nano-SIMS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted March 18, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, H.U., Kim, I.S., Choi, B.G. et al. On the Role of Grain Boundary Serration in Simulated Weld Heat-Affected Zone Liquation of a Wrought Nickel-Based Superalloy. Metall Mater Trans A 43, 173–181 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0837-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0837-2