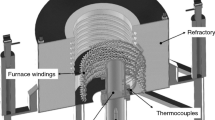
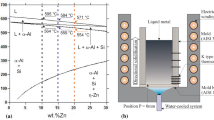
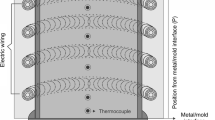
Abstract
Three Al-Ni hypoeutectic alloys were directionally solidified under upward unsteady-state heat-flow conditions. Primary (λ 1) and secondary (λ 2) dendrite arm spacings were measured along the castings for all alloys and correlated with transient solidification thermal variables. A combined theoretical and experimental approach was used to quantitatively determine such thermal variables, i.e., transient metal/mold heat-transfer coefficients, tip growth rates, thermal gradients, tip cooling rates, and local solidification time. The article also focuses on the dependence of dendrite arm spacings on the alloy solute content. Furthermore, the experimental data concerning the solidification of Al-1.0, 2.5, and 4.7 wt pct Ni alloys are compared with the main predictive dendritic models from the literature.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
ThermoCalc software is an exclusive copyright property of the STT Foundation (Foundation of Computational Thermodynamics, Stockholm).
Abbreviations
- A :
-
constant of the primary dendritic spacing power law (dimensionless)
- a 2 :
-
secondary dendrite calibration factor (dimensionless)
- B :
-
constant of the secondary dendritic spacing power law (dimensionless)
- C :
-
constant of Eq. [3] (dimensionless)
- c :
-
specific heat (J·kg−1·K−1)
- c′ :
-
pseudospecific heat (J·kg−1·K−1)
- C 0 :
-
alloy solute concentration (wt pct)
- C E :
-
eutectic composition (wt pct)
- D :
-
solute diffusivity (m2·s−1)
- f s :
-
local solid fraction (pct)
- G 0 ε :
-
characteristic parameter (60,000 × 6 K·m−1)
- \( \ifmmode\expandafter\bar\else\expandafter\fi{G}^{{E,B}} \) :
-
partial excess Gibbs energies of Al in the bulk (J·mol−1)
- \( \ifmmode\expandafter\bar\else\expandafter\fi{G}^{{E,S}} \) :
-
partial excess Gibbs energies of Al in the surface (J·mol−1)
- G L :
-
temperature gradient (K·m−1)
- h g :
-
global heat-transfer coefficient (W·m−2·K−1)
- i :
-
element position according to x and y axes (dimensionless)
- K :
-
thermal conductivity (W·m−1·K−1)
- k 0 :
-
partition coefficient (dimensionless)
- K eq :
-
equivalent thermal conductivity (W·m−1·K−1)
- L :
-
latent heat (J·kg−1)
- L T :
-
constant of Eq. [6] (dimensionless)
- m L :
-
liquidus slope (K·wt pct−1)
- N :
-
number of moles (dimensionless)
- N 0 :
-
Avogadro’s number (m−3)
- \( \ifmmode\expandafter\dot\else\expandafter\fi{q} \) :
-
rate of energy generation (W·m−3)
- R:
-
gas constant (J·mol−1·K−1)
- \( {\mathop T\limits^ \bullet }_{L} \) :
-
tip cooling rate (K·s−1)
- T :
-
temperature (K)
- t :
-
time (s)
- T f :
-
fusion temperature of the solvent (K)
- T liq :
-
liquidus temperature (K)
- T m :
-
melting temperature (K)
- T p :
-
initial melt temperature (K)
- t SL :
-
local solidification time (s)
- T sol :
-
solidus temperature (K)
- V :
-
molar volume (m3)
- V L :
-
tip growth rate (m·s−1)
- X :
-
molar fraction (dimensionless)
- x :
-
rectangular coordinate (m)
- ρ :
-
density (kg·m−3)
- Γ:
-
Gibbs–Thompson coefficient (K·m)
- Δt :
-
time interval (s)
- ΔT :
-
difference between liquidus and solidus equilibrium temperatures
- λ 1 :
-
primary dendrite arm spacing (μm)
- λ 2 :
-
secondary dendrite arm spacing (μm)
- σ SL :
-
surface energy (N·m−1)
- L :
-
liquid
- M :
-
mush
- S :
-
solid
References
H. Jones: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2005, vols. 413–414, pp. 165–73
V. Mertinger, G. Szabo, P. Barczy, A. Kovacs, G. Czel: Mater. Sci. Forum, 1996, vols. 215–216, pp. 331–38
A. Juarez-Hernandez, H. Jones: Scripta Mater., 1998, vol. 38, pp. 729–34
Y.X. Zhuang, X.M. Zhang, L.H. Zhu, Z.Q. Hu: Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2001, vol. 2, pp. 37–39
J.M.V. Quaresma, C.A. Santos, A. Garcia: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, vol. 31A, pp. 3167–77
W.R. Osório, A. Garcia: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2002, vol. 325, pp. 103–11
W.R. Osório, C.A. Santos, J.M.V. Quaresma, A. Garcia: J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 2003, vols. 143–144, pp. 703–09
W.R. Osório, P.R. Goulart, G.A. Santos, C. Moura Neto, A. Garcia: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37A, pp. 2525–38
J.D. Hunt: Int. Conf. Solidification and Casting of Metals, The Metals Society, London, 1979, pp. 3–9
W. Kurz, J.D. Fisher: Acta Metall., 1981, vol. 29, pp. 11–20
W. Kurz, J.D. Fisher: Fundamentals of Solidification, Trans Tech Publications, Aedermannsdorf, Switzerland, 1992, pp. 85–90
R. Trivedi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 977–82
K. Somboonsuk, J.T. Mason, R. Trivedi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 967–75
M. Gündüz, E. Çadirli: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2002, vol. 327, pp. 167–85
D. Bouchard, J.S. Kirkaldy: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1997, vol. 28B, pp. 651–63
J.D. Hunt, S.Z. Lu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, vol. 27A, pp. 611–23
D. Bouchard, J.S. Kirkaldy: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1996, vol. 27B, pp. 101–13
A. Mortesen: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 569–74
M. Chen, T.Z. Kattamis: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1998, vol. 247, pp. 239–47
O.L. Rocha, C.A. Siqueira, A. Garcia: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2003, vol. 361, pp. 111–18
O.L. Rocha, C.A. Siqueira, A. Garcia: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, vol. 34A, pp. 995–1006
M.D. Peres, C.A. Siqueira, A. Garcia: J. Alloys Compd., 2004, vol. 381, pp. 168–81
T. Okamoto, K. Kishitake: J. Cryst. Growth, 1975, vol. 29, pp. 137–46
U. Feurer and R. Wunderlin, cited by W. Kurz and D.J. Fisher: Fundamentals of Solidification, Trans Tech Publications, Ltd., Aedermannsdorf, Switzerland, 1986, pp. 214–16
D.H. Kirkwood: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1985, vol. 73, pp. L1–L4
J.A.V. Butler: Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 1932, vol. 135, pp. 348–75
W. Gasior, J. Pstruś, Z. Moser, A. Krzyżak, K. Fitzner: J. Phase Equilib. Diff., 2002, vol. 24, pp. 40–49
R. Picha, J. Vřešťál, A. Kroupa: Calphad, 2004, vol. 28, pp. 141–46
T.P. Hoar, D.A. Melford: Trans. Faraday Soc., 1957, vol. 53, pp. 315–26
T. Tanaka, T. Lida: Steel Res., 1994, vol. 65, pp. 21–28
T. Tanaka, K. Hack, T. Lida, S. Hara: Z. Metallkd., 1996, vol. 87, pp. 380–89
T. Tanaka, K. Hack, S. Hara: MRS Bull., 1999, vol. 24, pp. 45–50
M. Gunduz, E. Çardili: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2002, vol. 327, pp. 167–85
C.A. Santos, J.M.V. Quaresma, A. Garcia: J. Alloys Compd., 2001, vol. 319, pp. 174–86
I.L. Ferreira, J.E. Spinelli, J.C. Pires, A. Garcia: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2005, vol. 408, pp. 317–25
F.P. Incropera, D.P. Dewit: Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, Wiley, New York, NY, 1990, pp. 56–62
V.L. Voller, C.R. Swaminathan: Numer. Heat Transfer Part B, 1991, vol. 19, pp. 175–89
M.V. Canté, K.S. Cruz, J.E. Spinelli, N. Cheung, A. Garcia: Mater. Lett., 2007, vol. 61, pp. 2135–38
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by FAPESP (The Scientific Research Foundation of the State of São Paulo, Brazil), CNPq (The Brazilian Research Council), and FAEPEX–UNICAMP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 6, 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Canté, M., Spinelli, J., Ferreira, I. et al. Microstructural Development in Al-Ni Alloys Directionally Solidified under Unsteady-State Conditions. Metall Mater Trans A 39, 1712–1726 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-008-9536-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-008-9536-z