Abstract
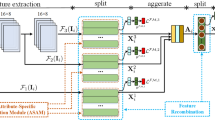
Pedestrian attribute recognition in surveillance scenarios is still a challenging task due to the inaccurate localization of specific attributes. In this paper, we propose a novel view-attribute localization method based on attention (VALA), which utilizes view information to guide the recognition process to focus on specific attributes and attention mechanism to localize specific attribute-corresponding areas. Concretely, view information is leveraged by the view prediction branch to generate four view weights that represent the confidences for attributes from different views. View weights are then delivered back to compose specific view-attributes, which will participate and supervise deep feature extraction. In order to explore the spatial location of a view-attribute, regional attention is introduced to aggregate spatial information and encode inter-channel dependencies of the view feature. Subsequently, a fine attentive attribute-specific region is localized, and regional weights for the view-attribute from different spatial locations are gained by the regional attention. The final view-attribute recognition outcome is obtained by combining the view weights with the regional weights. Experiments on three wide datasets (richly annotated pedestrian (RAP), annotated pedestrian v2 (RAPv2), and PA-100K) demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach compared with state-of-the-art methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Sudowe, H. Spitzer, B. Leibe. Person attribute recognition with a jointly-trained holistic CNN model. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop, IEEE, Santiago, Chile, pp. 329–377, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW.2015.51.
D. W. Li, X. T. Chen, Z. Zhang, K. Q. Huang. Pose guided deep model for pedestrian attribute recognition in surveillance scenarios. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, IEEE, San Diego, USA, pp. 1–6, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME.2018.8486604.
L. Bourdev, S. Maji, J. Malik. Describing people: A poselet-based approach to attribute classification. In Proceedings of International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, Barcelona, Spain, pp. 1543–1550, 2011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126413.
P. Z. Liu, X. H. Liu, J. J. Yan, J. Shao. Localization guided learning for pedestrian attribute recognition, [Online], Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.09102, 2018.
D. W. Li, Z. Zhang, X. T. Chen, K. Q. Huang. A richly annotated pedestrian dataset for person retrieval in real surveillance scenarios. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 1575–1590, 1919. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2878349.
N. Sarafianos, X. Xu, I. A. Kakadiaris. Deep imbalanced attribute classification using visual attention aggregation. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, Munich, Germany, pp. 708–725, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01252-6_42.
E. Yaghoubi, D. Borza, J. Neves, A. Kumar, H. Proença. An attention-based deep learning model for multiple pedestrian attributes recognition. Image and Vision Computing, vol. 102, Article number 103981, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2020.103981.
M. D. Wu, D. Huang, Y. F. Guo, Y. H. Wang. Distraction-aware feature learning for human attribute recognition via coarse-to-fine attention mechanism. In Proceedings of AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol.34, no.7, pp. 12394–12401, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6925.
J. Hu, L. Shen, G. Sun. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Salt Lake City, USA, pp. 7132–7141, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1102/CVPR.2018.00745.
S. Woo, J. Park, J. Y. Lee, I. S. Kweon. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, Munich, Germany, pp. 3–19, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1.
K. M. He, X. Y. Zhang, S. Q. Ren, J. Sun. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Las Vegas, USA, pp. 770–778, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90.
D. W. Li, Z. Zhang, X. T. Chen, H. B. Ling, K. Q. Huang. A richly annotated dataset for pedestrian attribute recognition, [Online], Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.07054, April 27, 2016.
X. H. Liu, H. Y. Zhao, M. Q. Tian, L. Sheng, J. Shao, S. Yi, J. J. Yan, X. G. Wang. HydraPlus-Net: Attentive deep features for pedestrian analysis. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, Venice, Italy, pp. 350–352, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1102/ICCV.2017.46.
C. Su, S. L. Zhang, J. L. Xing, W. Gao, Q. Tian. Deep attributes driven mutti-camera person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp. 475–491, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_30.
Y. T. Lin, L. Zheng, Z. D. Zheng, Y. Wu, Z. L. Hu, C. G. Yan, Y. Yang. Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning. Pattern Recognition, vol. 95, pp. 151–161, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.06.006.
Z. D. Zheng, X. D. Yang, Z. D. Yu, L. Zheng, Y. Yang, J. Kautz. Joínt discriminative and generative learníng for person re-identification. In Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Long Beach, USA, pp. 2133–2142, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00224.
Y. L. Tian, P. Luo, X. G. Wang, X. O. Tang. Pedestrian detection aided by deep learning semantic tasks. In Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Boston, USA, pp. 5079–5087, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299143.
X. B. Liu, Y. L. Xu, L. Zhu, Y. D. Mu. A stochastic attribute grammar for robust cross-view human tracking. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 28, no. 10, pp. 2884–2895, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2017.2781738.
X. W. Wang, T. Zhang, D. R. Tretter, Q. Lin. Personal clothing retrieval on photo collections by color and attributes. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, vol. 15, no. 8, pp. 2035–2045, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2013.2279658.
R. Feris, R. Bobbitt, L. Brown, S. Pankanti. Attribute-based people search: Lessons learnt from a practical surveillance system. In Proceedings of International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, ACM, Glasgow, UK, pp. 153–160, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/2578726.2578732.
J. E. Liu, B. Kuipers, S. Savarese. Recognizing human actions by attributes. In Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Colorado Springs, USA, pp. 3337–3344, 2011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2011.5995353.
X. F. Ji, Q. Q. Wu, Z. J. Ju, Y. Y. Wang. Study of human action recognition based on improved spatio-temporal features. International Journal of Automation and Computing, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 500–509, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-014-0831-4.
L. F. Wu, Q. Wang, M. Jian, Y. Qiao, B. X. Zhao. A comprehensive review of group activity recognition in videos. International Journal of Automation and Computing, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 334–350, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-020-1258-8.
Z. W. Xu, X. J. Wu, J. Kittler. STRNet: Triple-stream spatiotemporal relation network for action recognition. International Journal of Automation and Computing, vol. 18, no. 5, pp. 718–730, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-021-1289-9.
M. Fayyaz, J. Gall. SCT: Set constrained temporal transformer for set supervised action segmentation. In Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Seattle, USA, pp.498–507, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00058.
J. Li, S. Todorovic. Set-constrained viterbi for set-supervised action segmentation. In Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Seattle, USA, pp. 10817–10826, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01083.
Y. F. Huang, Y. Sugano, Y. Sato. Improving action segmentation via graph-based temporal reasoning. In Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Seattle, USA, pp. 14021–14031, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1009/CVPR42600.2020.01404.
J. Chen, Z. H. Li, J. B. Luo, C. L. Xu. Learning a weakly-supervised video actor-action segmentation model with a wise selection. In Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Seattle, USA, pp.9898–9908, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00992.
N. Dalal, B. Triggs. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, San Diego, USA, pp. 886–893, 2005. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2005.177.
R. Layne, T. Hospedales, S. G. Gong. Person re-identification by attributes. In Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference, Surrey, UK, Article number 24, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5244/C.26.24.
D. W. Li, X. T. Chen, K. Q. Huang. Multi-attribute learning for pedestrian attribute recognition m surveillance scenarios. In Proceedings of the 3rd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, pp. 111–115, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.0109/CPPR.2015.7486476.
J. J. Zhang, P. Y. Ren, J. M. Li. Deep template matching for pedestrian attribute recognition with the auxiliary supervision of attribute-wise keypoints, [Online], Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.06798, November 13, 2020.
J. Y. Wang, X. T. Zhu, S. G. Gong, W. Li. Attribute recognition by joint recurrent learning of context and correlation. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, Venice, Italy, pp. 531–540, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.65.
X. Zhao, L. F. Sang, G. G. Ding, Y. C. Guo, X. M. Jin. Grouping attribute recognition for pedestrian with joint recurrent learning. In Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI, Stockholm, Sweden, pp. 3177–3183, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2018/441.
C. F. Tang, L. Sheng, Z. X. Zhang, X. L. Hu. Improving pedestrian attribute recognition with weakly-supervised multi-scale attribute-specific localization. In Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, Seoul, Korea, pp. 4996–5005, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00510.
C. L. Zitnick, P. Dollár. Edge boxes: Locating object proposals from edges. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, Zurich, Switzerland, pp. 391–405, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_26.
Z. X. Feng, J. H. Lai, X. H. Xie. Learning view-specific deep networks for person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 27, no. 7, pp. 3472–3483, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2818438.
S. S. Farfade, M. J. Saberian, L. J. Li. Multi-view face detection using deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 5th ACM on International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, ACM, Shanghai, China, pp. 643–650, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/2671188.2749408.
H. Sadr, M. M. Pedram, M. Teshnehlab. Multi-view deep network: A deep model based on learning features from heterogeneous neural networks or sentiment analysis. IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 86984–86997, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2992063.
F. Zhu, H. S. Li, W. L. Ouyang, N. H. Yu, X. G. Wang. Learning spatial regularization with image-level supervisions or multi-label image classification. In Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Honolulu, USA, pp. 2027–2036, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.219.
Z. C. Tan, Y. Yang, J. Wan, H. Y. Hang, G. D. Guo, S. Z. Li. Attention-based pedestrian attribute analysis. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 28, no. 12, pp. 6126–6140, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2919199.
C. Szegedy, S. Ioffe, V. Vanhoucke, A. A. Alemi. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI Press, San Francisco, USA, pp. 4278–4284, 2017.
C. Szegedy, W. Liu, Y. Q. Jia, P. Sermanet, S. Reed, D. Anguelov, D. Erhan, V. Vanhoucke, A. Rabinovich. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Boston, USA, pp. 1–9, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594.
S. Ioffe, C. Szegedy. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, JMLR, Lille, France, pp. 448–456, 2015.
C. Szegedy, V. Vanhoucke, S. Ioffe, J. Shlens, Z. Wojna. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Las Vegas, USA, pp. 2818–2826, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.308.
H. Cai, C. Gan, T. Z. Wang, Z. K. Zhang, S. Han. Once-for-all: Train one network and specialize it for efficient deployment, [Online], Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.09791, 2019.
A. Howard, M. Sandler, B. Chen, W. J. Wang, L. C. Chen, M. X. Tan, G. Chu, V. Vasudevan, Y. K. Zhu, R. M. Pang, H, Adam, Q. Le. Searching for MobileNetV3. In Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, Seoul, Korea, pp. 1314–1324, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00140.
Y. B. Deng, P. Luo, C. C. Loy, X. O. Tang. Pedestrian attribute recognition at far distance. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, ACM, Lisboa, Portugal, pp. 789–792, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/2647868.2654966.
M. S. Sarfraz, A. Schumann, Y. Wang, R. Stiefelhagen. Deep view-sensitive pedestrian attribute inference in an end-to-end model, [Online], Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.06089, July 19, 2017.
H. Guo, K. Zheng, X. C. Fan, H. K. Yu, S. Wang. Visual attention consistency under image transforms for multi-label image classification. In Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Long Beach, USA, pp. 729–739, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00082.
J. Jia, H. J. Huang, W. J. Yang, X. T. Chen, K. Q. Huang. Rethinking of pedestrian attribute recognition: Realistic datasets with efficient method, [Online], Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11909, May 26, 2020.
H. T. Zeng, H. Z. Ai, Z. J. Zhuang, L. Chen. Multi-task learning via co-attentive sharing for pedestrian attribute recognition. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, IEEE, London, UK, pp. 1–6, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME46284.2020.9102757.
X. Y. Yu, W. C. Chen, Y. F. Jin, L. L. Ou. Pedestrian View-attribute Location and Recognition Method in Video Surveillance Scene Based on Attention Mechanism, CN113361336A, September 2021. (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFB1308000) and Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang province (No. LY21F 030018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Colored figures are available in the online version at https://link.springer.com/journal/11633
Wei-Chen Chen received the B. Eng. degree in new energy science and engineering from Tianjin University of Technology, China in 2020. She is currently a master student at Zhejiang University of Technology, China.
Her research interests include person detection, person re-identification, person tracking and pedestrian attribute recognition.
Xin-Yi Yu received the B. Eng. and Ph. D. degrees in mechanical design and theory from Harbin Institute of Technology, China in 2003 and 2009, respectively. He is engaged in postdoctoral work in Foshan Enterprise Postdoctoral Workstation, China from 2009 to 2012. He is with College of Information Engineering, Zhejiang University of Technology, China, as a lecturer since 2012. He was a recipient of the China Machinery Industry Technology.
His research interests include human-robot integration and intelligent manufacturing system.
Lin-Lin Ou received the B. Eng. and Ph. D. degrees in control science and engineering from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China in 2001 and 2006, respectively. She was with College of Information Engineering, Zhejiang University of Technology, China, a lecturer from 2006 to 2007 and later as an associate professor from 2008 to 2012. She is currently a professor since 2013. She was a recipient of the China Machinery Industry Science and Technology.
Her research interests include intelligent learning and robot system, multi-robot collaborative control, and human-robot integration.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, WC., Yu, XY. & Ou, LL. Pedestrian Attribute Recognition in Video Surveillance Scenarios Based on View-attribute Attention Localization. Mach. Intell. Res. 19, 153–168 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-022-1321-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-022-1321-8