Abstract
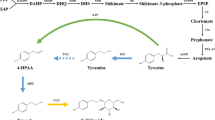
As a main component of efficiency in Rhodiola plants, salidroside is a promising environmental acclamation medicine and possesses specific medical properties against symptoms of fatigue, old age, microwave radiation, viral infections and tumors. Salidroside plays important roles, especially in military, aerospace, sport and healthcare medicine and has, therefore, recently, drawn more and closer attention. This article probes mainly into the probable biosynthetic pathway of salidroside following a brief introduction of the exploitation and utilization values of Rhodiola plants and the current condition of its natural resources. We have come to the conclusion that tyrosol, the aglycon of salidroside, is biosynthesized through the well-characterized shikimic acid pathway. A molecule of glucose is transferred by the UDP-glucosyltransferase (or possibly by the β-D-glucosidase too) to the tyrosol to form salidroside. On the other hand, salidroside may be degraded into tyrosol and glucose by β-D-glucosidase. Progress in research of these two key-enzymes, involved in the metabolism of salidroside, is finally elaborated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achnine L, Blancaflor E B, Rasmussen S, Dixon R A. 2004. Colocalization of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and cinnamate 4-hydroxylase for metabolic channeling in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Plant Cell, 16: 3,098–3,109
Bowles D, Lim E K, Poppenberger B, Vaistij F E. 2006. Glycosyltransferases of lipophilic small molecules. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol., 57: 567–597
Cheng Y H, Li P, Wang Q, Xian G Y. 2003. Experiment in cultivation and introduction of Rhodiola rosea L. J. Chin. Med. Mater., 26(11): 775–776 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
David R G. 2005. Evolution of flavors and scents. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol., 56: 301–325
Dharmawardhana D P, Ellis B E, Carison J E. 1995. A β-glucosidase from lodgepole pine xylem specific for the lignin precursor coniferin. Plant Physiol., 107: 331–339
Dixon R A, Paiva N L. 1995. Stress-induced phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell, 7: 1,085–1,097
Eimert K, Villand P, Kilian A. 1996. Cloning and characterization of several cDNAs for UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase from barley (Hordeurn vulgare) tissues. Gene, 170: 227–232
Engelberth J. 2006. Secondary metabolites and plant defense. In: Taiz L, Zeiger E (eds.), Plant Physiology, 4th ed. Sunderland, Massachusetts: Inc. Publishers, 315–341
Esen A, Blanchard D J. 2000. A specific β-glucosidase-aggregating factor is responsible for the β-glucosidase null phenotype in maize. Plant Physiol., 122: 563–572
Goossens A, Hakkinën S T, Laakso I, Seppänen-Laakso T, Biondi S, De Sutter V, Lammertyn F, Nuutila A M, Söderlund H, Zabeau M, Inzé D, Oksman-Caldentey K M. 2003. A functional genomics approach toward the understanding of secondary metabolism in plant cells. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 100: 8,595–8,600
Herrmann K M. 1995. The shikimate pathway as an entry to aromatic secondary metabolism. Plant Physiol., 107: 7–12
Hong Z L, Zhang Z M, Olson J M, Verma D P S. 2001. A novel UDP-glucose transferase is part of the callose synthase complex and interacts with phragmoplastin at the forming cell plate. Plant Cell, 13: 769–779
Jiang C J, Yu Y B. 2001. The research progress of PAL. J. Anhui Agric. Univ., 28(4): 425–430 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Kutchan T M. 2001. Ecological arsenal and developmental dispatcher: the paradigm of secondary metabolism. Plant Physiol., 125: 58–60
Li W, Huang Q N. 2003. Research and application of Rhodiola plants. J. Capital Normal Univ., 24(1): 55–59 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Liang Z H, Zheng G Z. 1981. Secondary metabolism of high plants. Plant Physiol. Commun., 17(1): 14–21 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Ma L Q. 2005. Cloning and Functional Analysis of Salidroside Biosynthesis related Genes in Rhodiola sachalinensis. Ph. D Dissertation. Jilin: Jilin Univertsity, 1–110 (in Chinese)
Mackenzie P I, Owens I S, Burchell B, Bock K W, Bairoch A, Belanger A, Belanger A, Fournel-Gigleux S, Green M, Hum D W, Iyanagi T, Lancet D, Louisot P, Magdalou J, Chowdhury J R, Ritter J K, Schachter H, Tephly T R, Tipton K F, Nebert D W. 1997. The UDP glycosyltransferase gene superfamily: recommended nomenclature update based on evolutionary divergence. Pharmacogenetics, 7: 255–269
Ming H Q. 1986. Synthesis and pharmacological action of salidroside. Pharm. Commun., 21(6): 373 (in Chinese)
Oba K, Conn E E, Canut H, Alain M B. 1981. Subcellular localization of 2-(β-D-glucosyloxy)-cinnamic acids and the related β-glucosidase in leaves of Melilotus alba Desr. Plant Physiol., 68: 1,359–1,363
Ritter H, Schulz G E. 2004. Structural basis for the entrance into the phenylpropanoid metabolism catalyzed by phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. Plant Cell, 16: 3,426–3,436
Song Y Y, Han H W, Hao S Y. 2003. Progress in the research of Rhodiola. Acta Acad. Med. CPAPF, 13(1): 66–68 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Sudha G, Ravishankar G A. 2002. Involvement and interaction of various signaling compounds on the plant metabolic events during defense response, resistance to stress factors, formation of secondary metabolites and their molecular aspects. Plant Cell, Tiss. Org. Cult., 71: 181–212
Tao X Y, Lu Y H. 2006. The biotransformation of natural medicines with enzyme method. In: Lu Y H, Wang J W, Wei D Z (eds.), The Biotransformation of Natural Medicines. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 110–153 (in Chinese)
Thorlby G, Fourrier N, Warren G. 2004. The sensitive to freezing gene, required for freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana, encodes a β-glucosidase. Plant Cell, 16: 2,192–2,203
Tikunov Y, Lommen A, Bovy A G, Verhoeven H A, Bino R J, Hall R D, Bovy A G. 2005. A novel approach for nontargeted data analysis for metabolomics: large-scale profiling of tomato fruit volatiles. Plant Physiol., 139: 1,125–1,137
Voll L M, Allaire E E, Fiene G, Weber A P M. 2004. The Arabidopsis phenylalanine insensitive growth mutant exhibits a deregulated amino acid metabolism. Plant Physiol., 136: 3,058–3,069
Wang L, Shi L L, Liu Y J. 2007. Effects of different light treatments on growth and PAL activity of the suspension-cultured cells of Rhodiola fastigiata. Sci. Silv. Sin., 43(6): 49–53 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Wang L L. 2003. Study on pharmacology and clinic of Rhodiola rosea L. and compound recipe preparation. Acta Chin. Med. Pharm., 31(1): 51–53 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Wang M L, Zhang F, Liu D S. 2006. Preliminary study on synthesis of salidroside through glucosylation of D-glucose and tyrosol catalyzed by microorganism. Chin. J. Catal., 27(3): 233–236 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Winkel B S J. 2004. Metabolic channeling in plants. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol., 55:85–107
Wolucka A B, Goosenens A, Linzé D. 2005. Methyl jasmonate stimulates in the de novo biosynthesis of vitamin C in plant cell suspensions. J. Exp. Bot., 419(56): 2,527–2,538
Wu X J, Liu D, Hu Z B. 2000. UDP-glucosyltransferasel. Plant Physiol. Commun., 36(3): 193–200 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Yin W B, Li W, Du G S, Huang Q N. 2004. Studies on tissue culture of Tibetan Rhodiola rosea. Acta Bot. Boreal-Occident. Sin., 4(8): 1,506–1,510 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Yu H L, Xu J H, Lin G Q. 2006. Application of glycosidase to glycoside synthesis. Chin. J. Org. Chem., 26(8): 1,052–1,058 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Zhao W, Jiang X. 2001. The bioactive research survey of Rhodiola plants. J. Health Toxicol., 15(1): 55–57 (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Zouhar J, Vevodova J, Marek J, Damborsky J, Su X D, Brzobohaty B. 2001. Insights into the functional architecture of the catalytic center of a maize β-glucosidase Zm-p60.1. Plant Physiol., 127: 973–985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Ll., Wang, L., Zhang, Yx. et al. Approaches to biosynthesis of salidroside and its key metabolic enzymes. For. Stud. China 9, 295–299 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-007-0047-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-007-0047-6