Abstract
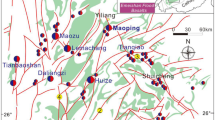
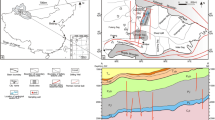
The Langdu skarn copper deposit in the Zhongdian area, Yunnan Province, China, has an average Cu grade of 6.49 %. The deposit is related to a porphyry intrusion (~216 Ma), which was emplaced in the Upper Triassic sedimentary rocks of the Tumugou and Qugasi Formations. At the Langdu skarn copper deposit, carbon and oxygen isotope ratios of fresh limestones (δ18O = 3.0–5.6 ‰ relative to V-SMOW; δ13C = 24.5–25.7 ‰ relative to PDB) and partly altered limestones (δ18O = 27–7.2 to −1.9 ‰; δ13C = 11.8–15.2 ‰) indicated that the deposit was a typical marine carbonate source. Oxygen and carbon isotope values for calcites formed at different hydrothermal stages are −9.1 to 0.2 and 10.1–16.3 ‰, respectively. Moreover, the carbon–oxygen isotopic composition of an ore-forming fluid (δ18O = 5.0–9.5 ‰, δ13C = −7.3 to −5.3 ‰) suggested the presence of magmatic water, which most likely came from the differentiation or melting of a homologous magma chamber. The deposition of Calcite I may arise from metasomatism in an open system with a progressively decreasing temperature. Later, the minerals chalcopyrite, pyrrhotite, quartz and Calcite II were precipitated due to immiscibility. Water–rock interaction could potentially be responsible for Calcite III precipitation in the post-ore stage.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bottinga Y (1969) Calculated fractionation factors for carbon and hydrogen isotopic exchange in the system, calcite-carbon dioxide-graphite-methane-hydrogen-water-vapor [J]. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 33:9–64
Choi SG, Kim ST, Lee JG (2003) Stable isotope systematics of Ulsan Fe-W skarn deposit, Korea [J]. J Geochem Explor 78–79:601–606
Matsuhisa Y, Morishita Y, Sato T (1985) Oxygen and carbon isotope variations in gold-bearing hydrothermal veins in the Kushikino mining area, southern Kynshu, Japan [J]. Econ Geol 80:283–293
O’Neil JR, Clayton RN, Mayeda TK (1969) Oxygen isotope fractionation in divalent metal carbonates [J]. J Chem Phy 51:5547–5558
Peng J, Hu R (2001) Carbon and oxygen isotope systematics in Xikuangshan giant antimony deposit, central Hunan [J]. Geol Rev 47:34–41 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ray JS, Ramesha R, Pandea K, Trivedi JR, Shukla PN, Patel PP (2000) Isotope andrare earth element chemistry of carbonatite ± alkaline complexes of Deccan volcanic province: implications to magmatic and alteration processes [J]. J Asian Earth Sci 18:177–194
Rye DM, Williams N (1981) Studies of the base metal sulfide deposits at McArthur River, Northern Territory, Australia: III. The stable isotope geochemistry of the H.Y.C. Ridge, and Cooley deposits [J]. Econ Geol 76:1–26
Zeng P, Wang H, Mo X, Yu X, Li W, Li T, Li H, Yang C (2004) Tectonic setting and prospects of porphyry copper deposits in Zhongdian island arc belt [J]. Acta Geosci Sin 25:535–540 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng YF (1990) Carbon-oxygen isotopic covariation in hydrothermal calcite during degassing of CO2: a quantitative evaluation and application to the Kushikino gold mining area in Japan. Miner [J]. Miner Depos 25:246–250
Zheng YF (2001) Theoretical modeling of stable isotope systems and its applications to geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits [J]. Miner Depos 20:56–71 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng YF, Hoefs J (1993) Carbon and oxygen isotopic covariations in hydrothermal calcites: theoretical modeling on mixing processes and application to Pb–Zn deposits in the Harz Mountains, Germany [J]. Miner Depos 28:79–89
Zhou JX, Huang ZL, Zhou MF, Li XB, Jin ZG (2013a) Constraints of C–O–S–Pb isotope compositions and Rb–Sr isotopic age on the origin of the Tianqiao carbonate-hosted Pb–Zn deposit, SW China [J]. Ore Geol Rev 53:77–92
Zhou JX, Huang ZL, Yan ZF (2013b) The origin of the Maozu carbonate-hosted Pb–Zn deposit, southwest China: constrained by C–O–S–Pb isotopic compositions and Sm–Nd isotopic age [J]. J Asian Earth Sci 73:39–47
Zhou JX, Gao JG, Chen D, Liu XK (2013c) Ore genesis of the Tianbaoshan carbonate-hosted Pb–Zn deposit, Southwest China: geologic and isotopic (C–H–O–S–Pb) evidence [J]. Int Geol Rev 55:1300–1310
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) project (40372049). The authors wish to thank C. Z. Yang (Branch of Mineral Resources Investigation, Yunnan Geological Survey, China) for their helpful discussions on the geology of the Zhongdian area and for information on the Langdu deposit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, T., Zhang, X., Han, R. et al. Carbon–oxygen isotopic covariations of calcite from Langdu skarn copper deposit, China: implications for sulfide precipitation. Chin. J. Geochem. 34, 21–27 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-014-0014-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-014-0014-6