Abstract
Purpose
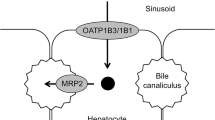
Our aim was to evaluate the hepatocyte transporters in focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) and FNH-like lesions and to correlate the grade of its expression with signal intensity on the hepatobiliary phase (HB phase) of gadoxetic-acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (EOB-MRI).
Materials and methods
Thirteen histopathological confirmed cases including eight with EOB-MRI were studied. Immunohistochemical staining for transporter was performed and its grade semiquantitatively analyzed.
Results
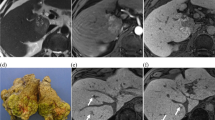
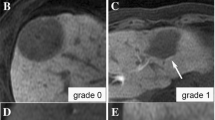
Histopathologically, ten cases showed almost equal organic anion transporter polypeptide (OATP) 8 expression relative to the surrounding liver; the remaining three showed stronger OATP8 expression. In eight cases with EOB-MRI, two demonstrated more hyperintensity on the HB phase, and their OATP8 expression was stronger compared with the surrounding liver. The remaining six cases showed isointensity on the HB phase and revealed almost equal OATP8 expression. The expression of export transporter multi-drug-resistant proteins (MRP) 1 and 2 were almost equal relative to the surrounding liver in most cases (11/12, 92 %; 11/12, 92 %, respectively), whereas MRP3 focally overexpressed in 75 % (9/12) of cases.
Conclusion
FNH and FNH-like nodules revealed equal or stronger OATP8 expression than background liver. OATP8 expression showed significant correlation with signal intensity on the HB phase.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FNH:
-
Focal nodular hyperplasia
- HB phase:
-
Hepatobiliary phase
- EOB-MRI:
-
Gadoxetic-acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging
- OATP:
-
Organic anion transporter polypeptides
- MRP:
-
Multi-drug-resistant proteins
- Gd-EOB-DTPA:
-
Gadoxetic acid
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- NTCP:
-
Na+ taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide
References
Vogl T, Kümmel S, Hammerstingl R, Schellenbeck M, Schumacher G, Balzer T, et al. Liver tumors: comparison of MR imaging with Gd-EOB-DTPA and Gd-DTPA. Radiology. 1996;200(1):59–67.
Bluemke D, Sahani D, Amendola M, Balzer T, Breuer J, Brown JJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of MR imaging with liver-specific contrast agent: U.S. multicenter phase III study. Radiology. 2005;237(1):89–98.
Reimer P, Schneider G, Schima W. Hepatobiliary contrast agents for contrast-enhanced MRI of the liver: properties, clinical development and applications. Eur Radiol. 2004;14(4):559–78.
Schuhmann-Giampieri G, Schmitt-Willich H, Press W, Negishi C, Weinmann H, Speck U. Preclinical evaluation of Gd-EOB-DTPA as a contrast agent in MR imaging of the hepatobiliary system. Radiology. 1992;183(1):59–64.
Huppertz A, Haraida S, Kraus A, Zech CJ, Scheidler J, Breuer J, et al. Enhancement of focal liver lesions at gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging: correlation with histopathologic findings and spiral CT—initial observations. Radiology. 2005;234(2):468–78.
Hamm B, Staks T, Mühler A, Bollow M, Taupitz M, Frenzel T, et al. Phase I clinical evaluation of Gd-EOB-DTPA as a hepatobiliary MR contrast agent: safety, pharmacokinetics, and MR imaging. Radiology. 1995;195(3):785–92.
Reimer P, Rummeny E, Shamsi K, Balzer T, Daldrup HE, Tombach B, et al. Phase II clinical evaluation of Gd-EOB-DTPA: dose, safety aspects, and pulse sequence. Radiology. 1996;199(1):177–83.
Zech C, Grazioli L, Breuer J, Reiser M, Schoenberg S. Diagnostic performance and description of morphological features of focal nodular hyperplasia in Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced liver magnetic resonance imaging: results of a multicenter trial. Invest Radiol. 2008;43(7):504–11.
Vander Borght S, Libbrecht L, Blokzijl H, Faber KN, Moshage H, Aerts R, et al. Diagnostic and pathogenetic implications of the expression of hepatic transporters in focal lesions occurring in normal liver. J Pathol. 2005;207(4):471–82.
Nakanuma Y. Non-neoplastic nodular lesions in the liver. Pathol Int. 1995;45(10):703–14.
Terminology of Nodular Hepatocellular Lesions. International working party. Hepatology. 1995;22(3):983–93.
Bioulac-Sage P, Balabaud C, Bedossa P, Scoazec JY, Chiche L, Dhillon AP, et al. Pathological diagnosis of liver cell adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia: Bordeaux update. J Hepatol. 2007;46(3):521–7.
Sugihara S, Nakashima O, Kiyomatsu K, Ijiri M, Edamitsu O, Kojiro M. A case of liver cirrhosis with a hyperplastic nodular lesion. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1990;40(9):699–703.
Terada T, Kitani S, Ueda K, Nakanuma Y, Kitagawa K, Masuda S. Adenomatous hyperplasia of the liver resembling focal nodular hyperplasia in patients with chronic liver disease. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1993;422(3):247–52.
Quaglia A, Tibballs J, Grasso A, Prasad N, Nozza P, Davies SE, et al. Focal nodular hyperplasia-like areas in cirrhosis. Histopathology. 2003;42(1):14–21.
An H, Illei P, Diflo T, John D, Morgan G, Teperman L, et al. Scirrhous changes in dysplastic nodules do not indicate high-grade status. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003;18(6):660–5.
Nakashima O, Kurogi M, Yamaguchi R, Miyaaki H, Fujimoto M, Yano H, et al. Unique hypervascular nodules in alcoholic liver cirrhosis: identical to focal nodular hyperplasia-like nodules? J Hepatol. 2004;41(6):992–8.
Wanless I, Mawdsley C, Adams R. On the pathogenesis of focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver. Hepatology. 1985;5(6):1194–200.
Bioulac-Sage P, Balabaud C, Wanless I. Diagnosis of focal nodular hyperplasia: not so easy. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001;25(10):1322–5.
Welch T, Sheedy PF 2nd, Johnson C, Stephens DH, Charboneau JW, Brown ML, et al. Focal nodular hyperplasia and hepatic adenoma: comparison of angiography, CT, US, and scintigraphy. Radiology. 1985;156(3):593–5.
Carlson S, Johnson C, Bender C, Welch T. CT of focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000;174(3):705–12.
Brancatelli G, Federle M, Grazioli L, Blachar A, Peterson M, Thaete L. Focal nodular hyperplasia: CT findings with emphasis on multiphasic helical CT in 78 patients. Radiology. 2001;219(1):61–8.
Miyayama S, Matsui O, Ueda K, Kifune K, Yamashiro M, Yamamoto T, et al. Hemodynamics of small hepatic focal nodular hyperplasia: evaluation with single-level dynamic CT during hepatic arteriography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000;174(6):1567–9.
Giovanoli O, Heim M, Terracciano L, Bongartz G, Ledermann HP. MRI of hepatic adenomatosis: initial observations with gadoxetic acid contrast agent in three patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;190(5):W290–3.
Kitao A, Zen Y, Matsui O, Gabata T, Kobayashi S, Koda W, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: signal intensity at gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging—correlation with molecular transporters and histopathologic features. Radiology. 2010;256(3):817–26.
Leonhardt M, Keiser M, Oswald S, Kühn J, Jia J, Grube M, et al. Hepatic uptake of the magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA: role of human organic anion transporters. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010;38(7):1024–8.
Narita M, Hatano E, Arizono S, Miyagawa-Hayashino A, Isoda H, Kitamura K, et al. Expression of OATP1B3 determines uptake of Gd-EOB-DTPA in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 2009;44(7):793–8.
Saito K, Kotake F, Ito N, Ozuki T, Mikami R, Abe K, et al. Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced MRI for hepatocellular carcinoma: quantitative evaluation of tumor enhancement in hepatobiliary phase. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2005;4(1):1–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yoneda, N., Matsui, O., Kitao, A. et al. Hepatocyte transporter expression in FNH and FNH-like nodule: correlation with signal intensity on gadoxetic acid enhanced magnetic resonance images. Jpn J Radiol 30, 499–508 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-012-0085-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-012-0085-4