Abstract
Objective
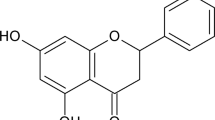
Secoemestrin C (SC), an epitetrathiodioxopiperazine isolated from Aspergillus nidulans, has been previously reported to have immunomodulatory and hepatoprotective effects against acute autoimmune hepatitis. However, the effect of SC on regulating the inflammation and its underlying mechanisms in the pathogenesis of psoriasis remain unclear. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of SC on inflammatory dermatosis both in vitro and in vivo.
Methods
In vitro, HaCaT cells were induced with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α, 10 ng/mL) to establish an inflammatory injury model, and the expression of nuclear transcription factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway components was measured using qRT-PCR and Western blotting. An in vivo mouse model of imiquimod (IMQ)-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation was used to evaluate the effectiveness of SC in alleviating psoriasis.
Results
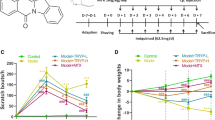
SC significantly blocked the activation of NF-κB signaling in TNF-α-stimulated HaCaT cells. In addition, systemic and local administration of SC improved psoriatic dermatitis in the IMQ-induced mouse model. SC reduced skin scale and significantly inhibited the secretion of inflammatory factors in skin lesions.
Conclusion
The protective effect of SC against psoriatic-associated inflammation reveals its potential therapeutic value for treating psoriasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parisi R, Symmons DPM, Griffiths CEM, et al. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: A systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J Invest Dermatol, 2013,133(2):377–385
Michalek IM, Loring B, John SM. A systematic review of worldwide epidemiology of psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2017,31(2):205–212
Kamiya K, Kishimoto M, Sugai J, et al. Risk factors for the development of psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci, 2019,20(18):4347
Kaushik SB, Lebwohl MG. Psoriasis: Which therapy for which patient: Psoriasis comorbidities and preferred systemic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2019,80(1):27–40
Tsuruta D. NF-kappaB links keratinocytes and lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov, 2009,3(1):40–48
Tokuyama M, Mabuchi T. New treatment addressing the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci, 2020,21(20):7488
Choy EHS, Panayi GS. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med, 2001,344(12):907–916
Duan H, Koga T, Kohda F, et al. Interleukin-8-positive neutrophils in psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci, 2001,26(2):119–124
Giustizieri ML, Mascia F, Frezzolini A, et al. Keratinocytes from patients with atopic dermatitis and psoriasis show a distinct chemokine production profile in response to T cell-derived cytokines. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2001,107(5):871–877
Tan X, Sun L, Li Q, et al. Secoemestrin C inhibits activation of NKT/conventional T cells and protects against concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis in mice. Am J Transl Res, 2020,12(7):3389–3401
Komine M, Rao LS, Freedberg IM, et al. Interleukin-1 induces transcription of keratin K6 in human epidermal keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol, 2001,116(2):330–338
Gillitzer R, Ritter U, Spandau U, et al. Differential expression of GRO-alpha and IL-8 mRNA in psoriasis: a model for neutrophil migration and accumulation in vivo. J Invest Dermatol, 1996,107(5):778–782
Langley RG, Krueger GG, Griffiths CE. Psoriasis: epidemiology, clinical features, and quality of life. Ann Rheum Dis, 2005,64(Suppl 2):ii18–23; discussion ii24–15
Singh R, Koppu S, Perche PO, et al. The cytokine mediated molecular pathophysiology of psoriasis and its clinical implications. Int J Mol Sci, 2021,22(23):12793
Shan X, Chen L, Cao M, et al. Effects of human soluble BAFF synthesized in Escherichia coli on CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes as well as NK cells in mice. Physiol Res, 2006,55(3):301–307
Li Y, Li X F, Ma Y, et al. Changes in the levels of CD4+ and CD8+ T-lymphocytes after strontium-89 chloride therapy for painful bone metastases in patients correlate with treatment efficacy. Cancer Biother Radiopharm, 2007,22(3):367–373
Zhang R, Wang YH, Shi X, et al. Sortilin regulates keratinocyte proliferation and apoptosis through the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. Life Sci, 2021,278: 119630
Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell, 2008,132(3):344–362
Cai Y, Xue F, Quan C, et al. A critical role of the IL-1β-IL-1R signaling pathway in skin inflammation and psoriasis pathogenesis. J Invest Dermatol, 2019,139(1):146–156
Su JY, Luo X, Zhang XJ, et al. Immunosuppressive activity of pogostone on T cells: Blocking proliferation via S phase arrest. Int Immunopharmacol, 2015,26(2):328–337
Yang Y, Zhang Y, Chen X, et al. Khasianine ameliorates psoriasis-like skin inflammation and represses TNF-α/NF-κB axis mediated transactivation of IL-17A and IL-33 in keratinocytes. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022,292:115124
Campanati A, Orciani M, Sorgentoni G, et al. Indirect co-cultures of healthy mesenchymal stem cells restore the physiological phenotypical profile of psoriatic mesenchymal stem cells. Clin Exp Immunol, 2018,193(2):234–240
Yang C, Zhang J, Ding M, et al. Ki67 targeted strategies for cancer therapy. Clin Transl Oncol, 2018,20(5):570–575
Goff KL, Karimkhani C, Boyers LN, et al. The global burden of psoriatic skin disease. Br J Dermatol, 2015,172(6):1665–1668
Campanati A, Ganzetti G, Sario AD, et al. The effect of etanercept on hepatic fibrosis risk in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, metabolic syndrome, and psoriasis. J Gastroenterol, 2013,48(7):839–846
Bach E, Nielsen RR, Vendelbo MH, et al. Direct effects of TNF-a on local fuel metabolism and cytokine levels in the placebo-controlled, bilaterally infused human leg: increased insulin sensitivity, increased net protein breakdown, and increased IL-6 release. Diabetes, 2013,62(12):4023–4029
Tracey D, Klareskog L, Sasso EH, et al. Tumor necrosis factor antagonist mechanisms of action: a comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther, 2008,117(2):244–279
Vergou T, Moustou AE, Sfikakis PP, et al. Pharmacodynamics of TNF-α inhibitors in psoriasis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol, 2011,4(4):515–523
Aggarwal BB, Gupta SC, Kim JH. Historical perspectives on tumor necrosis factor and its superfamily: 25 years later, a golden journey. Blood, 2012,119(3):651–665
Calip GS, Patel PR, Adimadhyam S, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in a cohort of adults with rheumatologic conditions. Int J Cancer, 2018,143(5):1062–1071
Fagerli KM, Kearsley-Fleet L, Mercer LK, et al. Malignancy and mortality rates in patients with severe psoriatic arthritis requiring tumour-necrosis factor alpha inhibition: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2019,58(1):80–85
Sedger LM, McDermott MF. TNF and TNF-receptors: From mediators of cell death and inflammation to therapeutic giants-past, present and future. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2014,25(4):453–472
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization or corporation or individual that can inappropriately influence this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Zb., Liu, Mj., Wang, J. et al. Secoemestrin C Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation in Mice by Suppressing the TNF-α/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. CURR MED SCI 44, 232–240 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-024-2828-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-024-2828-8