Summary
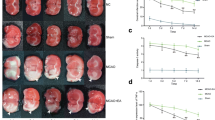
This study examined the effect of electro-acupuncture (EA) combined with transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) therapy at different time windows on learning and memory ability of rats with cerebral infarction and the underlying mechanism. Two hundred SD rats were randomly divided into four groups: normal group, sham-operated group, model group and EA+TMS group, and each group was then divided into five sub-groups in terms of the different time to start treatment post operation: 6, 12, 24, 48 and 72 h. Cerebral infarction models were established in the model and the EA+TMS groups by left middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/R). After treatment for 14 d, the Morris water maze test was applied to examine the spatial learning and memory abilities of rats. In infarcted area, the expression of caspase-3 was immunohistochemically detected, and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR was used to measure the expression of Bcl-2 mRNA. The results showed that in EA+TMS group compared with model group at the same treatment time windows, the escape latency was substantially shortened, the expression of caspase-3 was considerably decreased and the expression level of Bcl-2 mRNA significantly increased (P<0.05). In the EA+TMS sub-groups, the escape latency was shortest, the expression level of caspase-3 lowest, and the expression level of Bcl-2 mRNA highest at the treatment time window of 24 h. It was concluded that EA combined with TMS can promote neurological function of rats with cerebral infarction by increasing the expression level of Bcl-2 mRNA and decreasing the expression of caspase-3. The best time window is 24 h after perfusion treatment to ischemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang CX, Li ZR, Chen BY. Protective effect of electroaeupuncture on cerebral function via ameliorating oxidative stress in MCAO rat. Neurosci Bull, 2005, 21(2):153–157
Wang SJ, Omori N, Li F, et a1. Functional improvement by electro-acupuncture after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Neurol Res, 2003,25(5):516–521
Fujiki M, Kobayashi H, Abe T, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for protection against delayed neuronal death induced by transient ischemia. J Neurosurg, 2003,99(6):1063–1069
Huang XL, Han XH, Guo TC, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture combined with transcranial magnetic stimulation on VEGF and FIk-1 expression in cerebral ischemia in rats. Chin J Phys Med Rehabil (Chinese), 2004,26(10):581–584
Liao WJ, Liu SH, Fan M, et al. Modification of the preparation of models of focal ischemic brain injury with suture occlusion in rats. Chin J Phys Med Rehabil (Chinese), 2002,24(6): 345–348
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke, 1989,20(1):84–91
Deng CL, Yin KJ. Experimental acupuncture, first edition. Beijing: People’s Health Publishing House, 1998: 142–143
Tatemichi TK, Desmond DW, Mayeux R, et al. Dementia after stroke: baseline frequency, risks, and clinical features in a hospitalized cohort. Neurology, 1992,42(6): 1185–1193
Sharma S, Rakoczy S, Brown-Borg H. Assessment of spatial memory in mice. Life Sci, 2010, 87(17–18): 521–536
Lawrence MS, Ho DY, Sun GH, et a1. Over expression Bcl-2 with herpes simplex virus vectors protects CNS neurons against neurological insults in vitro and vivo. J Neuroscience, 1996,16(2):486–496
Cheng EH, Kirsch DG, Clem RJ, et al. Conversion of bcl-2 to a bax-like death effector by caspases. Science, 1997,278(5435):1966–1968
Qi J, Hong ZY, Xin H, et al. Neuroprotective effects of leonurine on ischemia/reperfusion-induced mitochondrial dysfunctions in rat cerebral cortex. Biol Pharm Bull, 2010,33(12):1958–1964
Ni B, Wu X, Su Y, et al. Transient global forebrain ischemia induces a prolonged expression of the Caspse-3 mRNA in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 1998,18(3):248–256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
This project was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30640010).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Peng, J., Song, Y. et al. Electro-acupuncture combined with transcranial magnetic stimulation improves learning and memory function of rats with cerebral infarction by inhibiting neuron cell apoptosis. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 32, 746–749 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-012-1028-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-012-1028-0