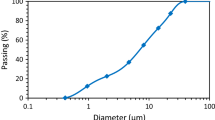
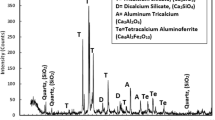
Abstract
To quantitatively estimate the workability of cement-based grouting material, from the perspective of rheology, the result of the static yield stress evaluated using the rate-controlled and stress-controlled modes, respectively, was compared using the Rheowin rheometer. Also, the correlation of workability and solid concentration of slurry with static yield stress was studied. Results show that the static yield stress of cement-based grouting slurry relates to the established slurry structure, and is the shear stress corresponding to the transformation of elastics to plastics; In rate-controlled mode, the static yield stress of the slurry is related to the shear rate. The higher the shear rate, the greater the yield stress of the slurry. For the stress-controlled mode, the result is more accurate and suitable for testing static yield stress under different water-cement ratios. Since the water-cement ratio has a good correspondence with the static yield stress and the static yield stress has a good correspondence with the slump flow of the slurry, the static yield stress is the minimum stress to be overcome when the slurry begins to flow and it reflects the yield behavior and structural stability of the cement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sumra, Yousuf P, Shafigh Z, et al. The pH of Cement-based Materials: A Review[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology. -Mater. Sci. Ed., 2020, 35(05): 908–924
Zhang Y, Li W, Li D. Preparation and Performance Research of Cement-based Grouting Materials with High Early Strength and Expansion[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2017, 32(5): 1 115–1 118
Roussel N, Ovarlez G, Garrault S, et al. The Origins of Thixotropy of Fresh Cement Pastes[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2012, 42(1): 148–157
Qian Y, Kawashima S. Use of Creep Recovery Protocol to Measure Static Yield Stress and Structural Rebuilding of Fresh Cement Pastes[J]. Cement & Concrete Research, 2016, 90: 73–79
Xiao J, Wang D, Zuo S, et al. Action Mechanism of Ground Limestone in Structural Build up of Cement Paste[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2018, 21(5): 707–713
Mahaut F, Chateau X, Coussot P, et al. Yield Stress and Elastic Modulus of Suspensions of Noncolloidal Particles in Yield Stress Fluids[J]. Journal of Rheology, 2008, 52(1): 287–313
Koehler E P, Fowler D W. Development and Use of a Portable Rheometer for Concrete[C]. Supplementary Proceedings of the Eighth CANMET/ACI International Conference on Recent Advances in Concrete Technology, Montreal, Canada, 2006
Lowke D, Kränkel T, Gehlen C, et al. Effect of Cement on Superplasticizer Adsorption, Yield Stress, Thixotropy and Segregation Resistance[M]. Design, Production and Placement of Self-consolidating Concrete. Springer: Dordrecht, 2010
Yuan Q, Zhou D, Khayat K H, et al. On the Measurement of Evolution of Structural Build-up of Cement Paste with Time by Static Yield Stress Test vs. Small Amplitude Oscillatory Shear Test[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2017, 99: 183–189
Mahaut F, Mokeddem S, Chateau X, et al. Effect of Coarse Particle Volume Fraction on the Yield Stress and Thixotropy of Cementitious Materials[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2008, 38(11): 1 276–1 285
Perrot A, Lecompte T, Khelifi H, et al. Yield Stress and Bleeding of Fresh Cement Pastes[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2012, 42(7): 937–944
Jiao D, An X, Shi C, et al. Effects of Paste Thickness on Coated Aggregates on Rheological Properties of Concrete[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2017, 45(9): 1 360–1 366
Xiao J, Wang D, Zuo S, et al. Shear Protocols of Cement Paste Based on Steady-State Rheological Test[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2017, 36(7): 2 387–2 391
Xiao J, Wang D, Zuo S, et al. Influence of Temperature on Structure of Fresh Cement Paste with Low Shear Rate[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2017(6): 835–839
Li Z, Wang D. Static Yield Stress and Viscoelasticity of Fresh Cement Paste Measured by Rotational Viscometer[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2017, 36(6): 1 818–1 822
Li F. Research on the Development of Restraint Stress and Stress Relaxation of Concrete at Early Ages[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2009
Wallevik O H, Feys D, Wallevik J E, et al. Avoiding Inaccurate Interpretations of Rheological Measurements for Cement-based Materials[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2015, 78: 100–109
Roussel N, Lemaître A, Flatt R J, et al. Steady State Flow of Cement Suspensions: A Micromechanical State of the Art[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2010, 40(1): 77–84
Rosquoët F, Alexis A, Khelidj A, et al. Experimental Study of Cement Grout: Rheological Behavior and Sedimentation[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2003, 33(5): 713–722
Nguyen V H, Remond S, Gallias J L. Influence of Cement Grouts Composition on the Rheological Behaviour[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2011, 41(3): 292–300
Funding
Funded by Science and Technology Program of Gansu Provincial Department of Housing and Construction (No.JK2021-11), National Natural Science Fundation of China (No.52161007), Science and Technology Project of Gansu Provincial Department of Transportation, Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province (No. 20JR10RA170)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nan, X., Chen, H., Li, R. et al. Static Yield Stress of Cement-based Grouting Material under Different Rheological Modes. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 37, 948–952 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-022-2617-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-022-2617-9