Abstract
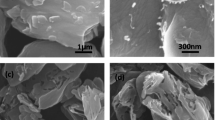
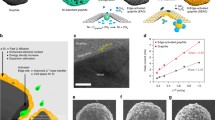
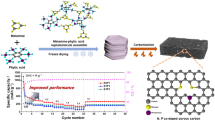
Nitrogen doped multi-channel graphite was successfully prepared by using nitrogen doping and KOH etching technologies. The three-electrode and EIS tests indicates that the etched graphite possesses lower electrochemical resistance than the pristine graphite. The coin cell tests demonstrate that N doped multichannel graphite possesses a specific capacity of 361 mAh/g and coulombic efficiencies of 91.4%. No dramatic irreversible capacity loss results from the increased specific surface area (from 1.60 to 2.08 m2/g), removing the need for a trade-off between irreversible capacity loss and surface area. Full polymer cells were fabricated and electrochemical capabilities were measured. In 3C fast charge protocol, the charging capacity can reach 51% within 10 min charge, and 100% within 30 min, demonstrating excellent fast charging characteristic. The fast charge cycle performance with 3C-rate charge and 1C-rate discharge from 4.35-3.0 V was conducted at RT temperature. The capacity retention is 94% after 600 cycles, which shows good cycle performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goodenough J B, Park K S. The Lithium Ion Rechargeable Battery: A Perspective[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(4): 1167–1176
Simon P, Gogotsi Y, Dunn B. Where Do Batteries End and Supercapacitors Begin[J]. Science, 2014, 6(343): 1210–1211
Kang B, Ceder G. Battery Materials for Ultrafast Charging and Discharging[ J]. Nature, 2009, 458: 190–198
Kang K, Meng Y S, Bréger J, et al. Electrodes with High Power and High Capacity for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries[J]. Science, 2006, 311(5763): 977–980
Zhang H G, Yu X D, Braun P V. Three-Dimensional Bicontinuous Ultrafast-Charge and Discharge Bulk Battery Electrodes[J]. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2011, 6: 277–281
Li N, Chen Z, Ren W, et al. Flexible Graphene-Based Lithium Ion Batteries with Ultrafast Charge and Discharge Rates[J]. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2012, 109(43): 17 360-17 365
Xin S, Guo Y G, Wan L J. Nanocarbon Networks for Advanced Rechargeable Lithium Batteries[J]. Accounts. Chem. Res., 2012, 45(10): 1759–1769
Gong Y J, Yang S B, Liu Z, et al. Graphene Network Back Boned Architectures for High Performance Lithium Storage[J]. Adv. Mater., 2013, 25(29), 3979–3984
Marsh H, Yan D S, O’Grady T M, et al. Formation of Active Carbons From Cokes Using Potassium Hydroxide[J]. Carbon, 1984, 22(6): 603–611
Rubino R S, Takeuchi E S. The Study Of Irreversible Capacity in Lithium-Ion Anodes Prepared with Thermally Oxidized Graphite[J]. J.Power. Source, 1999, 81–82: 373-377
Ein-Eli Yair, Koch V R. Chemical Oxidation: A Route to Enhanced Capacity in Li Ion Graphite Anodes[J]. J. Electrochem. Soc., 1997, 144(9): 2968–2973
Jang J W, Lee C E, Lyu S C, et al. Structural Study of Nitrogen-Doping Effects in Bamboo-Shaped Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes[J]. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, 84(15): 2877–2879
Ronning C, Feldermann H, Merk R, et al. Carbon Nitride Deposited Using Energetic Species: A Review on XPS Studies[J]. Phys. Rev. B, 1998, 58(4-15): 2207–2215
Marton D, Boyd K J, Al-Bayati AH, et al. Carbon Nitride Deposited Using Energetic Species: a Two-Phase System[J]. Phys. Rev. Lett., 1994, 73(1-4): 118–121
Wang H B, Zhang C J, Liu Z H, et al. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Nanosheets with Excellent Lithium Storage Properties[J]. J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21(14): 5430–5434
Czerw R, Terrones M, Charlier J C, et al. Identification of Electron Donor States in N-Doped Carbon Nanotubes[J]. Nano. Lett., 2001, 1(9): 457–460
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by College Scientific Research Project of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (No.NJZY18159) and Ph D Research Start-up Fund of Hebei GEO University (No.BQ2019003)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Wu, X. & Li, R. Nitrogen Doped Multi-channel Graphite for High Rate and High Capacity Li Ion Battery. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 35, 65–70 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-020-2228-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-020-2228-2