Abstract
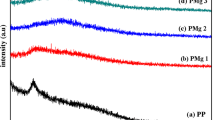
In recent years, there is a demand for electrochemical devices based on biopolymer electrolyte over synthetic polymer electrolyte. In this study, development of zinc ion conducting membrane using pectin and ZnCl2 has been made by solution casting technique. Developed polymer electrolyte membrane has been characterized by X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) to study the crystalline/amorphous nature of the polymer electrolyte. Fourier transform infrared analysis (FTIR) confirms the complex formation between polymer and salt. The glass transition temperature (Tg) of the biopolymer membrane has been studied by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). AC impedance technique has been used to study the ionic conductivity of the samples. The pectin with ZnCl2 in the ratio of 40 M.wt% of pectin:60 M.wt% of ZnCl2 exhibits the highest ionic conductivity in the order of 4.49 × 10−3 S/cm having high amorphous nature. Linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) confirms the highest ionic conductivity biopolymer membrane has got electrochemical window to 2.36 V. Using the highest conductivity polymer electrolyte, zinc ion battery has been fabricated and output voltage is measured. The open-circuit voltage of the constructed zinc ion battery is found to be 1.84 V.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu F et al (2021) Challenges and recent progress on key materials for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Adv Energy Mater 11(2):2000787
Sakunthala A et al (2010) Synthesis of compounds, Li (MMn11/6) O4 (M= Mn1/6, Co1/6,(Co1/12Cr1/12),(Co1/12Al1/12),(Cr1/12Al1/12)) by polymer precursor method and its electrochemical performance for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 55(15):4441–4450
Virya A, Lian K (2017) Polyacrylamide-lithium chloride polymer electrolyte and its applications in electrochemical capacitors. Electrochem Commun 74:33–37
Ramesh S, Arof A (2001) Ionic conductivity studies of plasticized poly (vinyl chloride) polymer electrolytes. Materials Science and Engineering: B 85(1):11–15
Premalatha M et al (2016) Characterization of blend polymer PVA-PVP complexed with ammonium thiocyanate. Ionics 22(8):1299–1310
Sikkanthar S et al (2015) Electrical conductivity characterization of polyacrylonitrile-ammonium bromide polymer electrolyte system. J Solid State Electrochem 19(4):987–999
Sikkanthar S et al (2016) Structural, electrical conductivity, and transport analysis of PAN–NH4Cl polymer electrolyte system. Ionics 22(7):1085–1094
Karthikeyan S et al (2016) Structural, electrical and electrochemical properties of polyacrylonitrile-ammonium hexaflurophosphate polymer electrolyte system. J Polym Res 23(3):1–10
Manjuladevi R et al (2017) Mg-ion conducting blend polymer electrolyte based on poly (vinyl alcohol)-poly (acrylonitrile) with magnesium perchlorate. Solid State Ion 308:90–100
Vijaya N et al (2012) Structural, vibrational, thermal, and conductivity studies on proton-conducting polymer electrolyte based on poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone). Ionics 18(1):91–99
Ramalingaiah S et al (1996) Conductivity and discharge characteristic studies of novel polymer electrolyte based on PEO complexed with Mg (NO3) 2 salt. Mater Lett 29(4-6):285–289
Nechifor C-D et al (2015) Study on glucose release ability from hydroxypropyl cellulose films. Polymer Bulletin 72(3):549–563
Hemalatha R et al (2019) Preparation and characterization of proton-conducting polymer electrolyte based on PVA, amino acid proline, and NH4Cl and its applications to electrochemical devices. Ionics 25(1):141–154
Pandi DV et al (2016) Development and characterization of proton conducting polymer electrolyte based on PVA, amino acid glycine and NH4SCN. Solid State Ion 298:15–22
Selvasekarapandian S et al (2010) Characterization of PVA–NH4NO3 polymer electrolyte and its application in rechargeable proton battery. J Physical Soc Japan 79(Suppl. A):163–168
Nusrath Unnisa C et al (2018) Development of poly (glycerol suberate) polyester (PGS)–PVA blend polymer electrolytes with NH4SCN and its application. Ionics 24(7):1979–1993
Rajendran S, Uma T (2000) Characterization of plasticized PMMA-LiBF4 based solid polymer electrolytes. Bull Mater Sci 23(1):27–29
Ramesh S, Liew C-W, Arof A (2011) Ion conducting corn starch biopolymer electrolytes doped with ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. J Non Cryst Solids 357(21):3654–3660
Boopathi G et al (2017) Development of proton conducting biopolymer membrane based on agar–agar for fuel cell. Ionics 23(10):2781–2790
Selvalakshmi S et al (2017) Study on NH4I composition effect in agar–agar-based biopolymer electrolyte. Ionics 23(10):2791–2797
Monisha S et al (2017) Preparation and characterization of cellulose acetate and lithium nitrate for advanced electrochemical devices. Ionics 23(10):2697–2706
Sampath M et al (2016) Preparation and characterization of biopolymer electrolyte based on cellulose acetate for potential applications in energy storage devices. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 27
Premalatha M et al (2018) Structural and electrical characterization of tamarind seed polysaccharide (TSP) doped with NH4HCO2. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1942. AIP Publishing LLC, pp 070005–070009
Premalatha M et al (2017) Tamarind seed polysaccharide (TSP)-based Li-ion conducting membranes. Ionics 23(10):2677–2684
Nirmala Devi G et al (2017) Synthesis and characterization of dextrin-based polymer electrolytes for potential applications in energy storage devices. Ionics 23(12):3377–3388
Muthukrishnan M et al (2019) Synthesis and characterization of pectin-based biopolymer electrolyte for electrochemical applications. Ionics 25(1):203–214
Moniha V et al (2018) Conductive bio-polymer electrolyte iota-carrageenan with ammonium nitrate for application in electrochemical devices. J Non Cryst Solids 481:424–434
Karthikeyan S et al (2017) Proton-conducting I-Carrageenan-based biopolymer electrolyte for fuel cell application. Ionics 23(10):2775–2780
Moniha V et al (2018) Synthesis and characterization of bio-polymer electrolyte based on iota-carrageenan with ammonium thiocyanate and its applications. J Solid State Electrochem 22(10):3209–3223
Aziz SB, Abidin ZHZ, Arof AK (2010) Effect of silver nanoparticles on the DC conductivity in chitosan–silver triflate polymer electrolyte. Physica B: Condensed Matter 405(21):4429–4433
Nik Aziz N, Idris N, Isa M (2010) Solid polymer electrolytes based on methylcellulose: FT-IR and ionic conductivity studies. International journal of polymer analysis and characterization 15(5):319–327
Khiar A, Arof AK (2010) Conductivity studies of starch-based polymer electrolytes. Ionics 16(2):123–129
Mishra R, Banthia A, Majeed A (2012) Pectin based formulations for biomedical applications: a review. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 5(4):1–7
Carbinatto FM et al (2012) Physical properties of pectin–high amylose starch mixtures cross-linked with sodium trimetaphosphate. Int J Pharm 423(2):281–288
Srivastava P, Malviya R (2011) Sources of pectin, extraction and its applications in pharmaceutical industry− An overview. IJNPR 2(1)
Zaitseva O et al (2020) Pectins as a universal medicine. Fitoterapia 146:104676
Perumal P, Christopher Selvin P, Selvasekarapandian S (2018) Characterization of biopolymer pectin with lithium chloride and its applications to electrochemical devices. Ionics 24(10):3259–3270
Kavitha S et al (2016) Vibrational, electrical and optical studies on pectin-based polymer electrolyte. Int Res J Eng Technol 3(7):1385–1390
Vijaya N et al (2017) Proton-conducting biopolymer electrolytes based on pectin doped with NH4X (X= Cl, Br). Ionics 23(10):2799–2808
Kiruthika S et al (2019) Eco-friendly biopolymer electrolyte, pectin with magnesium nitrate salt, for application in electrochemical devices. J Solid State Electrochem 23(7):2181–2193
Chitra R et al (2019) Synthesis and characterization of iota-carrageenan solid biopolymer electrolytes for electrochemical applications. Ionics 25(5):2147–2157
Hodge R, Edward GH, Simon GP (1996) Water absorption and states of water in semicrystalline poly (vinyl alcohol) films. Polymer 37(8):1371–1376
Gnanasambandam R, Proctor A (2000) Determination of pectin degree of esterification by diffuse reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem 68(3):327–332
Maciel VBV, Yoshida CM, Franco TT (2015) Chitosan/pectin polyelectrolyte complex as a pH indicator. Carbohydr Polym 132:537–545
Manjuladevi R et al (2018) Preparation and characterization of blend polymer electrolyte film based on poly (vinyl alcohol)-poly (acrylonitrile)/MgCl2 for energy storage devices. Ionics 24(4):1083–1095
Premalatha M et al (2016) Investigations on proton conducting biopolymer membranes based on tamarind seed polysaccharide incorporated with ammonium thiocyanate. J Non Cryst Solids 453:131–140
Boukamp BA (1986) A nonlinear least squares fit procedure for analysis of immittance data of electrochemical systems. Solid State Ion 20(1):31–44
Bhuvaneswari B et al (2022) Structural, thermal and electrochemical characterization of cellulose acetate–based solid biopolymer electrolyte for zinc ion batteries. Ionics 28(8):3865–3875
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Eswaragomathy, S., Selvanayagam, S., Selvasekarapandian, S. et al. Preparation of pectin biopolymer electrolyte for zinc-ion battery application. Ionics 29, 2329–2340 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-023-05005-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-023-05005-y