Abstract
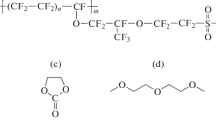
The Nafion-117 membranes in the Li+ form with pore-intercalated aprotonic organic solvents were prepared. The prepared materials were characterized by IR, impedance, and 7Li NMR spectroscopy. The solvent uptake of the membranes is shown to be controlled by the composition of organic solvents and their mixtures as well as by the conditions of the preliminary treatment of the initial membranes. For the Nafion-117 membrane, the degree of solvation can be improved by the preliminary treatment with alcohols, especially by the thermal treatment in methanol. Conductivity of the membranes is shown to increase with increasing content of the sorbed solvents. The best conductivity at 25 °C (2.5 × 10−3 and 1.6 × 10−3 S cm−1) was attained for the electrolytes based on the Nafion-117 membrane in lithium form with sorbed ethylene carbonate-propylene carbonate and ethylene carbonate-dimethoxyethane mixtures, respectively.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruno S, Jürgen G (2010) Lithium batteries: status, prospects and future. J Power Sources 195(9):2419–2430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.11.048
Yue L, Ma J, Zhang J, Zhao J, Dong S, Liu Z, Cui G, Chen L (2016) All solid-state polymer electrolytes for high-performance lithium ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater 5:139–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2016.07.003
Xu K (2004) Nonaqueous liquid electrolyte for lithium-based rechargeable batteries. Chem Rev 104:4303–4417. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr030203g
Xu K (2014) Electrolytes and interphases in Li-ion batteries and beyond. Chem Rev 114(23):11503–11618. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500003w
Quartarone E, Mustarelli P (2011) Electrolytes for solid-state lithium rechargeable batteries: recent advances and perspectives. Chem Soc Rev 40(5):2525–2540. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cs00081g
Yong T, Zhang L, Wang J, Mai Y, Yan X, Zhao X (2016) Novel choline-based ionic liquids as safe electrolytes for high-voltage lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 328:397–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.08.044
Pan XN, Hou J, Liu L, Yang PX, Zhang JQ, An MZ, Li N (2017) A piperidinium-based ester-functionalized ionic liquid as electrolytes in Li/LiFePO4 batteries. Ionics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2104-z
Ahmad S (2009) Polymer electrolytes: characteristics and peculiarities. Ionics 15(3):309–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-008-0309-x
Austin S, Johnsi M (2016) Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. Ionics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1924-6
Armand M (1983) Polymer electrolytes—an overview. Solid State Ionics 9 & 10:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2738(83)90083-8
Lightfoot P, Mehta MA, Bruce PG (1993) Crystal structure of the polymer electrolyte poly(ethy1ene oxide)3: LiCF3SO3. Science 262(5135):3. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.262.5135.883
Naveen KK, Kang M, Sivaiah K, Ravi M, Ratnakaram YC (2016) Enhanced electrical properties of polyethylene oxide (PEO) + polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP):Li+blended polymer electrolyte films with addition of Ag nanofiller. Ionics 22(6):815–825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1599-4
Sun B, Mindemark J, Edström K, Brandell D (2014) Polycarbonate-based solid polymer electrolytes for Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 262:738–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2013.08.014
Fonseca CP, Neves S (2002) Characterization of polymer electrolytes based on poly(dimethyl siloxane-co-ethylene oxide). J Power Sources 104:5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7753(01)00902-8
Sanginov EA, Evshchik EY, Kayumov RR, Dobrovol’skii YA (2015) Lithium-ion conductivity of the Nafion membrane swollen in organic solvents. Russ J Electrochem 51(10):986–990. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1023193515100122
Aldebert P, Guglieimi M, Pineri M (1991) Ionic conductivity of bulk, gels and solutions of perfluorinated ionomer membranes. Polymer J 23(5):8. https://doi.org/10.1295/polymj.23.399
Berezina NP, Timofeev SV, Kononenko NA (2002) Effect of conditioning techniques of perfluorinated sulphocationic membranes on their hydrophylic and electrotransport properties. J Memb Sci 209:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(02)00368-X
Volkov V, Volkov E, Timofeev S, Sanginov E, Pavlov A, Safronova E, Stenina I, Yaroslavtsev A (2010) Diffusion mobility of alkali metals in perfluorinated sulfocationic and carboxylic membranes as probed by 1H, 7Li, 23Na, and 133Cs NMR spectroscopy. Russ J Inorg Chem 55(3):318–324. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0036023610030022
Sanginov EA, Kayumov RR, Shmygleva LV, Lesnichaya VA, Karelin AI, Dobrovolsky YA (2017) Study of the transport of alkali metal ions in a nonaqueous polymer electrolyte based on Nafion. Solid State Ionics 300:26–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2016.11.017
Cai Z, Liu Y, Liu S, Li L, Zhang Y (2012) High performance of lithium-ion polymer battery based on non-aqueous lithiated perfluorinated sulfonic ion-exchange membranes. Energy Environ Sci 5(2):5690–5693. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1ee02708e
Karelin AI, Kayumov RR, Sanginov EA, Dobrovolsky YA (2017) Structure of lithium ion-conducting polymer membranes based on Nafion plasticized with dimethylsulfoxide. Petrol Chem 56(11):1020–1026. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0965544116110074
Phair JW, Badwal SPS (2006) Review of proton conductors for hydrogen separation. Ionics 12:103–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-006-0016-4
Karpenko-Jereb LV, Kelterer A-M, Berezina NP, Pimenov AV (2013) Conductometric and computational study of cationic polymer membranes in H+ and Na+-forms at various hydration levels. J Memb Sci 444:127–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.05.012
Safronova E, Golubenko D, Pourcelly G, Yaroslavtsev A (2015) Mechanical properties and influence of straining on ion conductivity of perfluorosulfonic acid Nafion®-type membranes depending on water uptake. J Memb Sci 473:218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.09.031
Yaroslavtsev AB, Karavanova YA, Safronova EY (2011) Ionic conductivity of hybrid membranes. Petrol Chem 51(7):473–479. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0965544111070140
Doyle M, Lewittes ME, Roelofs MG, Perusich SA, Lowrey RE (2001) Relationship between ionic conductivity of perfluorinated ionomeric membranes and nonaqueous solvent properties. J Memb Sci 184:257–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(00)00642-6
Safronova E, Safronov D, Lysova A, Parshina A, Bobreshova O, Pourcelly G, Yaroslavtsev A (2017) Sensitivity of potentiometric sensors based on Nafion ®-type membranes and effect of the membranes mechanical, thermal, and hydrothermal treatments on the on their properties. Sensors Actuat B Chem 240:1016–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.010
Liu Y, Cai Z, Tan L, Li L (2012) Ion exchange membranes as electrolyte for high performance Li-ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci 5(10):9007. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ee22753c
Yaws L (2014) Thermophysical properties of chemicals and hydrocarbons. 2nd edit. Chapter 19. Elsevier, Amsterdam. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-081551596-8.50024-9
Casciola M, Alberti G, Sganappa M, Narducci N (2006) Factors affecting the stability of Nafion conductivity at high temperature and relative humidity. Desalination 200:639–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.03.450
Alberti G, Narducci R, Sganappa M (2008) Effects of hydrothermal/thermal treatments on the water-uptake of Nafion membranes and relations with changes of conformation, counter-elastic force and tensile modulus of the matrix. J Power Sources 178:575–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.09.034.22–27
Collette F, Thominette F, Mendil-Jakani H, Gebel G (2013) Structure and transport properties of solution-cast Nafion membranes subjected to hygrothermal aging. J Membr Sci 435:242–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.02.002
Kuwertz R, Kirstein C, Turek T, Kunz U (2016) Influence of acid pretreatment on ionic conductivity of Nafion membranes. J Membr Sci 500:225–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2015.11.022
DeBonis D, Mayer M, Omosebi A, Besser RS (2016) Analysis of mechanism of Nafion conductivity change due to hot pressing treatment. Renew Energy 89:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.11.081
Wang M, Zhao F, Dong S (2004) A single ionic conductor based on Nafion and its electrochemical properties used as lithium polymer electrolyte. J Phys Chem B 108:1365–1370. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp036661a
Socrates G (2001) Infrared and raman characteristic group frequencies. Tables and charts, 3rd edn. Wiley, Baffins Lane
Chia C-H, Wu Z, C-H W, Cheng R-H, Ding S (2012) Resolve the pore structure and dynamics of Nafion 117: application of high resolution 7Li solid state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mater Chem 22(42):22440. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm34057g
Volkov VI, Marinin AA (2013) NMR methods for studying ion and molecular transport in polymer electrolytes. Russ Chem Rev 82(3):248–272. https://doi.org/10.1070/RC2013v082n03ABEH004278
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project no. 17-79-30054.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voropaeva, D.Y., Novikova, S.A., Kulova, T.L. et al. Conductivity of Nafion-117 membranes intercalated by polar aprotonic solvents. Ionics 24, 1685–1692 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2333-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2333-1