Abstract
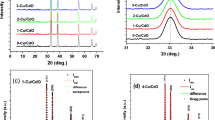
The various mole percent (1–5%) of Eu3+-doped ZnSe thin films were fabricated on the indium-doped tin oxide (ITO) conducting glass substrate by single-step electrochemical deposition (ECD) process in an aqueous medium at 50 °C. The structural, optical, magnetic, and electrochemical properties were characterized as a function of the Eu3+ ion concentration. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses evidenced that the films were hexagonal wurtzite structure along with the (101) preferential orientation. High-resolution scanning electron microscopy (HRSEM) results revealed that the thin films show a spherical like structure for 1–3% of Eu3+-doped ZnSe films. Further, increasing of Eu3+ concentration (4 and 5%), the surface morphology of thin films was observed as agglomerated grain-like structure. The band gap energy of Eu3+-doped ZnSe thin films (2.35 to 2.49 eV) determined by UV-Vis spectra showed a blue shift of absorption edge compared to the pure ZnSe thin film (2.33 eV). The increased band gap by doping of Eu3+ is due to the quantum size effect. The PL emission intensity enhanced by increasing Eu3+ concentration which revealed the enhanced radiative recombination in the luminescence process. The magnetic study revealed that Eu3+-doped ZnSe thin films were ferromagnetic in nature. Electrochemical impedance analysis indicated that 4% of Eu3+-doped ZnSe thin films showed a lower charge transfer resistance (352 Ω) and excellent properties compared to the other samples. Further, the photoelectrochemical measurements carried out for the optimized 4% Eu3+-doped ZnSe thin film revealed the faster migration of photoinduced charge carriers. The present investigation demonstrates that the electrochemically deposited Eu3+-doped ZnSe thin film is a promising candidate for electrochemical device applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei A, Zhao X, Liu J, Zhao Y (2013) Investigation on the structure and optical properties of chemically deposited ZnSe nanocrystalline thin films. Physica B 41:0120–0125
Moses Ezhil Raj A, Mary Delphine S, Sanjeeviraja C, Jayachandran M (2010) Growth of ZnSe thin layers on different substrates and their structural consequences with bath temperature. Physica B 405:2485–2491
Prabukanthan P, Harichandran G (2014) Electrochemical deposition of n-type ZnSe thin film buffer layer for solar cells. J Electrochem Soc 14:D736–D741
Lohar GM, Dhaygude HD, Relekar BP, Rath MC, Fulari VJ (2016) Effect of 10 MeV energy of electron irradiation on Fe2+ doped ZnSe nanorods and their modified properties. Ionics 22:1451–1460
Sai Prasanna CM, Austin Suthanthirara S (2016) Electrical, structural, and morphological studies of honeycomb-like microporous zinc-ion conducting poly (vinyl chloride)/poly (ethyl methacrylate) blend-based polymer electrolytes. Ionics 22:389–404
Feng S, Yang R, Ding X, Li J, Guo C, Qu L (2015) Sensitive electrochemical sensor for the determination of pentachlorophenol in fish meat based on ZnSe quantum dots decorated multiwall carbon nanotubes nanocomposite. Ionics 21:3257–3326
Radevici I, Sushkevich K, Huhtinen H, Nedeoglo D, Paturi P (2015) Influence of the ytterbium doping technique on the luminescent properties of ZnSe single crystals. J Lumin 158:236–242
Xu J, Wanga W, Zhang X, Chang X, Shi Z, Haarberg GM (2015) Electrodeposition of ZnSe thin film and its photocatalytic properties. J Alloys Compd 632:778–782
Doña JM, Herrero J (1995) Chemical-bath deposition of ZnSe thin films: process and material characterization. J Electrochem Soc 142(3):764–770
Liu J, Wei AX, Zhuang MX, Zhao Y (2013) Investigation of the ZnSxSe1-x thin films prepared by chemical bath deposition. J Mater Sci-Mater Electron 24:1348–1353
Samantilleke AP, Boyle MH, Young J, Dharmadas IM (1998) Growth of n-type and p-type ZnSe thin films using an electrochemical technique for application in larger area optoelectronic devices. J Mater Sci - Mater Electron 9:231–235
Kowalik R, Fitzner K (2009) Analysis of the mechanism for electrodeposition of the ZnSe phase on Cu substrate. J Electroanal Chem 633:78–84
Chubenko EB, Klyshko AA, Petrovich VA, Bondarenko VP (2009) Electrochemical deposition of zinc selenide and cadmium selenide onto porous silicon from aqueous acidic solutions. Thin Solid Films 517:5981–5987
Jia L, Kou H, Jiang Y, Yu S, Li J, Wang C (2013) Electrochemical deposition semiconductor ZnSe on a new substrate CNTs/PVA and its photoelectrical properties. Electrochim Acta 107:71–77
Riveros G, Gomez H, Henrquez R, Schrebler R, Marotti RE, Dalchiele EA (2001) Electrodeposition and characterization of ZnSe semiconductor thin films. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 70:255–268
Bouroushian M, Kosanovic T, Loizos Z, Spyrellis N (2002) Electrochemical formation of zinc selenide from acidic aqueous solutions. J Solid State Electrochem 6:272–278
Bouroushian M, Kosanovic T, Spyrellis N (2005) Oriented [1 1 1] ZnSe electrodeposits grown on polycrystalline CdSe substrates. J Cryst Growth 277:335–344
Natarajan C, Sharon M, Levy-Clement C, Neumann-Spallart M (1994) Electrodeposition of zinc selenide. Thin Solid Films 237:118–123
Kumar SR, Nuthalapati M, Maity J (2012) Development of nanocrystalline ZnSe thin film through electrodeposition from a non-aqueous solution. Scripta Mater 67:396–399
Kumar P, Singh J, Pandey MK, Jeyanthi CE, Siddheswaran R, Paulraj M, Hui KN, Hui KS (2014) Synthesis, structural, optical and Raman studies of pure and lanthanum doped ZnSe nanoparticles. Mater Res Bull 49:144–150
Liu N, Zhou W, Xu L, Tong L, Zhou J, Su W, Yu Y, Xu J, Ma Z (2012) Enhanced luminescence of ZnSe:Eu3+/ZnS core-shell quantum dots. J Non-Cryst Solids 358:2353–2356
Yashaswini AK, Pandurangappa C (2014) Solvothermal synthesis, characterization and photoluminescence studies of ZnS:Eu nanocrystals. Opt Mater 37:537–542
Lohar GM, Jadhav ST, Takale MV, Patil RA, Mab YR, Rath MC, Fulari VJ (2015) Photoelectrochemical cell studies of Fe2+ doped ZnSe nanorods using the potentiostatic mode of electrodeposition. J Colloid Interface Sci 458:136–146
Metina H, Durmus S, Erata S, Ari M (2011) Characterization of chemically deposited ZnSe/SnO2/glass films: influence of annealing in Ar atmosphere on physical properties. Appl Surf Sci 257:6474–6480
Zeng QZ, Xue SL, Wu SX, Gan KX, Xu L, Han JW, Zhou WK, Shi YT, Zou RJ (2015) Synthesis, field emission and optical properties of ZnSe nanobelts, nanorods and nanocones by hydrothermal method. Mater Sci Semicond Process 31:189–194
Prabukanthan P, Rajesh Kumar T, Harichandran G (2015) Effect of Sm3+ on the structural, optical, magnetic and electrical properties of electrochemical deposition of ZnSe thin films. Mater Res Express 2:09610
Lohar GM, Shinde SK, Rath MC, Fulari VJ (2014) Structural, optical, photoluminescence, electrochemical and photoelectrochemical properties of Fe doped ZnSe hexagonal nanorods. Mater Sci Semicond Process 26:548–554
Yadav K, Dwivedi Y, Jaggi N (2015) Structural and optical properties of Ni doped ZnSe nanoparticles. J Lumin 158:181–187
Mathew S, Rejikumar PR, Xavier J, Unnikrishnan NV (2007) Optical studies on Eu3+/ZnSe nanocrystal in silica hosts. Opt Mater 29:1689–1692
Theerthagiri J, Senthil RA, Priya A, Madhavan J, Michael RJV (2014) Muthupandian Ashokkumar, Photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical studies of visible-light active a-Fe2O3–g-C3N4 nanocomposites. RSC Adv 4:38222
Acknowledgments
P.P. would like to acknowledge the financial support of Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology (DST), Fast Track Research Scheme, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajesh Kumar, T., Prabukanthan, P., Harichandran, G. et al. Optical, magnetic, and photoelectrochemical properties of electrochemically deposited Eu3+-doped ZnSe thin films. Ionics 23, 2497–2507 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2090-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2090-1