Abstract
Purpose
Surgical action triplet recognition is a clinically significant yet challenging task. It provides surgeons with detailed information about surgical scenarios, thereby facilitating clinical decision-making. However, the high similarity among action triplets presents a formidable obstacle to recognition. To enhance accuracy, prior methods necessitated the utilization of larger models, thereby incurring a considerable computational burden.
Methods
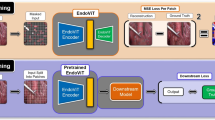
We propose a novel framework known as the Lite and Mega Models (LAM). It comprises a CNN-based fully fine-tuned model (LAM-Lite) and a parameter-efficient fine-tuned model based on the foundation model using Transformer architecture (LAM-Mega). Temporal multi-label data augmentation is introduced for extracting robust class-level features.
Results
Our study demonstrates that LAM outperforms prior methods across various parameter scales on the CholecT50 dataset. Using fewer tunable parameters, LAM achieves a mean average precision (mAP) of 42.1%, a 3.6% improvement over the previous state of the art.
Conclusion
Leveraging effective structural design and robust capabilities of the foundational model, our proposed approach successfully strikes a balance between accuracy and computational efficiency. The source code is accessible at https://github.com/Lycus99/LAM.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wagner M, Brandenburg JM, Bodenstedt S, Schulze A, Jenke AC, Stern A, Daum MTJ, Mündermann L, Kolbinger FR, Bhasker N, Schneider G, Krause-Jüttler G, Alwanni H, Fritz-Kebede F, Burgert O, Wilhelm D, Fallert J, Nickel F, Maier-Hein L, Dugas M, Distler M, Weitz J, Müller-Stich B-P, Speidel S (2022) Surgomics: personalized prediction of morbidity, mortality and long-term outcome in surgery using machine learning on multimodal data. Surg Endosc 36(11):8568–8591
Mascagni P, Alapatt D, Sestini L, Altieri MS, Madani A, Watanabe Y, Alseidi A, Redan JA, Alfieri S, Costamagna G, Boskoski I, Padoy N, Hashimoto DA (2022) Computer vision in surgery: from potential to clinical value. NPJ Digit Med 5(1):163
Ward TM, Mascagni P, Ban Y, Rosman G, Padoy N, Meireles O, Hashimoto DA (2021) Computer vision in surgery. Surgery 169(5):1253–1256
Maier-Hein L, Eisenmann M, Sarikaya D et al (2022) Surgical data science-from concepts toward clinical translation. Med Image Anal 76:102306
Li Y, Xia T, Luo H, He B, Jia F (2023) MT-FiST: a multi-task fine-grained spatial-temporal framework for surgical action triplet recognition. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 27(10):4983–4994
Sharma S, Nwoye CI, Mutter D, Padoy N (2023) Rendezvous in time: an attention-based temporal fusion approach for surgical triplet recognition. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 18:1053–1059
Nwoye CI, Gonzalez C, Yu T, Mascagni P, Mutter D, Marescaux J, Padoy N (2020) Recognition of instrument-tissue interactions in endoscopic videos via action triplets. In: MICCAI (LNCS), vol 12263, pp 364–374
Nwoye CI, Yu T, Gonzalez C, Seeliger B, Mascagni P, Mutter D, Marescaux J, Padoy N (2022) Rendezvous: attention mechanisms for the recognition of surgical action triplets in endoscopic videos. Med Image Anal 78:102433
Xi N, Meng J, Yuan J (2022) Forest graph convolutional network for surgical action triplet recognition in endoscopic videos. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32(12):8550–8561
Yamlahi A, Tran TN, Godau P, Schellenberg M, Michael D, Smidt F-H, Nölke J-H, Adler TJ, Tizabi MD, Nwoye CI, Padoy N, Maier-Hein L (2023) Self-distillation for surgical action recognition. In: MICCAI (LNCS), vol 14228, pp 637–646
Ban Y, Eckhoff JA, Ward TM, Hashimoto DA, Meireles OR, Rus D, Rosman G (2024) Concept graph neural networks for surgical video understanding. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 43(1):264–274
Zhao S, Liu Y, Wang Q, Sun D, Liu R, Zhou SK (2022) Murphy: relations matter in surgical workflow analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.12719
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2015) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR. pp 770–778
Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, Hu H, Wei Y, Zhang Z, Lin S, Guo B (2021) Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: ICCV, pp 10012–10022
Houlsby N, Giurgiu A, Jastrzebski S, Morrone B, de Laroussilhe Q, Gesmundo A, Attariyan M, Gelly S (2019) Parameter-efficient transfer learning for NLP. In: ICML, pp 2790–2799
Yang T, Zhu Y, Xie Y, Zhang A, Chen C, Li M (2023) AIM: adapting image models for efficient video action recognition. In: ICLR
Radford A, Kim JW, Hallacy C, Ramesh A, Goh G, Agarwal S, Sastry G, Askell A, Mishkin P, Clark J, Krueger G, Sutskever I (2021) Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: ICML, pp 8748–8763
Cai Y, Zhou Y, Han Q, Sun J, Kong X, Li J, Zhang X (2022) Reversible column networks. In: ICLR
Liu Z, Mao H, Wu C-Y, Feichtenhofer C, Darrell T, Xie S (2022) A ConvNet for the 2020s. In: CVPR, pp 11976–11986
Yu BXB, Chang J, Wang H, Liu L, Wang S, Wang Z, Lin J, Xie L, Li H, Lin Z, Tian Q, Chen CW (2023) Visual tuning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.06061
Zhang H, Cisse M, Dauphin Y N, Lopez-Paz D (2018) Mixup: beyond Empirical Risk Minimization. In: ICLR
Wu H, Song C, Yue S, Wang Z, Xiao J, Liu Y (2022) Dynamic video mix-up for cross-domain action recognition. Neurocomputing 471:358–368
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X, Unterthiner T, Dehghani M, Minderer M, Heigold G, Gelly S, Uszkoreit J, Houlsby N (2020) An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. In: ICLR
Gui S, Wang Z, Chen J, Zhou X, Zhang C, Cao Y (2024) MT4MTL-KD: a multi-teacher knowledge distillation framework for triplet recognition. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 43(4):1628–1639
Nwoye CI, Padoy N (2022) Data splits and metrics for method benchmarking on surgical action triplet datasets. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.05235
Nwoye CI, Alapatt D, Yu T, Vardazaryan A, Xia F, Zhao Z, Xia T, Jia F, Yang Y, Wang H, Yu D, Zheng G, Duan X, Getty N, Sanchez-Matilla R, Robu M, Zhang L, Chen H, Wang J, Wang L, Zhang B, Gerats B, Raviteja S, Sathish R, Tao R, Kondo S, Pang W, Ren H, Abbing JR, Sarhan MH, Bodensteddt S, Bhasker N, Oliveira B, Torres HR, Ling L, Gaida F, Czempiel T, Vilaca JL, Morais P, Fonseca J, Egging RM, Wijma IN, Qian C, Bian G, Li Z, Balasubramanian V, Sheet D, Luengo I, Zhu Y, Ding S, Aschenbrenner J-A, van der Kar NE, Xu M, Islam M, Seenivasan L, Jenke A, Stoyanov D, Mutter D, Mascagni P, Seeliger B, Gonzalez C, Padoy N (2023) CholecTriplet 2021: a benchmark challenge for surgical action triplet recognition. Med Image Anal 86:102803
Nwoye CI, Yu T, Sharma S, Murali A, Alapatt D, Vardazaryan A, Yuan K, Hajek J, Reiter W, Yamlahi A, Smidt F-H, Zou X, Zhen G, Oliveira B, Torres HR, Kondo S, Kasai S, Holm F, Özsoy E, Gui S, Li H, Raviteja S, Sathish R, Poudel P, Bhattarai B, Wang Z, Rui G, Schellenberg M, Vilaca JL, Czempiel T, Wang Z, Sheet D, Thapa SK, Berniker M, Godau P, Morais P, Regmi S, Tran TN, Fonseca J, Nölke J-H, Lima E, Vazquez E, Maier-Hein L, Navab N, Mascagni P, Seeliger B, Gonzalez C, Mutter D, Padoy N (2023) CholecTriplet2022: show me a tool and tell me the triplet-an endoscopic vision challenge for surgical action triplet detection. Med Image Anal 89:102888
Funding
The present study was supported in part by the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (SGDX20230116092200001), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 62172401 and 82227806), the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 2022A1515010439 and 2022A0505020019), the Shenzhen Key Basic Research Grant (No. JCYJ20220818101802005), the Zhuhai Science and Technology Program (No. ZH22017002210017PWC), and the Education Science Planning Program of Guangdong Department of Education (Higher Education Special Project) (No. 2022GXJK325).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest with regard to this study.
Ethical approval
The data used in this paper are a public dataset.
Informed consent
The data used in this paper are a public dataset.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Bai, B. & Jia, F. Parameter-efficient framework for surgical action triplet recognition. Int J CARS (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-024-03147-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-024-03147-6