Abstract
Purpose
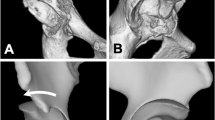
Periacetabular osteotomies are a family of surgical procedures used to treat hip dysplasia. In a periacetabular osteotomy, the operating surgeon aims to increase acetabular coverage of the femoral head. The surgical correction has mechanical goals of increasing the stability of the joint and to improving the pressure distribution across the acetabulum. Although it is known that bone will remodel under changing load at the microstructural level, it is unclear whether there is any gross remodeling of the acetabulum or the femoral head in response to the change in loading following a periacetabular osteotomy. This observational study aims to quantify the shape of operative and contralateral hip joint surfaces pre and postoperatively to determine whether there are gross morphological changes in the shape of any of the bony articular surfaces of the joint.
Methods
Preoperative and postoperative computed tomography (CT) scans were segmented as triangulated meshes. The bony articular surfaces of these meshes were then isolated. The vertices of these surfaces were fit to spheres and to general ellipsoids and, in the case of the acetabulum, examined in anatomical coordinate frames to look for changes between pre and postoperative segmentations.
Results
Spherical fit results were consistent preoperatively and postoperatively, with small changes in the radii of the spheres of best fit for both operative and nonoperative hips. Ellipsoid fitting showed variations between preoperative and postoperative scans in both eccentricity and orientation.
Conclusions
Because there is no clear evidence of gross articular surface remodeling, periacetabular osteotomy for an adult should be planned with the expectation that the patient’s existing articular structure will be preserved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Janssen D, Kalchschmidt K, Katthagen BD (2009) Triple pelvic osteotomy as treatment for osteoarthritis secondary to developmental dysplasia of the hip. Int Orthop 33: 1555–1559
Okano K, Enomoto H, Osaki M, Shindo H (2008) Outcome of rotational acetabular osteotomy for early hip osteoarthritis secondary to dysplasia related to femoral head shape. Acto Orthop 79(1): 12–17
Zhao X, Chosa E, Totoribe K, Deng G (2010) Effect of periacetabular osteotomy for acetabular dysplasia clarified by three- dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Sci 15: 632–640
Parfitt AM (1994) Osteonal and hemi-osteonal remodelling: the spatial and temporal framework for signal traffic in adult human bone. J Cell Biochem 55: 273–286
Robling AG, Castillo AB, Turner CH (2006) Biomechanical and molecular regulation of bone remodeling. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 8: 455–498
van Oers RFM, Ruimerman R, Tanck E, Hilbers PAJ, Huiskes R (2008) A unified theory for osteonal and hemi-osteonal remodeling. Bone 42: 250–259
Weinstein SL, Mubarak SJ, Wenger DR (2003) Developmental hip dysplasia and dislocation. J Bone Jt Surg Am 85: 1824–1832
Sugano N, Noble PC, Kamaric E, Salama JK, Ochi T, Tullos HS (1998) The morphology of the femur in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Jt Surg Br 80: 711–719
Weinstein SL (1987) Natural history of congenital hip dislocation (CDH) and hip dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res 5: 62–76
Murphy SB, Ganz R, Muller ME (1995) The prognosis in untreated dysplasia of the hip. a study of radiographic factors that predict the outcome. J Bone Jt Surg Am 77: 985–989
Ganz R, Klaue K, Vinh TS, Mast JW (1988) A new periacetabular osteotomy for the treatment of hip dysplasias: technique and preliminary results. Clin Orthop 232: 26–36
Mechlenburg I, Nyengaard JR, Rømer L, Søballe K (2005) Prospective bone density changes after periacetabular osteotomy: a methodological study. Int Orthop 29(5): 281–286
Krishnan V, Davidovitch Z (2006) Cellular, molecular and tissue-level reactions to orthodontic force. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 129: 469e1–469e32
Robling AG, Hinant FM, Burr DB, Turner CH (2002) Improved bone structure and strength after long-term mechanical loading is greatest if loading is separated into short bouts. J Bone Miner Res 17: 1545–1554
Ilizarov GA, Ledyaev VI (1992) The replacement of long tubular bone defects by lengthening distraction osteotomy of one of the fragments. Clin Orthop 280: 7–10
McCarthy JG, Stelnicki EJ, Mehrara BJ, Longaker MT (2001) Distraction osteogenesis of the craniofacial skeleton. Plast Reconstr Surg 107: 1812–1827
Walmsley T (1928) The articular mechanism of the diarthroses. J Bone Jt Surg Am 10: 40–45
Bullough P, Goodfellow J, Greenwald AS, O’Connor JJ (1968) Incongruent surfaces in the human hip joint. Nature 217: 1290
Greenwald AS, O’Connor JJ (1971) The transmission of load through the human hip joint. J Biomech 4: 507–528
Afoke NYP, Byers PD, Hutton WC (1987) Contact pressures in the human hip joint. J Bone Jt Surg 69B: 536–541
von Eisenhart R, Adam C, Steinlechner M, Müller-Gerbl M (1999) Quantitative determination of joint incongruity and pressure distribution during simulated gait and cartilage thickness in the human hip joint. J Bone Jt Surg 17: 532–539
Gu D, Chen Y, Dai K, Zhang S, Yuan J (2008) The shape of the acetabular cartilage surface: a geometric morphometric study using three-dimensional scanning. Med Eng Phys 30: 1024–1031
Menschik F (1997) The hip joint as a conchoids shape. J Biomech 30(4): 971–973
Ellis RE, Rasquinha B, Wood GCA, Rudan JF (2010) 3D shape analysis of arthritic hips: a preliminary study. Int J CARS S137–S142
Anstey J, Smith EJ, Rudan JF, Ellis RE (2010) On the use of laser scans to validate reverse engineering of bony anatomy. Stud Health Technol Inform. IOS Press, Amsterdam, 2010. Accepted on 28 Sep, 2010
Markovsky I, Kukush A, Van Huffel S (2004) Consistent least squares fitting of ellipsoids. Numer Math 98: 177–194
Rasquinha B, Rudan J, Wood G, Ellis RE (2010) Ellipsoid fitting of dysplastic and early articular hip surfaces. Proc Ortho Res Soc Accepted on 30 Sep, 2010
Lewinnek GE, Lewis JL, Tarr R, Compere CL, Zimmerman JR (1978) Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Jt Surg Am 60: 217–220
Mechlenburg I, Kold S, Søballe K (2009) No change detected by DEXA in bone mineral density after periacetabular osteotomy. Acta Orthop Belg 75(6): 761–766
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rasquinha, B.J., Sayani, J., Rudan, J.F. et al. Articular surface remodeling of the hip after periacetabular osteotomy. Int J CARS 7, 241–248 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-011-0641-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-011-0641-x