Abstract
Purpose
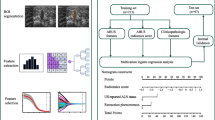
This study aimed to develop a radiomics nomogram based on grayscale ultrasound (US) to distinguish triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) from non-triple-negative breast cancer (NTNBC) prior to surgery.
Methods
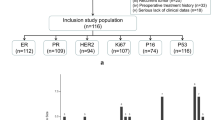
A retrospective analysis of 454 breast carcinoma patients confirmed by pathology was conducted, with 317 patients in the training dataset (59 with TNBC) and 137 patients in the validation dataset (27 with TNBC). Clinical information, conventional US features, and radiomics features were collected, and the Radscore model was constructed after feature selection. Independent risk factors were identified using univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis. The nomogram model was assessed using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, calibration curve, decision curve analysis (DCA), net reclassification improvement (NRI) and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI).
Results
Tumor shape, margin, and calcification were independent risk factors in the clinical prediction model. Additionally, 16 radiomics features were selected to construct the Radscore model out of a total of 474 extracted features. The radiomics nomogram model, which incorporated tumor shape, margin, calcification, and Radscore, achieved an AUC value of 0.837 in the training dataset and 0.813 in the validation dataset, outperforming both the Radscore and clinical models in terms of predictive performance. The significant improvement of NRI and IDI indicated that the Radscore may be useful biomarkers for TNBC.
Conclusion
The US-based radiomics nomogram showed satisfactory preoperative prediction of TNBC.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TNBC:
-
Triple-negative breast cancer
- NTNBC:
-
Non-triple-negative breast cancer
- 2D:
-
Two-dimensional
- US:
-
Ultrasound
- CUS:
-
Conventional ultrasound
- Radscore:
-
Radiomic signature
- AIC:
-
Akaike information criterion
- DCA:
-
Decision curve analysis
- ICC:
-
Interclass correlation coefficient
- LASSO:
-
Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator
References
Xu M, Tang Q, Li M, Liu Y, Li F (2021) An analysis of Ki-67 expression in stage 1 invasive ductal breast carcinoma using apparent diffusion coefficient histograms. Quant Imaging Med Surg 11:1518–1531
Ge S, Yixing Y, Jia D, Ling Y (2022) Application of mammography-based radiomics signature for preoperative prediction of triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Med Imaging 22:166
Xu M, Li F, Yu S et al (2022) Value of histogram of gray-scale ultrasound image in differential diagnosis of small triple negative breast invasive ductal carcinoma and fibroadenoma. Cancer Manag Res 14:1515–1524
Du Y, Zha H, Wang H et al (2022) Ultrasound-based radiomics nomogram for differentiation of triple-negative breast cancer from fibroadenoma. Br J Radiol 95:20210598
Son J, Lee SE, Kim EK, Kim S (2020) Prediction of breast cancer molecular subtypes using radiomics signatures of synthetic mammography from digital breast tomosynthesis. Sci Rep 10:21566
Zhang HX, Sun ZQ, Cheng YG, Mao GQ (2019) A pilot study of radiomics technology based on X-ray mammography in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Xray Sci Technol 27:485–492
Feng Q, Hu Q, Liu Y, Yang T, Yin Z (2020) Diagnosis of triple negative breast cancer based on radiomics signatures extracted from preoperative contrast-enhanced chest computed tomography. BMC Cancer 20:579
Leithner D, Bernard-Davila B, Martinez DF et al (2020) Radiomic signatures derived from diffusion-weighted imaging for the assessment of breast cancer receptor status and molecular subtypes. Mol Imag Biol 22:453–461
Wen B, Kong W, Zhang Y, Xue H, Wu M, Wang F (2022) Association between contrast-enhanced ultrasound characteristics and molecular subtypes of breast cancer. J Ultrasound Med 41:2019–2031
Xu ML, Zeng SE, Li F, Cui XW, Liu GF (2022) Preoperative prediction of lymphovascular invasion in patients with T1 breast invasive ductal carcinoma based on radiomics nomogram using grayscale ultrasound. Front Oncol 12:1071677
Zha HL, Zong M, Liu XP et al (2021) Preoperative ultrasound-based radiomics score can improve the accuracy of the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center nomogram for predicting sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer. Eur J Radiol 135:109512
Jiang M, Li CL, Luo XM et al (2021) Ultrasound-based deep learning radiomics in the assessment of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 147:95–105
Zhou P, Jin C, Lu J et al (2021) The Value of nomograms in pre-operative prediction of lymphovascular invasion in primary breast cancer undergoing modified radical surgery: based on multiparametric ultrasound and clinicopathologic indicators. Ultrasound Med Biol 47:517–526
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ (2011) Strategies for subtypes–dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2011. Ann Oncol 22:1736–1747
Feng Q, Chen Y, Liao Z et al (2018) Corpus callosum radiomics-based classification model in Alzheimer’s disease: a case-control study. Front Neurol 9:618
Zhang J, Wang G, Ren J et al (2022) Multiparametric MRI-based radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of lymphovascular invasion and clinical outcomes in patients with breast invasive ductal carcinoma. Eur Radiol 32:4079–4089
Xu M, Yang H, Yang Q et al (2023) Radiomics nomogram based on digital breast tomosynthesis: preoperative evaluation of axillary lymph node metastasis in breast carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149:9317–9328
Yang Y, Zou X, Zhou W et al (2022) Multiparametric MRI-based radiomic signature for preoperative evaluation of overall survival in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma after partial hepatectomy. J Magn Reson Imaging 56:739–751
Li JW, Zhang K, Shi ZT et al (2018) Triple-negative invasive breast carcinoma: the association between the sonographic appearances with clinicopathological feature. Sci Rep 8:9040
Lee SE, Han K, Kwak JY, Lee E, Kim EK (2018) Radiomics of US texture features in differential diagnosis between triple-negative breast cancer and fibroadenoma. Sci Rep 8:13546
Moon WK, Huang YS, Lo CM et al (2015) Computer-aided diagnosis for distinguishing between triple-negative breast cancer and fibroadenomas based on ultrasound texture features. Med Phys 42:3024–3035
Choi YJ, Seong MH, Choi SH et al (2011) Ultrasound and clinicopathological characteristics of triple receptor-negative breast cancers. J Breast Cancer 14:119–123
Yang Q, Liu HY, Liu D, Song YQ (2015) Ultrasonographic features of triple-negative breast cancer: a comparison with other breast cancer subtypes. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16:3229–3232
Moasser MM (2007) The oncogene HER2: its signaling and transforming functions and its role in human cancer pathogenesis. Oncogene 26:6469–6487
Choi JJ, Kim SH, Kang BJ, Song BJ (2016) Detectability and usefulness of automated whole breast ultrasound in patients with suspicious microcalcifications on mammography: comparison with handheld breast ultrasound. J Breast Cancer 19:429–437
Hrkac PA, Ivanac G, Brkljacic B (2018) US and MRI in the evaluation of mammographic BI-RADS 4 and 5 microcalcifications. Diagn Interv Radiol 24:187–194
Kang SS, Ko EY, Han BK, Shin JH (2008) Breast US in patients who had microcalcifications with low concern of malignancy on screening mammography. Eur J Radiol 67:285–291
Wang D, Liu M, Zhuang Z et al (2022) Radiomics analysis on digital breast tomosynthesis: preoperative evaluation of lymphovascular invasion status in invasive breast cancer. Acad Radiol 29(12):1773–1782
Fang C, Zhang J, Li J et al (2022) Clinical-radiomics nomogram for identifying HER2 status in patients with breast cancer: a multicenter study. Front Oncol 12:922185
Xie T, Wang Z, Zhao Q et al (2019) Machine learning-based analysis of Mr Multiparametric Radiomics for the subtype classification of breast cancer. Front Oncol 9:505
Xie Y, Wang M, Xia H et al (2023) Development and validation of a CECT-based radiomics model for predicting IL1B expression and prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Front Oncol 13:1121485
Zhang D, Wei Q, Wu GG et al (2021) Preoperative prediction of microvascular invasion in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma based on radiomics nomogram using contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Front Oncol 11:709339
Gao Y, Luo Y, Zhao C et al (2021) Nomogram based on radiomics analysis of primary breast cancer ultrasound images: prediction of axillary lymph node tumor burden in patients. Eur Radiol 31:928–937
Funding
This study has received funding by Wu Jieping Medical Foundation (Project No. 320.6750.19089–40); Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan (Project No. 20220203113SF); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 52275006); Climbing Foundation Clinical Research Project of National Cancer Center (Project No. NCC201917B04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was conceived and designed by FL and G-FL. FL and S-EZ acquired the data, while M-LX, FL, and S-EZ analyzed and interpreted the data. M-LX and FL drafted the manuscript, which was critically revised for important intellectual content by M-LX, FL, and G-FL. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This retrospective study was approved by the ethics committee of the Hubei Cancer Hospital (No.: LLHBCH2021YN-001).
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Consent to publish
As this study was retrospective in nature, the requirement for obtaining informed consent for publication was waived.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Zeng, S., Li, F. et al. Utilizing grayscale ultrasound-based radiomics nomogram for preoperative identification of triple negative breast cancer. Radiol med 129, 29–37 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-023-01739-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-023-01739-x