Abstract
Purpose
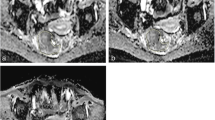
To evaluate the image quality qualitatively and quantitatively, as well as apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of modified reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) using spatially tailored two-dimensional radiofrequency pulses with tilted excitation plane (tilted r-DWI) based on single-shot echo planar imaging (SS-EPI) compared with full-size field-of-view DWI (f-DWI) using readout segmented (RS)-EPI in patients with rectal cancer.
Materials and methods
Twenty-two patients who underwent an MRI for further evaluation of rectal cancer were included in this retrospective study. All MR images were analyzed to compare image quality, lesion conspicuity, and artifacts between f-DWI with RS-EPI and tilted r-DWI with SS-EPI. Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), and ADC values were also compared. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test or paired t test was performed to compare the qualitative and quantitative assessments.
Results
All image quality scores, except aliasing artifacts, were significantly higher (p < 0.01 for all) in tilted r-DWI than f-DWI with RS-EPI. CNR in tilted r-DWI was significantly higher than in f-DWI with RS-EPI (p < 0.01), while SNR was not significantly different. Regarding the ADC values, no significant difference was observed between tilted r-DWI and f-DWI with RS-EPI (p = 0.27).
Conclusion
Tilted r-DWI provides a better image quality with fewer artifacts and higher rectal lesion conspicuity than f-DWI with RS-EPI, indicating the feasibility of this MR sequence in evaluating rectal cancer in clinical practice.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soyer P, Lagadec M, Sirol M, Dray X, Duchat F, Vignaud A, Fargeaudou Y, Place V, Gault V, Hamzi L, Pocard M, Boudiaf M (2010) Free-breathing diffusion-weighted single-shot echo-planar MR imaging using parallel imaging (GRAPPA 2) and high b value for the detection of primary rectal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Imaging 10(1):32–39. https://doi.org/10.1102/1470-7330.2010.0011
Kaur H, Choi H, You YN, Rauch GM, Jensen CT, Hou P, Chang GJ, Skibber JM, Ernst RD (2012) MR imaging for preoperative evaluation of primary rectal cancer: practical considerations. Radiographics 32(2):389–409. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.322115122
Curvo-Semedo L, Lambregts DM, Maas M, Beets GL, Caseiro-Alves F, Beets-Tan RG (2012) Diffusion-weighted MRI in rectal cancer: apparent diffusion coefficient as a potential noninvasive marker of tumor aggressiveness. J Magn Reson Imaging 35(6):1365–1371. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.23589
Jung SH, Heo SH, Kim JW, Jeong YY, Shin SS, Soung MG, Kim HR, Kang HK (2012) Predicting response to neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy in locally advanced rectal cancer: diffusion-weighted 3 Tesla MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 35(1):110–116. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.22749
Porter DA, Heidemann RM (2009) High resolution diffusion-weighted imaging using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging, parallel imaging and a two-dimensional navigator-based reacquisition. Magn Reson Med 62(2):468–475. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.22024
Xia CC, Liu X, Peng WL, Li L, Zhang JG, Meng WJ, Deng XB, Zuo PL, Li ZL (2016) Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging improves the image quality of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in rectal cancer: comparison with single-shot echo-planar diffusion-weighted sequences. Eur J Radiol 85(10):1818–1823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.08.008
Hosseiny M, Sung KH, Felker E, Suvannarerg V, Tubtawee T, Shafa A, Arora KR, Ching J, Gulati A, Azadikhah A, Zhong X, Sayre J, Lu D, Raman SS (2022) Read-out segmented echo planar imaging with two-dimensional navigator correction (RESOLVE): an alternative sequence to improve image quality on diffusion-weighted imaging of prostate. Br J Radiol 95(1136):20211165. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20211165
Tang C, Lin MB, Xu JL, Zhang LH, Zuo XM, Zhang ZS, Liu MX, Xu JM (2018) Are ADC values of readout-segmented echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging (RESOLVE) correlated with pathological prognostic factors in rectal adenocarcinoma? World J Surg Oncol 16(1):138. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1445-z
Xia CC, Pu J, Zhang JG, Peng WL, Li L, Zhao F, Zhang K, Li YM, Liu KL, Meng WJ, Deng XB, Zhou XY, Li ZL (2018) Readout-segmented echo-planar diffusion-weighted MR for the evaluation of aggressive characteristics of rectal cancer. Sci Rep 8(1):12554. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30488-5
Attenberger UI, Tavakoli A, Stocker D, Stieb S, Riesterer O, Turina M, Schoenberg SO, Pilz L, Reiner CS (2020) Reduced and standard field-of-view diffusion weighted imaging in patients with rectal cancer at 3 T-Comparison of image quality and apparent diffusion coefficient measurements. Eur J Radiol 131:109257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109257e
Hu L, Zhou DW, Fu CX, Benkert T, Jiang CY, Li RT, Wei LM, Zhao JG (2021) Advanced zoomed diffusion-weighted imaging vs. full-field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging in prostate cancer detection: a radiomic features study. Eur Radiol 31(3):1760–1769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07227-4
Jang S, Lee JM, Yoon JH, Bae JS (2021) Reduced field-of-view versus full field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging for the evaluation of complete response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. Abdominal Radiol (New York) 46(4):1468–1477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02763-5
Takeuchi M, Matsuzaki K, Harada M (2022) The feasibility of reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging in evaluating bladder invasion of uterine cervical cancer. Br J Radiol 95(1129):20210692. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20210692
Finsterbusch J (2012) Improving the performance of diffusion-weighted inner field-of-view echo-planar imaging based on 2D-selective radiofrequency excitations by tilting the excitation plane. J Magn Reson Imaging 35(4):984–992. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.23522
He YL, Hausmann D, Morelli JN, Attenberger UI, Schoenberg SO, Riffel P (2016) Renal zoomed EPI-DWI with spatially-selective radiofrequency excitation pulses in two dimensions. Eur J Radiol 85(10):1773–1777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.07.022
Hwang J, Hong SS, Kim HJ, Chang YW, Nam BD, Oh E, Lee E, Cha H (2018) Reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted MRI in patients with cervical cancer. Br J Radiol 91(1087):20170864. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20170864
Mannelli L, Monti S, Corrias G, Fung MM, Nyman C, Golia Pernicka JS, Do RKG (2019) Comparison of navigator triggering reduced field of view and large field of view diffusion-weighted imaging of the pancreas. J Comput Assist Tomogr 43(1):143–148. https://doi.org/10.1097/RCT.0000000000000778
Zhao L, Madore B, Panych LP (2005) Reduced field-of-view MRI with two-dimensional spatially-selective RF excitation and UNFOLD. Magn Reson Med 53(5):1118–1125. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.20458
Finsterbusch J (2010) Fast-spin-echo imaging of inner fields-of-view with 2D-selective RF excitations. J Magn Reson Imaging 31(6):1530–1537. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.22196
Hu L, Wei L, Wang S, Fu C, Benker T, Zhao J (2021) Better lesion conspicuity translates into improved prostate cancer detection: comparison of non-parallel-transmission-zoomed-DWI with conventional-DWI. Abdom Radiol (New York) 46(12):5659–5668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03268-5
Lee EJ, Hwang J, Chang YW, Hong SS, Oh E, Nam BD, Sung JK, Thomas B (2021) Modified reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate: comparison with reduced field-of-view imaging and single shot echo-planar imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 45(3):367–373. https://doi.org/10.1097/RCT.0000000000001156
Tanabe M, Higashi M, Benkert T, Imai H, Miyoshi K, Kameda F, Ariyoshi S, Ihara K, Ito K (2021) Reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the pancreas with tilted excitation plane: a preliminary study. J Magn Reson Imaging 54(3):715–720. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.27590
Kundel HL, Polansky M (2003) Measurement of observer agreement. Radiology 228(2):303–308. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2282011860
Singer L, Wilmes LJ, Saritas EU, Shankaranarayanan A, Proctor E, Wisner DJ, Chang B, Joe BN, Nishimura DG, Hylton NM (2012) High-resolution diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in patients with locally advanced breast cancer. Acad Radiol 19(5):526–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2011.11.003
Chen M, Feng C, Wang Q, Li J, Wu S, Hu D, Deng B, Li Z (2021) Comparison of reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and conventional DWI techniques in the assessment of Cervical carcinoma at 3.0 T: image quality and FIGO staging. Eur J Radiol 137:109557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.109557
Meng X, Hu H, Wang Y, Hu D, Li Z, Feng C (2021) Application of bi-planar reduced field-of-view DWI (rFOV DWI) in the assessment of muscle-invasiveness of bladder cancer. Eur J Radiol 136:109486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109486
Peng Y, Tang H, Hu X, Shen Y, Kamel I, Li Z, Hu D (2019) Rectal cancer invasiveness: whole-lesion diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) histogram analysis by comparison of reduced field-of-view and conventional DWI techniques. Sci Rep 9(1):18760. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-55059-0
Wu S, Zou X, Wang Q, Hu D, Li Z, Xu C (2020) Gallbladder carcinoma: an initial clinical experience of reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted MRI. Cancer Imag 20(1):50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40644-020-00326-x
Nougaret S, Reinhold C, Mikhael HW, Rouanet P, Bibeau F, Brown G (2013) The use of MR imaging in treatment planning for patients with rectal carcinoma: have you checked the “DISTANCE”? Radiology 268(2):330–344. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.13121361
Peng Y, Li Z, Tang H, Wang Y, Hu X, Shen Y, Hu D (2018) Comparison of reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and conventional DWI techniques in the assessment of rectal carcinoma at 3.0 T: image quality and histological T staging. J Magn Reson Imaging 47(4):967–975. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25814
Kim YJ, Kim SH, Kang BJ, Park CS, Kim HS, Son YH, Porter DA, Song BJ (2014) Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging in diffusion-weighted MR imaging in breast cancer: comparison with single-shot echo-planar imaging in image quality. Korean J Radiol 15(4):403–410. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.4.403
Peng Y, Tang H, Meng X, Shen Y, Hu D, Kamel I, Li Z (2020) Histological grades of rectal cancer: whole-volume histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient based on reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging. Quant Imaging Med Surg 10(1):243–256. https://doi.org/10.21037/qims.2019.11.17
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MT, MY, TY, TU and KI contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by AI, MT, KI, KH, MH and KI. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AI and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Two authors (Thomas Benkert and Hiroshi Imai) were employees of Siemens Healthcare, but the other authors, who are not Siemens Healthcare employees, had control of inclusion of any data and information. Atsuo Inoue, Masahiro Tanabe, Kenichiro Ihara, Keiko Hideura, Mayumi Higashi, Masatoshi Yamane, Takahiro Yamaguchi, Takaaki Ueda, and Katsuyoshi Ito declare they have no financial interests.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Institutional Review Board of Yamaguchi University Hospital (September 5, 2022/No 2022–094).”
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, A., Tanabe, M., Ihara, K. et al. Evaluation of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the rectal cancers: comparison between modified reduced field-of-view single-shot echo-planar imaging with tilted two-dimensional radiofrequency excitation pulses and conventional full field-of-view readout-segmented echo-planar imaging. Radiol med 128, 1192–1198 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-023-01699-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-023-01699-2