Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the technical success, efficacy, and safety of a newly designed partially covered bilateral self-expanding metallic stent (SEMS) in patients with malignant biliary obstruction.
Material and methods
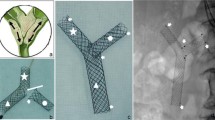
From May 2016 to November 2017, ten patients with malignant hilar biliary stenosis (bismuth type II–IV) underwent stent placement with the newly designed partially covered T/Y-configured SEMS. Technical success, drainage catheter removal, jaundice remission, early and late complications, stent patency, and overall survival were analyzed.
Results
The stent was successfully deployed in all patients. The total bilirubin level significantly decreased one month after stent placement (P < 0.05). Drainage catheter removal rate was 90%. Two cases (20%) experienced early complications (bile duct hemorrhage and cholangitis) and two cases (20%) experienced late complications (hepatic abscess and cholangitis). During the follow-up (mean 276 days; range 57–503 days) stent occlusion occurred in three patients (30%), and two patents died of hepatic failure. The median stent patency and overall survival were 275 days (95% CI 223.8–326.3 days) and 428.9 days (95% CI 347.9–509.8 days), respectively.
Conclusion
The newly designed partially covered T/Y-configured SEMS is technically feasible and clinically effective for biliary trifurcation obstruction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asadi H, Hollingsworth R, Pennycooke K et al (2016) A review of percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage at a tertiary referral centre. Clin Radiol 71:1312
Yang MJ, Kim JH, Hwang JC et al (2018) Prospective multicenter study of the challenges inherent in using large cell-type stents for bilateral stent-in-stent placement in patients with inoperable malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Gut Liver 12:722–727
Jeon CH, Yoon CJ, Seong NJ, Lee H, Hwang JH, Kim J (2018) Percutaneous stent placement for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: a comparison between criss-cross and T-configuration techniques. Clin Radiol 73:412
Jiao D, Huang K, Zhu M et al (2017) Placement of a newly designed Y-configured bilateral self-expanding metallic stent for hilar biliary obstruction: a pilot study. Dig Dis Sci 62:253–263
Sacks D, McClenny TE, Cardella JF, Lewis CA (2003) Society of interventional radiology clinical practice guidelines. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:S199–202
Sugimoto M, Takagi T, Suzuki R et al (2017) Predictive factors for the failure of endoscopic stent-in-stent self-expandable metallic stent placement to treat malignant hilar biliary obstruction. World J Gastroenterol 23:6273–6280
Hwang JC, Kim JH, Lim SG, Kim SS, Yoo BM, Cho SW (2011) Y-shaped endoscopic bilateral metal stent placement for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: prospective long-term study. Scand J Gastroenterol 46:326–332
Kim DU, Kang DH, Kim GH et al (2013) Bilateral biliary drainage for malignant hilar obstruction using the ‘stent-in-stent’ method with a Y-stent: efficacy and complications. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25:99–106
Lee JM, Lee SH, Chung KH et al (2015) Small cell- versus large cell-sized metal stent in endoscopic bilateral stent-in-stent placement for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Dig Endosc 27:692–699
Naitoh I, Nakazawa T, Ban T et al (2015) 8-mm versus 10-mm diameter self-expandable metallic stent in bilateral endoscopic stent-in-stent deployment for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 22:396–401
Heo JY, Lee HS, Son JH, Lee SH, Bang S (2018) Clinical outcomes of bilateral stent-in-stent placement using self-expandable metallic stent for high-grade malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Yonsei Med J 59:827–833
Gwon DI, Ko GY, Yoon HK et al (2010) Prospective evaluation of a newly designed T-configured stent graft system for palliative treatment of advanced hilar malignant biliary obstructions. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21:1410–1418
Gwon DI, Ko GY, Yoon HK et al (2012) Safety and efficacy of percutaneous Y-configured covered stent placement for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: a prospective, pilot study. J Vasc Interv Radiol 23:528–534
Kang BC, Lee SW, Chung HH (2013) A newly designed Y-shaped covered stent in the palliative treatment of hepatic hilar malignant obstruction: case report. Korean J Radiol 14:97–101
Yoo SS, Jeong S, Lee DH (2013) Endoscopic bilateral stenting of malignant hilar bile duct obstruction using novel partially covered self-expandable metal stents. Endoscopy 45(Suppl 2):E328–E329
Yun JH, Jung GS, Park JG et al (2016) Malignant hilar biliary obstruction: treatment by means of placement of a newly designed Y-shaped branched covered stent. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 39:582–590
Inoue T, Okumura F, Naitoh I et al (2016) Feasibility of the placement of a novel 6-mm diameter threaded fully covered self-expandable metal stent for malignant hilar biliary obstructions (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 84:352–357
Kitamura K, Yamamiya A, Ishii Y, Mitsui Y, Nomoto T, Yoshida H (2017) Side-by-side partially covered self-expandable metal stent placement for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Endosc Int Open 5:E1211–E1217
Zhu YQ, Edmonds L, Wei LM et al (2017) Technical feasibility and tissue reaction after silicone-covered biodegradable magnesium stent insertion in the oesophagus: a primary study in vitro and in vivo. Eur Radiol 27:2546–2553
Kapoor BS, Mauri G, Lorenz JM (2018) Management of biliary strictures: state-of-the-art review. Radiology 289(3):590–603
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Key Scientific Research Projects of Higher Education Institutions in Henan Province (20A320024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This prospective study was approved by the institutional review board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional and/or National Research Committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, D., Wang, J., Han, B. et al. Placement of a newly designed partially covered T- or Y-configured self-expanding metallic stent for hilar biliary obstruction: technical note. Radiol med 125, 999–1007 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-020-01196-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-020-01196-w