Abstract
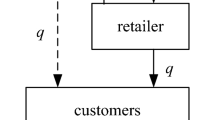
In this paper, we study make-or-buy decisions with the consideration of retail-level competition, in which a supplier provides substitutable products to two retailers. One incumbent retailer is capable of producing the product in-house and makes the make-or-buy decision, while the rival retailer can only outsource from the supplier. Intuitively, the incumbent will not outsource if the wholesale price is higher than its production cost. However, we illustrate this may not be true when the supplier also supplies the retail rival. In this case, the incumbent may accept a high wholesale price to limit the suppliers incentive to serve the retail rival on particularly favorable terms. Moreover, under certain circumstances, the supplier may charge a wholesale price lower than its production cost to attract orders from the incumbent, which can generate for the supplier and the incumbent a higher total profit than the situation in which the incumbent makes the product in-house.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson E, Parker, G (2002). The effect of learning on the make/buy decision. Production and Operations Management 11(3): 313–339.
Arruñada B, Vázque XH (2006). Whenyour contract manufacturer becomes your competitor. Harvard Business Review 84(9): 135.
Arya A, Mittendorf B, Sappington, D (2008). The makeor-buy decision in the presence of a rival: Strategic outsourcing to a common supplier. Management Science 54(10): 1747–1758.
Bardhan I, Mithas S, Lin, S (2007). Performance impacts of strategy, information technology applications, and business process outsourcing in U.S. manufacturing plants. Production and Operations Management 16(6): 747–762.
Buehler S, Haucap, J (2006). Strategic outsourcing revisited. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization 61(3): 325–338.
Cachon G, Harker, PT (2002). Competition and outsourcing with scale economies. Management Science 48(10): 1314–1333.
Casale, FJ (2000). Outsourcing index 2000: Strategic insights into U.S. outsourcing. The Outsourcing Institute, New York.
Chen J, Guo, Z (2014). Strategic sourcing in the presence of uncertain supply and retail competition. Production and Operations Management 23(10): 1748–1760.
Chen, Y (2010). Strategic outsourcing between rivals. Annals of Economics and Finance 11(2): 301–311.
Chen Y, Ishikaw J, Yu, Z (2004). Trade liberalization and strategic outsourcing. Journal of International Economics 63: 419–436.
Feng Q, Lu, L (2012). The strategic perils of low cost outsourcing. Management Science 58(6): 1196–1210.
Gilbert, SM, Xia Y, Yu, G (2006). Strategic outsourcing for competing oems that face cost reduction opportunities. IIE Transactions 38(11): 903–915.
Kaya M, Özer Ö (2009). Quality risk in outsourcing: Non contractible product quality and private quality cost formation. Naval Research logistics 56(7): 669–685.
Kim, B (2003). Dynamic outsourcing to contract manufacturers with different capabilities of reducing the supply cost. International Journal of Production Economics 86(1): 63–80.
Lim, WS, Tan, SJ (2010). Outsourcing suppliers as downstream competitors: Biting the hand that feeds. European Journal of Operational Research 203(2): 360–369.
Lu Q, Meng F, Goh, M (2014). Choice of supply chain governance: Self-managing or outsourcing? International Journal of Production Economics 154: 32–38.
Prahalad, CK, Hamel, G (1990). The core competence of the corporation. Harvard Business Review 68(3): 79–91.
Pun H, Heese HS (2014). Outsourcing to suppliers with unknown capabilities. European Journal of Operational Research 234(1): 108–118.
Salop, SC, Scheffman DT (1987). Cost-raising strategies. The Journal of Industrial Economics 36(1): 19–34.
Shy O, Stenbacka, R (2003). Strategic outsourcing. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization 50(2): 203–224.
Taylor, TA, Plambeck, EL (2007). Supply chain relationships and contracts: The impact of repeated interaction on capacity investment and procurement. Management Science 53(10): 1577–1593.
Wu F, Li H, Chu L, Sculli, D (2005). An outsourcing decision model for sustaining long-termperformance. Naval Research logistics 43(12): 2513–2535.
Xiao T, Xia Y, Zhang, GP (2014). Strategic outsourcing decisions for manufacturers competing on product quality. IIE Transactions 46(4): 313–329.
Zhang B, Du, S (2010). Multi-product newsboy problem with limited capacity and outsourcing. European Journal of Operational Research 202(1): 107–113.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank referees for their help to improve the quality of the paper. This paper has been supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China 71831007, 71571079, 71571160 and Social Science Foundation in Zhejiang Province 13ZJQN041YB, and by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, No.2019kfyXMBZ046
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jianbin Li is a professor in the School of Management at the Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China. He received his Ph.D. in applied mathematics from the Wuhan University in 2007. His research focuses on e-commerce, health care administration, logistics and supply chain management. He has published in Production and Operations Management, Decision Sciences, European Journal of Operational Research, and many others. He is an Editorial Board Member of Journal of Systems Science and Mathematical Sciences, etc.
Yingying Wang is a master candidate in the School of Management at the Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China. Her research interests focuses on logistics and supply chain management.
Xiaomeng Luo is an associate professor in the School of Business Administration at the Southwestern University of Finance and Economics, China. She received her Ph.D. in marketing from the City University of Hong Kong in 2016. Her research focuses on supply chain management, e-commerce, operations management and marketing interface.
Weihua Zhou is a professor in School of Management at Zhejiang University, China. He received his Ph.D. in Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management from The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology in 2007. His current research interests include logistics and supply chain management, supply chain finance. He has authored or co-authored about 20 papers in several academic journals, including Operations Research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Wang, Y., Luo, X. et al. Make or Buy in the Presence of Strategic Competition on Substitutable Products. J. Syst. Sci. Syst. Eng. 28, 657–673 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11518-019-5415-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11518-019-5415-y