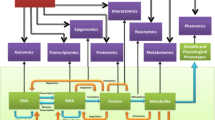
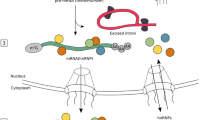
Abstract
Background
With the given diversity and abundance of several targets of miRNAs, they functionally appear to interact with several elements of the multiple cellular networks to maintain physiologic homeostasis. They can function as tumor suppressors or oncogenes, whose under or overexpression has both diagnostic and prognostic significance in various cancers while being implicated as prospective regulators of age-related disorders (ARD) as well. Establishing a concatenate between ARD and cancers by looking into the insights of the shared miRNAs may have a practical relevance.
Methods
In the present work, we performed network analysis of miRNA-disease association and miRNA-target gene interaction to prioritize miRNAs that play significant roles in the manifestation of cancer as well as ARD. Also, we developed a repository that stores miRNAs common to both ARD and cancers along with their target genes.
Results
We have comprehensively curated all miRNAs that we found to be shared in both the diseases in the human genome and established a database, miRACA (Database for microRNAs Associated with Cancers and ARD) that currently houses information of 1648 miRNAs that are significantly associated with 38 variants supported with pertinent data. It has been made available online at http://genomeinformatics.dtu.ac.in/miraca/ for easy retrieval and utilization of data by the scientific community.
Conclusion
To the best of our knowledge, our database is the first attempt at compilation of such data. We believe this work may serve as a significant resource and facilitate the analysis of miRNA regulatory mechanisms shared between cancers and ARD to apprehend disease etiology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal V, Bell G W, Nam J W, Bartel D P (2015). Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife, 4: e05005
Bartel D P (2004). MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell, 116(2): 281–297
Chang-Hao Tsao S, Behren A, Cebon J, Christophi C (2015). The role of circulating microRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 20(1): 78–104
Dalmay T, Edwards D R (2006). MicroRNAs and the hallmarks of cancer. Oncogene, 25(46): 6170–6175
Dellago H, Preschitz-Kammerhofer B, Terlecki-Zaniewicz L, Schreiner C, Fortschegger K, Chang M W, Hackl M, Monteforte R, Kühnel H, Schosserer M, Gruber F, Tschachler E, Scheideler M, Grillari-Voglauer R, Grillari J, Wieser M (2013). High levels of oncomiR-21 contribute to the senescence-induced growth arrest in normal human cells and its knock-down increases the replicative lifespan. Aging Cell, 12(3): 446–458
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack F J (2006). Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 6(4): 259–269
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya S N, Sonenberg N (2008). Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet, 9(2): 102–114
Gan J, Qu Y, Li J, Zhao F, Mu D (2015). An evaluation of the links between microRNA, autophagy, and epilepsy. Rev Neurosci, 26(2): 225–237
Gramantieri L, Fornari F, Callegari E, Sabbioni S, Lanza G, Croce C M, Bolondi L, Negrini M (2008). MicroRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med, 12(6a 6A): 2189–2204
Griffiths-Jones S (2006). miRBase: the microRNA sequence database. Methods Mol Biol, 342: 129–138
Guo H, Ingolia N T, Weissman J S, Bartel D P (2010). Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature, 466(7308): 835–840
Hanahan D, Weinberg R A (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. Cell, 100 (1): 57–70
He H, Baldwin G S (2008). Rho GTPases and p21-activated kinase in the regulation of proliferation and apoptosis by gastrins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 40(10): 2018–2022
He H, Yim M, Liu K H, Cody S C, Shulkes A, Baldwin G S (2008). Involvement of G proteins of the Rho family in the regulation of Bcl-2-like protein expression and caspase 3 activation by Gastrins. Cell Signal, 20(1): 83–93
He X, Zhang J (2006). Why do hubs tend to be essential in protein networks? PLoS Genet, 2(6): e88
Huang W, Sherman B T, Lempicki R A (2009a). Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res, 37(1): 1–13
Huang W, Sherman B T, Lempicki R A (2009b). Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc, 4(1): 44–57
Hulsen T, de Vlieg J, Alkema W (2008). BioVenn-a web application for the comparison and visualization of biological lists using areaproportional Venn diagrams. BMC Genomics, 9(1): 488
Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E (2011). Gene silencing by microRNAs: contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet, 12(2): 99–110
Hwang H W, Mendell J T (2006). MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer, 94(6): 776–780
Iorio M V, Ferracin M, Liu C G, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M, Ménard S, Palazzo J P, Rosenberg A, Musiani P, Volinia S, Nenci I, Calin G A, Querzoli P, Negrini M, Croce C M (2005). MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res, 65(16): 7065–7070
Jung H J, Suh Y (2012). MicroRNA in Aging: From Discovery to Biology. Curr Genomics, 13(7): 548–557
Kang J, Pervaiz S (2013). Crosstalk between Bcl-2 family and Ras family small GTPases: potential cell fate regulation? Front Oncol, 2: 206
Kayani Mu, Kayani M A, Malik F A, Faryal R (2011). Role of miRNAs in breast cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 12(12): 3175–3180
Landskron G, De la Fuente M, Thuwajit P, Thuwajit C, Hermoso M A (2014). Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. J Immunol Res, 2014: 149185
Lee R C, Feinbaum R L, Ambros V (1993). The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell, 75(5): 843–854
Lewis B P, Burge C B, Bartel D P (2005). Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell, 120(1): 15–20
Li Y, Qiu C, Tu J, Geng B, Yang J, Jiang T, Cui Q (2014). HMDD v2.0: a database for experimentally supported human microRNA and disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res, 42(Database issue): D1070–D1074
López-Otín C, Blasco M A, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G (2013). The hallmarks of aging. Cell, 153(6): 1194–1217
Lu J, Getz G, Miska E A, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert B L, Mak R H, Ferrando A A, Downing J R, Jacks T, Horvitz H R, Golub T R (2005). MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature, 435(7043): 834–838
Mi H, Lazareva-Ulitsky B, Loo R, Kejariwal A, Vandergriff J, Rabkin S, Guo N, Muruganujan A, Doremieux O, Campbell M J, Kitano H (2005). The PANTHER database of protein families, subfamilies, functions and pathways. Nucleic Acids Res, 33(suppl_1):D284–8.
Mi H, Muruganujan A, Casagrande J T, Thomas P D (2013). Large-scale gene function analysis with the PANTHER classification system. Nat Protoc, 8(8): 1551–1566
Mulrane L, McGee S F, Gallagher W M, O’Connor D P (2013). miRNA dysregulation in breast cancer. Cancer Res, 73(22): 6554–6562
Palmero E I, de Campos S G, Campos M, de Souza N C, Guerreiro I D, Carvalho A L, Marques M M (2011). Mechanisms and role of microRNA deregulation in cancer onset and progression. Genet Mol Biol, 34(3): 363–370
Ponnappan S, Ponnappan U (2011). Aging and immune function: molecular mechanisms to interventions. Antioxid Redox Signal, 14 (8): 1551–1585
Ro S, Park C, Young D, Sanders K M, Yan W (2007). Tissue-dependent paired expression of miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res, 35(17): 5944–5953
Rozengurt E, Walsh J H (2001). Gastrin, CCK, signaling, and cancer. Annu Rev Physiol, 63(1): 49–76
Serpico D, Molino L, Di Cosimo S (2014). microRNAs in breast cancer development and treatment. Cancer Treat Rev, 40(5): 595–604
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga N S,Wang J T, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003). Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res, 13(11): 2498–2504
Srivastava I, Gahlot L K, Khurana P, Hasija Y (2016). dbAARD & AGP: A computational pipeline for the prediction of genes associated with age related disorders. J Biomed Inform, 60: 153–161
Takahashi R U, Miyazaki H, Ochiya T (2015). The roles of microRNAs in breast cancer. Cancers (Basel), 7(2): 598–616
Volinia S, Calin G A, Liu C G, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, Prueitt R L, Yanaihara N, Lanza G, Scarpa A, Vecchione A, Negrini M, Harris C C, Croce C M (2006). A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103(7): 2257–2261
Wang L, Chadwick W, Park S S, Zhou Y, Silver N, Martin B, Maudsley S (2010). Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor system: modulatory role in aging and neurodegeneration. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets, 9(5): 651–660
Wu L, Fan J, Belasco J G (2006). MicroRNAs direct rapid deadenylation of mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103(11): 4034–4039
Yip K W, Reed J C (2008). Bcl-2 family proteins and cancer. Oncogene, 27(50): 6398–6406
Zhang L, Huang J, Yang N, Greshock J, Megraw M S, Giannakakis A, Liang S, Naylor T L, Barchetti A, Ward M R, Yao G, Medina A, O’brien-Jenkins A, Katsaros D, Hatzigeorgiou A, Gimotty P A, Weber B L, Coukos G (2006). microRNAs exhibit high frequency genomic alterations in human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103 (24): 9136–9141
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, R., Gahlot, L.K. & Hasija, Y. miRACA: A database for miRNAs associated with cancers and age related disorders (ARD). Front. Biol. 13, 36–50 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-018-1481-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-018-1481-7