Abstract
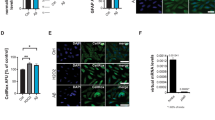
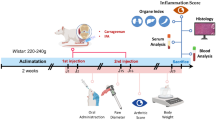
The etiology of neuropathic pain is mostly caused by mechanical deformation and neuroinflammation, of which neuroinflammation is the main cause of chronic neuropathic pain. Activation of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway mediates elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines, and we clearly demonstrated by in vivo and in vitro Western blot experiments that β-sitosterol significantly inhibited the elevated Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) expression levels and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activation associated with inflammatory responses. In cellular experiments, we clearly saw that both β-sitosterol and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway inhibitors could inhibit M1 proinflammatory phenotype expression and promote M2 anti-inflammatory phenotype expression in GMI-R1 microglia by flow cytometry and immunofluorescence assays. Therefore, we suggest that β-sitosterol can affect microglial polarization by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway thereby reducing neuroinflammation and thus alleviating neuropathic pain.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Code Availability
All software used in the course of this study is officially licensed software.
Abbreviations
- TLR4:
-
Toll-like receptor 4
- MyD88:
-
Myeloid differentiation factor 88 l
- IKK:
-
IκB kinase
- IκB:
-
Inhibitor of NF-κB
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-Kappa B
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1 beta
- IL-4:
-
Interleukin-4
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IL-8:
-
Interleukin-8
- IL-10:
-
Interleukin-10
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon-γ
- Cox-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- IBA-1:
-
Ionized calcium binding adapter molecule 1
- iNOS:
-
Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase
- Arg-1:
-
Arginase 1
- CCI:
-
Chronic constriction injury
- SD:
-
Sprague-Dawley
References
Aravalli RN, Peterson PK et al (2007) Toll-like receptors in defense and damage of the central nervous system. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 2:297–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-007-9071-5
Bradford PG, Awad AB (2010) Modulation of signal transduction in cancer cells by phytosterols. Biofactors 36:241–247. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.97
Chang S, Li X et al (2022) Kaempferol exerts a neuroprotective effect to reduce neuropathic pain through TLR4/NF-ĸB signaling pathway. Phytother Res 36:1678–1691. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7396
Cheng S, Zhang Y et al (2021) LncRNA HOTAIR participates in microglia activation and inflammatory factor release by regulating the ubiquitination of MYD88 in traumatic brain injury. J Mol Neurosci 71:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01623-7
Donnelly CR, Andriessen AS et al (2020) Central nervous system targets: glial cell mechanisms in chronic pain. Neurotherapeutics 17:846–860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-020-00905-7
Gogoleva VS, Drutskaya MS et al (2019) The role of microglia in the homeostasis of the central nervous system and neuroinflammation. Mol Biol 53:790–798. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0026898419050057
Hu Y, Liu Q et al (2019) MicroRNA-362–3p attenuates motor deficit following spinal cord injury via targeting paired box gene 2. J Integr Neurosci 18:57–64. https://doi.org/10.31083/j.jin.2019.01.12
Jayaraman S, Devarajan N et al (2021) β-sitosterol circumvents obesity induced inflammation and insulin resistance by down-regulating IKKβ/NF-κB and JNK signaling pathway in adipocytes of type 2 diabetic rats. Molecules 26:2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26072101
Jin X, Liu MY et al (2019) Baicalin mitigates cognitive impairment and protects neurons from microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via suppressing NLRP 3 inflammasomes and TLR 4/NF-κB signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther 25:575–590. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13086
Jin J, Guo J et al (2020) M2-like microglia polarization attenuates neuropathic pain associated with Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 76:1255–1265. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-200099
Jones PJH, Shamloo M et al (2018) Progress and perspectives in plant sterol and plant stanol research. Nutr Rev 76:725–746. https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuy032
Kawai T, Akira S (2007) Signaling to NF-κB by toll-like receptors. Trends Mol Med 13:460–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2007.09.002
Kim KA, Lee IA et al (2014) β-Sitosterol attenuates high-fat diet-induced intestinal inflammation in mice by inhibiting the binding of lipopolysaccharide to toll-like receptor 4 in the NF-κB pathway. Mol Nutr Food Res 58:963–972. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201300433
Lan X, Han X et al (2017) Modulators of microglial activation and polarization after intracerebral haemorrhage. Nat Rev Neurol 13:420–433. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2017.69
Lehnardt S, Lachance C et al (2002) The toll-like receptor TLR4 is necessary for lipopolysaccharide-induced oligodendrocyte injury in the CNS. J Neurosci 22:2478–2486. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.22-07-02478.2002
Li C, Chen T et al (2018) Schisantherin A attenuates neuroinflammation in activated microglia: role of Nrf2 activation through ERK phosphorylation. Cell Physiol Biochem 47:1769–1784. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491059
Li X, Wu G et al (2020) Oleanolic acid administration alleviates neuropathic pain after a peripheral nerve injury by regulating microglia polarization-mediated neuroinflammation. RSC Adv 10:12920–12928. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA10388K
Liu R, Hao D et al (2019) β-Sitosterol modulates macrophage polarization and attenuates rheumatoid inflammation in mice. Pharm Biol 57:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2019.1577461
Lu Y-C, Yeh W-C et al (2008) LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 42:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2008.01.006
Moreau RA, Whitaker BD et al (2002) Phytosterols, phytostanols, and their conjugates in foods: structural diversity, quantitative analysis, and health-promoting uses. Prog Lipid Res 41:457–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0163-7827(02)00006-1
Nayak D, Roth TL et al (2014) Microglia development and function. Ann Rev Immunol 32:367–402. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-032713-120240
Nazeam JA, El-Hefnawy HM et al (2018) Chemical profile and antihyperlipidemic effect of Portulaca oleracea L. seeds in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Nat Prod Res 32:1484–1488. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1353507
Orihuela R, McPherson CA et al (2016) Microglial M1/M2 polarization and metabolic states. Br J Pharmacol 173:649–665. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13139
Ostlund RE Jr (2004) Phytosterols and cholesterol metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol 15:37–41. https://doi.org/10.1097/00041433-200402000-00008
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Verri WA et al (2017) Nociceptor sensory neuron–immune interactions in pain and inflammation. Trends Immunol 38:5–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2016.10.001
Qie S, Ran Y et al (2020) Candesartan modulates microglia activation and polarization via NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 34:2058738420974900. https://doi.org/10.1177/2058738420974900
Ransohoff RM (2016) A polarizing question: do M1 and M2 microglia exist? Nat Neurosci 19:987–991. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4338
Reinicke M, Leyh J et al (2021) Plant sterol-poor diet is associated with pro-inflammatory lipid mediators in the murine brain. Int J Mol Sci 22:13207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413207
Ren K, Dubner R (2010) Interactions between the immune and nervous systems in pain. Nat Med 16:1267–1276. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2234
Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Sato K (2021) Central nervous system developmental regulation of microglia via cytokines and chemokines. Yakugaku Zasshi 141:359–368. https://doi.org/10.1248/yakushi.20-00198-4
Sillerud LO, Yang Y et al (2020) Longitudinal monitoring of microglial/macrophage activation in ischemic rat brain using Iba-1-specific nanoparticle-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 40:S117–S133. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678x20953913
Skaper SD, Facci L et al (2017) Neuroinflammation, mast cells, and glia: dangerous liaisons. Neuroscientist 23:478–498. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858416687249
Sommer C, Leinders M et al (2018) Inflammation in the pathophysiology of neuropathic pain. Pain 159:595–602. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001122
Stemkowski PL, Smith PA (2012) Sensory neurons, ion channels, inflammation and the onset of neuropathic pain. Can J Neurol Sci 39:416–435. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0317167100013937
Subhramanyam CS, Wang C et al (2019) Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol 94:112–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2019.05.004
Sun Y, Gao L et al (2020) β-sitosterol alleviates inflammatory response via inhibiting the activation of ERK/p38 and NF-κB pathways in LPS-exposed BV2 cells. BioMed Res Int 2020:7532306. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7532306
Tang J, Xu L et al (2021) Effect of gut microbiota on LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating the TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 91:107272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107272
Ton B-HT, Chen Q et al (2013) Activation profile of dorsal root ganglia Iba-1 (+) macrophages varies with the type of lesion in rats. Acta Histochem 115:840–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acthis.2013.04.007
Treede R-D, Jensen TS et al (2008) Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 70:1630–1635. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000282763.29778.59
Ueno M, Fujita Y et al (2013) Layer V cortical neurons require microglial support for survival during postnatal development. Nat Neurosci 16:543–551. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3358
Valerio M, Awad AB (2011) β-Sitosterol down-regulates some pro-inflammatory signal transduction pathways by increasing the activity of tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 in J774A.1 murine macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol 11:1012–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2011.02.018
Vanmierlo T, Bogie JFJ et al (2015) Plant sterols: friend or foe in CNS disorders? Prog Lipid Res 58:26–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2015.01.003
Wang XL, Chen F et al (2021) Oxymatrine inhibits neuroinflammation byRegulating M1/M2 polarization in N9 microglia through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 100:108139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108139
Winkler JK, Warner K (2008) The effect of phytosterol concentration on oxidative stability and thermal polymerization of heated oils. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 110:455–464. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.200700265
Wu L, Du L et al (2021) Silencing TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway alleviated inflammation of corneal epithelial cells infected by ISE. Inflammation 44:633–644. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01363-1
Wu C-C, Chang C-Y et al (2022) Preventive intrathecal injection of bupivacaine alleviated microglia activation and neuropathic pain in a rat model of chronic constriction injury. Int J Mol Sci 23:7197. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23137197
Xu X, Piao H-N et al (2020) Arctigenin protects against depression by inhibiting microglial activation and neuroinflammation via HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB and TNF-α/TNFR1/NF-κB pathways. Br J Pharmacol 177:5224–5245. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.15261
Yang W-C, Li T-t et al (2022) Molecular hydrogen mediates neurorestorative effects after stroke in diabetic rats: the TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory pathway. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 18:90–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-022-10051-w
Yoon C, Wook YY et al (1994) Behavioral signs of ongoing pain and cold allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain 59:369–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3959(94)90023-x
Zhang J, Zheng Y et al (2019) Curcumin inhibits LPS-induced neuroinflammation by promoting microglial M2 polarization via TREM2/ TLR4/ NF-κB pathways in BV2 cells. Mol Immunol 116:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2019.09.020
Zhang D, Sun J et al (2020) Therapeutic effect of Tetrapanax papyriferus and hederagenin on chronic neuropathic pain of chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve rats based on KEGG pathway prediction and experimental verification. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 2020:2545806. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2545806
Zhang Y, Liu W et al (2021a) Metformin corrects glucose metabolism reprogramming and NLRP3 inflammasome-induced pyroptosis via inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB/PFKFB3 Signaling in trophoblasts: implication for a potential therapy of preeclampsia. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:1806344. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1806344
Zhang D, Sun J et al (2021b) Protective effect of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid against H(2)O(2)-induced injury in Schwann cells based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. Exp Ther Med 22:1241. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2021.10676
Zhao J, Bi W et al (2019) Neuroinflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide causes cognitive impairment in mice. Sci Rep 9:5790. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42286-8
Zusso M, Lunardi V et al (2019) Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin attenuate microglia inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-kB pathway. J Neuroinflammation 16:148. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1538-9
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81874404; grant no. 82274294), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant no. 2023TQ0135), Technology Innovation Team project (No. S2021TDZ085) of Guangdong Provincial Drug Administration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yachun Zheng, Di Zhang and Guoping Zhao contributed substantially to the experimental design, data analysis, experimental procedures and wrote manuscript text. Shiquan Chang and Zifeng Zhuang assisted with the English writing. Si Waimei, Xin Li, Zenni Chen, Bei Jing reviewed the manuscript. Our special thanks to Yuyue Li for his support in image processing. Guoping Zhao and Di Zhang is the corresponding author. All data were generated in house, and no paper mill was used. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work and ensure its integrity and accuracy.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Animal experiments were approved by the Jinan University Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments. Animal ethics application No.20220314-12.
Consent for Publication
All authors agree to publish the paper.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Zhao, J., Chang, S. et al. β-Sitosterol Alleviates Neuropathic Pain by Affect Microglia Polarization through Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 18, 690–703 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-023-10091-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-023-10091-w