Abstract
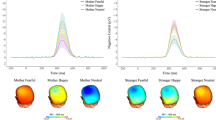
Postpartum substance use can have lasting impacts on caregiving and child development. Prior work examining maternal substance use and neural responses to infant cues has employed unknown infant face and cry stimuli, categorizing mothers as either substance-using or not, potentially overlooking the complexity and dynamic nature of current substance use. Here, 106 postpartum women were presented with own and unknown infant cues while electroencephalography (EEG) was recorded. Current substance use was assessed through an inclusive continuous approach. The central finding was that higher levels of current substance use were associated with longer delays in the N170 response to infant faces regardless of familiarity, replicating previous work using categorical substance use assessments (i.e., present or absent). Findings highlight the feasibility of continuous measures of substance use and suggest that salience of own infant cues may not be sufficient to override substance use effects on maternal processing of infant cues.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arce Rentería, M., Byrd, D., Coulehan, K., Miranda, C., Fuentes, A., Rosario, A. K., Morris, E. P., & Rivera Mindt, M. (2020). Neurocognitive intra-individual variability within HIV+ adults with and without current substance use. Neuropsychology, 34(3), 321–330. https://doi.org/10.1037/neu0000612
Bentin, S., Allison, T., Puce, A., Perez, E., & McCarthy, G. (1996). Electrophysiological studies of face perception in humans. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 8(6), 551–565. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.1996.8.6.551
Bornstein, M. H., Arterberry, M. E., & Mash, C. (2013). Differentiated brain activity in response to faces of “own” versus “unfamiliar” babies in primipara mothers: An electrophysiological study. Developmental Neuropsychology, 38(6), 365–385. https://doi.org/10.1080/87565641.2013.804923
Bunderson, M., Diaz, D., Maupin, A., Landi, N., Potenza, M. N., Mayes, L. C., & Rutherford, H. J. V. (2020). Prior reproductive experience modulates neural responses to infant faces across the postpartum period. Social Neuroscience, 15(6), 650–654. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470919.2020.1847729
Cacciola, J. S., Alterman, A. I., McLellan, A. T., Lin, Y.-T., & Lynch, K. G. (2007). Initial evidence for the reliability and validity of a “Lite” version of the Addiction Severity Index. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 87(2), 297–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2006.09.002
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Lawrencee Erlbaum Associates.
Cole, P. M., Barrett, K. C., & Zahn-Waxler, C. (1992). Emotion displays in two-year-olds during mishaps. Child Development, 63(2), 314–324. https://doi.org/10.2307/1131481
Doi, H., & Shinohara, K. (2012). Event-related potentials elicited in mothers by their own and unfamiliar infants’ faces with crying and smiling expression. Neuropsychologia, 50(7), 1297–1307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.02.013
Dunst, C. J. (2008). Caregiver sensitivity, contingent social responsiveness, and secure infant attachment. Journal of Early and Intensive Behavior Intervention, 5(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0100409
Eimer, M. (2000). The face-specific N170 component reflects late stages in the structural encoding of faces. NeuroReport, 11(10), 2319–2324.
Ekman, P., & Friesen, W. V. (1975). Unmasking the face: A guide to recognizing emotions from facial clues (pp. xii, 212). Prentice-Hall.
Ferree, T. C., Luu, P., Russell, G. S., & Tucker, D. M. (2001). Scalp electrode impedance, infection risk, and EEG data quality. Clinical Neurophysiology, 112(3), 536–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1388-2457(00)00533-2
Forray, A., & Foster, D. (2015). Substance use in the perinatal period. Current Psychiatry Reports, 17(11), 91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-015-0626-5
Fukushima, S., Kuga, H., Oribe, N., Mutou, T., Yuzuriha, T., Ozawa, H., & Ueno, T. (2020). Behavioural cue reactivity to alcohol-related and non-alcohol-related stimuli among individuals with alcohol use disorder: An fMRI study with a visual task. PLoS ONE, 15(7), e0229187. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0229187
Gajewski, P. D., Schlegel, K., & Stoerig, P. (2008). Effects of human race and face inversion on the N170. Journal of Psychophysiology, 22(4), 157–165. https://doi.org/10.1027/0269-8803.22.4.157
Grasso, D. J., Moser, J. S., Dozier, M., & Simons, R. (2009). ERP correlates of attention allocation in mothers processing faces of their children. Biological Psychology, 81(2), 95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2009.03.001
Gratton, G., Coles, M. G., & Donchin, E. (1983). A new method for off-line removal of ocular artifact. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 55(4), 468–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(83)90135-9
Gray, H. M., Ambady, N., Lowenthal, W. T., & Deldin, P. (2004). P300 as an index of attention to self-relevant stimuli. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 40(2), 216–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1031(03)00092-1
Hawk, B. N., McCall, R. B., Groark, C. J., Muhamedrahimov, R. J., Palmov, O. I., & Nikiforova, N. V. (2018). Caregiver sensitivity and consistency and children’s prior family experience as contexts for early development within institutions. Infant Mental Health Journal, 39(4), 432–448. https://doi.org/10.1002/imhj.21721
Holbrook, B. D., & Rayburn, W. F. (2014). Teratogenic risks from exposure to illicit drugs. Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinics of North America, 41(2), 229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ogc.2014.02.008
Kang, E., Keifer, C. M., Levy, E. J., Foss-Feig, J. H., McPartland, J. C., & Lerner, M. D. (2018). Atypicality of the N170 event-related potential in autism spectrum disorder: A meta-analysis. Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, 3(8), 657–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpsc.2017.11.003
Kim, S., Iyengar, U., Mayes, L. C., Potenza, M. N., Rutherford, H. J. V., & Strathearn, L. (2017). Mothers with substance addictions show reduced reward responses when viewing their own infant’s face.https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23731
Kneeland, E. T., Griffin, M. L., Taghian, N., Weiss, R. D., & McHugh, R. K. (2019). Associations between pain catastrophizing and clinical characteristics in adults with substance use disorders and co-occurring chronic pain. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 45(5), 488–494. https://doi.org/10.1080/00952990.2019.1581793
Kuehn, B. (2019). Vaping and Pregnancy. JAMA, 321(14), 1344. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.3424
Lachowsky, N. J., Dulai, J. J. S., Cui, Z., Sereda, P., Rich, A., Patterson, T. L., Corneil, T. T., Montaner, J. S. G., Roth, E. A., Hogg, R. S., & Moore, D. M. (2017). Lifetime doctor-diagnosed mental health conditions and current substance use among gay and bisexual men living in Vancouver, Canada. Substance Use & Misuse, 52(6), 785–797. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826084.2016.1264965
Landi, N., Montoya, J., Kober, H., Rutherford, H., Mencl, E., Worhunsky, P., Potenza, M. N., & Mayes, L. (2011). Maternal neural responses to infant cries and faces: Relationships with substance use. Frontiers in Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2011.00032
Li, G.-L., Wu, J.-T., Xia, Y.-H., He, Q.-G., & Jin, H.-G. (2020). Review of semi-dry electrodes for EEG recording. Journal of Neural Engineering, 17(5), 051004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/abbd50
Lowell, A. F., Maupin, A. N., Landi, N., Potenza, M. N., Mayes, L. C., & Rutherford, H. J. V. (2020). Substance use and mothers’ neural responses to infant cues. Infant Mental Health Journal, 41(2), 264–277. https://doi.org/10.1002/imhj.21835
Lowell, A. F., Dell, J., Potenza, M. N., Strathearn, L., Mayes, L. C., & Rutherford, H. J. V. (2021). Adult attachment is related to maternal neural response to infant cues: An ERP study. Attachment & Human Development, 0(0), 1–18.https://doi.org/10.1080/14616734.2021.1880057
Massachusetts Department of Public Health. (2017). Data brief: an assessment of opiod-related overdoses in Massachusetts 2011–2015. https://www.mass.gov/doc/data-brief-chapter-55-opioid-overdose-study-august-2017/download. Accessed 1 Nov 2021
Maupin, A. N., Hayes, N. J., Mayes, L. C., & Rutherford, H. J. V. (2015). The application of electroencephalography to investigate the neural bases of parenting: A review. Parenting, Science and Practice, 15(1), 9–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/15295192.2015.992735
Maupin, A. N., Rutherford, H. J. V., Landi, N., Potenza, M. N., & Mayes, L. C. (2019). Investigating the association between parity and the maternal neural response to infant cues. Social Neuroscience, 14(2), 214–225. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470919.2017.1422276
McLellan, A. T., Luborsky, L., Woody, G. E., & O’Brien, C. P. (1980). An improved diagnostic evaluation instrument for substance abuse patients. The Addiction Severity Index. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 168(1), 26–33. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005053-198001000-00006
McPartland, J., Dawson, G., Webb, S. J., Panagiotides, H., & Carver, L. J. (2004). Event-related brain potentials reveal anomalies in temporal processing of faces in autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 45(7), 1235–1245. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2004.00318.x
Mekonen, T., Fekadu, W., Mekonnen, T. C., & Workie, S. B. (2017). Substance use as a strong predictor of poor academic achievement among university students. Psychiatry Journal, 2017, e7517450. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7517450
NIAAA. (2020). National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/brochures-and-fact-sheets/understanding-alcohol-use-disorder. Accessed 13 Sept 2021
NIAAA. (2021). National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/brochures-and-fact-sheets/alcohol-facts-and-statistics. Accessed 13 Sept 2021
NIDA. (2020). What is the scope of cocaine use in the United States? National Institute on Drug Abuse. https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/cocaine/what-scope-cocaine-use-in-united-states. Accessed 11 Jan 2022
Noll, L. K., Mayes, L. C., & Rutherford, H. J. V. (2012). Investigating the impact of parental status and depression symptoms on the early perceptual coding of infant faces: An event-related potential study. Social Neuroscience, 7(5), 525–536. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470919.2012.672457
Oosterman, M., & Schuengel, C. (2008). Attachment in foster children associated with caregivers’ sensitivity and behavioral problems. Infant Mental Health Journal, 29(6), 609–623. https://doi.org/10.1002/imhj.20198
Parker, T. C., Crowley, M. J., Naples, A. J., Rolison, M. J., Wu, J., Trapani, J. A., & McPartland, J. C. (2021). The N170 event-related potential reflects delayed neural response to faces when visual attention is directed to the eyes in youths with ASD. Autism Research: Official Journal of the International Society for Autism Research, 14(7), 1347–1356. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.2505
Pengpid, S., & Peltzer, K. (2019). Early substance use initiation and psychological distress among adolescents in five ASEAN countries: A cross-sectional study. Psychology Research and Behavior Management, 12, 1003–1008. https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S223624
Proverbio, A. M., Brignone, V., Matarazzo, S., Del Zotto, M., & Zani, A. (2006). Gender and parental status affect the visual cortical response to infant facial expression. Neuropsychologia, 44(14), 2987–2999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.06.015
Purhonen, M., Valkonen-Korhonen, M., & Lehtonen, J. (2008). The impact of stimulus type and early motherhood on attentional processing. Developmental Psychobiology, 50(6), 600–607. https://doi.org/10.1002/dev.20321
Rodriguez, J. J., & Smith, V. C. (2019). Epidemiology of perinatal substance use: Exploring trends in maternal substance use. Seminars in Fetal & Neonatal Medicine, 24(2), 86–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.siny.2019.01.006
Rutherford, H. J. V., Maupin, A. N., Landi, N., Potenza, M. N., & Mayes, L. C. (2017). Current tobacco-smoking and neural responses to infant cues in mothers. Parenting, 17(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/15295192.2017.1262176
Rutherford, H. J. V., Maupin, A. N., & Mayes, L. C. (2019). Parity and neural responses to social and non-social stimuli in pregnancy. Social Neuroscience, 14(5), 545–548. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470919.2018.1518833
Rutherford, H. J. V., Yip, S. W., Worhunsky, P. D., Kim, S., Strathearn, L., Potenza, M. N., & Mayes, L. C. (2020). Differential responses to infant faces in relation to maternal substance use: An exploratory study. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 207, 107805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2019.107805
Rutherford, H. J. V., Kim, S., Yip, S. W., Potenza, M. N., Mayes, L. C., & Strathearn, L. (2021). Parenting and addictions: Current insights from human neuroscience. Current Addiction Reports, 8(3), 380–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40429-021-00384-6
Salti, M., Bar-Haim, Y., & Lamy, D. (2012). The P3 component of the ERP reflects conscious perception, not confidence. Consciousness and Cognition, 21(2), 961–968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2012.01.012
SAMHSA. (2020). 2020 National Survey of Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) Releases | CBHSQ Data. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/release/2020-national-survey-drug-use-and-health-nsduh-releases. Accessed 12 Aug 2021
SAMHSA. (2021). 2020 NSDUH Detailed Tables | CBHSQ Data. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/report/2020-nsduh-detailed-tables. Accessed 10 Mar 2022
Schneider, W., Eschman, A., & Zuccolotto, A. (2002). E-Prime User’s Guide. Psychology Software Incorporated.
Sobell, L. C., Brown, J., Leo, G. I., & Sobell, M. B. (1996). The reliability of the Alcohol Timeline Followback when administered by telephone and by computer. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 42(1), 49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/0376-8716(96)01263-X
Staton-Tindall, M., Sprang, G., Clark, J., Walker, R., & Craig, C. D. (2013). Caregiver substance use and child outcomes: A systematic review. Journal of Social Work Practice in the Addictions, 13(1), 6–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/1533256X.2013.752272
Suchman, N. E., DeCoste, C. L., McMahon, T. J., Dalton, R., Mayes, L. C., & Borelli, J. (2017). Mothering From the Inside Out: Results of a second randomized clinical trial testing a mentalization-based intervention for mothers in addiction treatment. Development and Psychopathology, 29(2), 617–636. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579417000220
Taber-Thomas, S. M., & Knutson, J. F. (2021). Association between mothers’ alcohol use histories and deficient parenting in an economically disadvantaged sample. Child Maltreatment, 26(1), 40–49. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077559520925550
Tsantefski, M., Humphreys, C., & Jackson, A. C. (2014). Infant risk and safety in the context of maternal substance use. Children and Youth Services Review, 47, 10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2013.10.021
Vickerman, K. A., Carpenter, K. M., Raskob, M. K., Nash, C. M., Vargas-Belcher, R. A., & Beebe, L. A. (2021). Vaping and e-cigarettes within the evolving tobacco quitline landscape. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 60(3, Supplement 2), S142–S153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2020.07.013
Zuckermann, A. M. E., Williams, G. C., Battista, K., Jiang, Y., de Groh, M., & Leatherdale, S. T. (2020). Prevalence and correlates of youth poly-substance use in the COMPASS study. Addictive Behaviors, 107, 106400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106400
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health [R01 DA026437-08].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Kathryn M. Wall, Helena J. V. Rutherford, and Linda C. Mayes; methodology: Kathryn M. Wall, Helena J. V. Rutherford, and Linda C. Mayes; formal analysis and investigation: Kathryn M. Wall, Jaclyn Dell, and Helena J. V. Rutherford; writing—original draft preparation: Kathryn M. Wall and Helena J. V. Rutherford; writing—review and editing: Kathryn M. Wall, Jaclyn Dell, Amanda Lowell, Linda C. Mayes, Marc N. Potenza, and Helena J. V. Rutherford; funding acquisition: Linda C. Mayes; Resources: Linda C. Mayes and Helena J. V. Rutherford; supervision: Linda C. Mayes and Helena J. V. Rutherford.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the Yale University Human Investigation Committee.
Consent to Participate
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000 (5). Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Competing Interests
Kathryn M. Wall, Jaclyn Dell, Amanda Lowell, Linda C. Mayes, and Helena J. V. Rutherford declare no conflicts of interest. Marc N. Potenza has consulted for and advised Opiant Pharmaceuticals, Idorsia Pharmaceuticals, AXA, Game Day Data and the Addiction Policy Forum; has been involved in a patent application with Yale University and Novartis; has received research support from the Mohegan Sun Casino and Connecticut Council on Problem Gambling; has participated in surveys, mailings, or telephone consultations related to drug addiction, impulse control disorders, or other health topics; and has consulted for law offices and gambling entities on issues related to impulse control or addictive disorders.
Disclaimer
The views presented in this manuscript are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the funding agencies.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wall, K.M., Dell, J., Lowell, A. et al. Current Substance Use and Maternal Neural Responses to Infant Faces and Cries. Int J Ment Health Addiction (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-022-00947-2
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-022-00947-2