Abstract
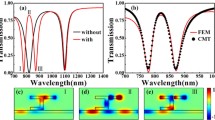
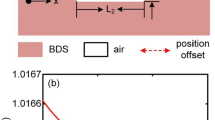
The phenomenon of plasmon-induced transparency (PIT) is realized a in surface plasmon polariton waveguide at near-infrared frequencies. The right-angled slot and rectangle cavity placed inside one of the metallic claddings are respectively utilized to obtain bright and dark modes in a typical bright-dark mode waveguide. A PIT transmission spectrum of the waveguide is generated due to the destructive interference between the bright and dark modes, and the induced transparency peak can be manipulated by adjusting the size of the bright and dark resonators and the coupling distance between them. Subsequently, spectral splitting based on the PIT structure is studied numerically and analytically. Simulation results indicate that double electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT)-like peaks emerge in the broadband transmission spectrum by adding another rectangle cavity, and the corresponding physical mechanism is presented. Our novel plasmonic structure and the findings pave the way for new design and engineering of highly integrated optical circuit such as nanoscale optical switching, nanosensor, and wavelength-selecting nanostructure.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleischhauer M, Imamoglu A, Marangos JP (2005) Electromagnetically induced transparency: optics in coherent media. Rev Mod Phys 77(2):633
Harris SE (2008) Electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys Today 50(7):36–42
Boller KJ, Imamoğlu A, Harris SE (1991) Observation of electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys Rev Lett 66(20):2593
Phillips DF, Fleischhauer A, Mair A, Walsworth RL, Lukin MD (2001) Storage of light in atomic vapor. Phys Rev Lett 86(5):783
Papasimakis N, Fedotov VA, Zheludev NI, Prosvirnin SL (2008) Metamaterial analog of electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys Rev Lett 101(25):253903
Kekatpure RD, Barnard ES, Cai W, Brongersma ML (2010) Phase-coupled plasmon-induced transparency. Phys Rev Lett 104(24):243902
Han Z, Bozhevolnyi SI (2011) Plasmon-induced transparency with detuned ultracompact Fabry-Perot resonators in integrated plasmonic devices. Opt Express 19(4):3251–3257
Totsuka K, Kobayashi N, Tomita M (2007) Slow light in coupled-resonator-induced transparency. Phys Rev Lett 98(21):213904
Zhang J, Xiao S, Jeppesen C, Kristensen A, Mortensen NA (2010) Electromagnetically induced transparency in metamaterials at near-infrared frequency. Opt Express 18(16):17187–17192
Tassin P, Zhang L, Koschny T, Economou EN, Soukoulis CM (2009) Low-loss metamaterials based on classical electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys Rev Lett 102(5):053901
Liu N, Weiss T, Mesch M, Langguth L, Eigenthaler U, Hirscher M, Giessen H (2009) Planar metamaterial analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency for plasmonic sensing. Nano Lett 10(4):1103–1107
Liu N, Langguth L, Weiss T, Kästel J, Fleischhauer M, Pfau T, Giessen H (2009) Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the Drude damping limit. Nat Mater 8(9):758–762
Boyd RW, Gauthier DJ (2006) Photonics: transparency on an optical chip. Nature 441(7094):701–702
Zia R, Schuller JA, Chandran A, Brongersma ML (2006) Plasmonics—the wave of chip-scale device technologies. Mater Today 9:20–27
Bozhevolnyi SI, Volkov VS, Devaux E, Laluet JY, Ebbesen TW (2006) Channel plasmon subwavelength waveguide components including interferometers and ring resonators. Nature 440(7083):508–511
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424(6950):824–830
Zentgraf T, Zhang S, Oulton RF, Zhang X (2009) Ultranarrow coupling-induced transparency bands in hybrid plasmonic systems. Phys Rev B 80(19):195415
Neutens P, Van Dorpe P, De Vlaminck I, Lagae L, Borghs G (2009) Electrical detection of confined gap plasmons in metal–insulator–metal waveguides. Nat Photonics 3(5):283–286
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6(12):4370
Zhang S, Genov DA, Wang Y, Liu M, Zhang X (2008) Plasmon-induced transparency in metamaterials. Phys Rev Lett 101(4):047401
Nordlander P, Oubre C, Prodan E, Li K, Stockman MI (2004) Plasmon hybridization in nanoparticle dimers. Nano Lett 4(5):899–903
Zhang Z, Zhang L, Li H, Chen H (2014) Plasmon induced transparency in a surface plasmon polariton waveguide with a comb line slot and rectangle cavity. Appl Phys Lett 104(23):231114
Hu F, Yi H, Zhou Z (2011) Wavelength demultiplexing structure based on arrayed plasmonic slot cavities. Opt Lett 36(8):1500–1502
Chen J, Li Z, Yue S, Xiao J, Gong Q (2012) Plasmon-induced transparency in asymmetric T-shape single slit. Nano Lett 12(5):2494–2498
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61505052, 11074069, 61176116).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, DM., Zhai, X., Wang, LL. et al. Plasmon-Induced Transparency in a Surface Plasmon Polariton Waveguide with a Right-Angled Slot and Rectangle Cavity. Plasmonics 11, 1151–1155 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0153-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0153-6