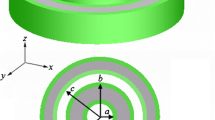
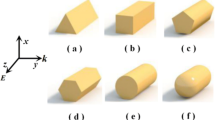
Abstract
Numerical methods are very important for designing nanodevices since localized surface plasmon resonance is sensitive to the geometric parameters. Especially, as for nano-biosensor, the proper choice of design tool is very critical in terms of the accuracy and simulation time. In this paper, we compare the discrete dipole approximation (DDA) with the finite integration technique (FIT) of the full-wave electromagnetic commercial software (CST Microwave Studio) in worldwide use with popularity. The refractive index sensitivity of rhombic hybrid Au–Ag nanostructures is calculated and compared in visible wavelength using DDA and FIT. Comparing the calculated results, the DDA has two advantages over the FIT: easy control of geometric parameter and less simulation time without compromising the accuracy. The limitations of the DDA will be deliberated as well.



Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Haynes CL, McFarland AD, Zhao L, Van Duyne RP, Schatz GC, Gunnarsson L, Prikulis J, Kasemo B, Käll M (2003) Nanoparticle optics: the importance of radiative dipole coupling in two-dimensional nanoparticle arrays. J Phys Chem B 107:7337–7342. doi:10.1021/jp034234r
Haynes CL, Van Duyne RP (2003) Dichroic optical properties of extended nanostructures fabricated using angle-resolved nanosphere lithography. Nano Lett 3:939–943. doi:10.1021/nl0342287
Andersen PC, Rowlen KL (2002) Brilliant optical properties of nanometric noble metal spheres, rods, and aperture arrays. Appl Spectrosc 56:124A–135A, IDS Number: 558UT
Fu Y, Zhou W, Lim LEN (2008) Near-field behavior of zone-plate-like plasmonic nanostructures. J Opt Soc Am A 25(1):238–249. doi:10.1364/JOSAA.25.000238
Haes AJ, Zou S, Schatz GC, Van Duyne RP (2004) A nanoscale optical biosensor: the long range distance dependence of the localized surface plasmon resonance of noble metal nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 108:109–116. doi:10.1021/jp0361327
Zhu SL, Li F, Luo XG, Du CL, Fu YQ (2008) A localized surface plasmon resonance nanosensor based on rhombic Ag nanoparticle array. Sens Actuators B Chem 134:193–198. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2008.04.028
Mie G (1908) Beiträge zur Optik trüber Medien, speziell kolloidaler Metallösungen. Ann Phys (Leipz) 25:377–445. doi:10.1002/andp.19083300302
Aden AL, Kerker M (1951) Scattering of electromagnetic waves from two concentric spheres. J App Phys 22:1242–1246. doi:10.1063/1.1699834
Draine BT, Flatau PJ (1994) Discrete-dipole approximation for scattering calculations. J Opt Soc Am A 11:1491–1499. doi:10.1364/JOSAA.11.001491
Skarlatos A, Schuhmann R, Weiland T (2005) Solution of radiation and scattering problems in complex environments using a hybrid finite integration technique—uniform theory of diffraction approach. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 53(10):3347–3357. doi:10.1109/TAP.2005.856358
Clemens M, Feigh S, Weiland T (2005) Construction principles of multigrid smoothers for Curl–Curl equations. IEEE Trans Magn 41(5):1680–1683. doi:10.1109/TMAG.2005.846086
Weiland T (1977) A discretization model for the solution of Maxwell’s equations for six-component fields. Archiv fuer Elektronik und Uebertragungstechnik 31(3):116–120
Futamata M, Maruyama Y, Ishikawa M (2003) Local electric field and scattering cross section of Ag nanoparticles under surface plasmon resonance by finite difference time domain method. J Phys Chem B 107:7607–7617. doi:10.1021/jp022399e
Oubre C, Nordlander P (2004) Optical properties of metallodielectric nanostructures calculated using the finite difference time domain method. J Phys Chem B 108:17740–17747. doi:10.1021/jp0473164
Han JG, Ren WX, Huang Y (2009) A spline wavelet finite element formulation of thin plate bending. Eng Comput 25(4):319–326. doi:10.1007/s00366-009-0124-7
Pisano AA, Sofi A, Fuschi P (2009) Finite element solutions for Eringen-type nonlocal elastic 2D problems. Int J Solids Struct 46(21):3836–3849. doi:10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2009.07.009
Zhu SL, Zhou W (2009) Effect of gold-coating on the sensitivity of the rhombic silver nanostructures array. Plasmonics 4:303–306. doi:10.1007/s11468-009-9106-2
Krietenstein B, Schuhmann R, Thoma P, Weiland T (1998) The perfect boundary approximation technique facing the challenge of high precision field computation. Proceedings of the XIX International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC’98), Chicago, USA, pp 860–862
Weiland T (2003) RF & microwave simulators—from component to system design. Proceedings of the European Microwave Week (EUMW 2003), München, vol 2, October, pp 591–596. IDS Number: BY41G
Zhu SL, Du CL, Fu YQ (2009) Tuning optical properties of rhombic hybrid Au–Ag nanoparticles: a discrete dipole approximation calculation. Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience 6:1034–1038. doi:10.1166/jctn.2009.1140
Zhu SL, Zhou W (2010) Optical characters of rhombic hybrid Au–Ag nanostructures calculated by discrete dipole approximation method. Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience 7(3):634–637. doi:10.1166/jctn.2010.1406
Acknowledgment
The work was supported by the A*STAR (Agency for Science, Technology and Research), Singapore, under SERC grant no. 0721010023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S., Zhou, W., Park, GH. et al. Numerical Design Methods of Nanostructure Array for Nanobiosensing. Plasmonics 5, 267–271 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-010-9137-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-010-9137-8