Abstract
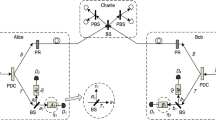
Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution (MDI-QKD) provides us a powerful approach to resist all attacks at detection side. Besides the unconditional security, people also seek for high key generation rate, but MDI-QKD has relatively low key generation rate. In this paper, we provide an efficient approach to increase the key generation rate of MDI-QKD by adopting multiple degrees of freedom (DOFs) of single photons to generate keys. Compared with other high-dimension MDI-QKD protocols encoding in one DOF, our protocol is more flexible, for our protocol generating keys in independent subsystems and the detection failure or error in a DOF not affecting the information encoding in other DOFs. Based on above features, our MDI-QKD protocol may have potential application in future quantum communication field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. H. Bennett and G. Brassard, in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India IEEE, New York, 175 (1984)
A. K. Ekert, Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem, Phys. Rev. Lett. 67(6), 661 (1991)
H. K. Lo and H. F. Chau, Unconditional security of quantum key distribution over arbitrarily long distances, Science 283(5410), 2050 (1999)
N. J. Cerf, M. Bourennane, A. Karlsson, and N. Gisin, Security of quantum key distribution using d-level systems, Phys. Rev. Lett. 88(12), 127902 (2002)
D. Stucki, N. Gisin, O. Guinnard, G. Ribordy, and H. Zbinden, Quantum key distribution over 67 km with a plug play system, New J. Phys. 4, 41 (2002)
F. Grosshans, G. Van Assche, J. Wenger, R. Brouri, N. J. Cerf, and P. Grangier, Quantum key distribution using gaussian-modulated coherent states, Nature 421(6920), 238 (2003)
H. K. Lo, H. F. Chau, and M. Ardehali, Efficient quantum key distribution scheme and a proof of its unconditional security, J. Cryptol. 18(2), 133 (2005)
T. Schmitt-Manderbach, H. Weier, M. Fürst, R. Ursin, F. Tiefenbacher, T. Scheidl, J. Perdigues, Z. Sodnik, C. Kurtsiefer, J. G. Rarity, A. Zeilinger, and H. Weinfurter, Experimental demonstration of free-space decoy-state quantum key distribution over 144 km, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98(1), 010504 (2007)
M. Koashi, Simple security proof of quantum key distribution based on complementarity, New J. Phys. 11(4), 045018 (2009)
S. Wang, W. Chen, Z. Q. Yin, D. Y. He, C. Hui, P. L. Hao, G. J. Fan-Yuan, C. Wang, L. J. Zhang, J. Kuang, S. F. Liu, Z. Zhou, Y. G. Wang, G. C. Guo, and Z. F. Han, Practical gigahertz quantum key distribution robust against channel disturbance, Opt. Lett. 43(9), 2030 (2018)
X. D. Wu, Y. J. Wang, H. Zhong, Q. Liao, and Y. Guo, Plug-and-play dual-phase-modulated continuous variable quantum key distribution with photon subtraction, Front. Phys. 14(4), 41501 (2019)
S. Wang, D. Y. He, Z. Q. Yin, F. Y. Lu, C. H. Cui, W. Chen, Z. Zhou, G. C. Guo, and Z. F. Han, Beating the fundamental rate-distance limit in a proof-of-principle quantum key distribution system, Phys. Rev. X 9(2), 021046 (2019)
F. H. Xu, X. F. Ma, Q. Zhang, H. K. Lo, and J. W. Pan, Secure quantum key distribution with realistic devices, Rev. Mod. Phys. 92(2), 025002 (2020)
Y. Zhang and Q. Ni, Design and analysis of random multiple access quantum key distribution, Quant. Engineer. 2(1), e31 (2020)
G. Chai, D. W. Li, Z. W. Cao, M. Zhang, P. Huang, and G. Zeng, Blind channel estimation for continuous-variable quantum key distribution, Quant. Engineer. 2(2), e37 (2020)
M. J. He, R. Malaney, and J. Green, Multimode CV-QKD with non-Gaussian operations, Quant. Engineer. 2, e40 (2020)
H. K. Lo, M. Curty, and K. Tamaki, Secure quantum key distribution, Nat. Photonics 8(8), 595 (2014)
B. Qi, C. H. F. Fung, H. K. Lo, and X. F. Ma, Time-shift attack in practical quantum cryptosystems, Quantum Inf. Comput. 7, 73 (2007)
Y. Zhao, C. H. F. Fung, B. Qi, C. Chen, and H. K. Lo, Quantum hacking: experimental demonstration of timeshift attack against practical quantum-keydistribution systems, Phys. Rev. A 78(4), 042333 (2008)
N. Jain, C. Wittmann, L. Lydersen, C. Wiechers, D. Elser, C. Marquardt, V. Makarov, and G. Leuchs, Device calibration impacts security of quantum key distribution, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107(11), 110501 (2011)
L. Lydersen, C. Wiechers, C. Wittmann, D. Elser, J. Skaar, and V. Makarov, Hacking commercial quantum cryptography systems by tailored bright illumination, Nat. Photonics 4(10), 686 (2010)
H. W. Li, S. Wang, J. Z. Huang, W. Chen, Z. Q. Yin, F. Y. Li, Z. Zhou, D. Liu, Y. Zhang, G. C. Guo, W. S. Bao, and Z. F. Han, Attacking a practical quantum-key-distribution system with wavelength dependent beam-splitter and multiwavelength sources, Phys. Rev. A 84(6), 062308 (2011)
J. Z. Huang, C. Weedbrook, Z. Q. Yin, S. Wang, H. W. Li, W. Chen, G. C. Guo, and Z. F. Han, Quantum hacking of a continuous-variable quantum-key distribution system using a wavelength attack, Phys. Rev. A 87(6), 062329 (2013)
V. Makarov and J. Skaar, Faked states attack using detector efficiency mismatch on SARG04, phase-time, DPSK, and Ekert protocols, Quantum Inf. Comput. 8, 6 (2007)
V. Makarov, A. Anisimov, and J. Skaar, Effects of detector efficiency mismatch on security of quantum cryptosystems, Phys. Rev. A 74(2), 022313 (2006)
Y. Zhao, B. Qi, and H. K. Lo, Quantum key distribution with an unknown and untrusted source, Phys. Rev. A 77(5), 052327 (2008)
X. Peng, H. Jiang, B. J. Xu, X. F. Ma, and H. Guo, Experimental quantum-key distribution with an untrusted source, Opt. Lett. 33(18), 2077 (2008)
G. Brassard, N. Lütkenhaus, T. Mor, and B. C. Sanders, Limitations on practical quantum cryptography, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(6), 1330 (2000)
W. Y. Hwang, Quantum key distribution with high loss: Toward global secure communication, Phys. Rev. Lett. 91(5), 057901 (2003)
H. K. Lo, X. F. Ma, and K. Chen, Decoy state quantum key distribution, Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(23), 230504 (2005)
X. B. Wang, Beating the photon-number-splitting attack in practical quantum cryptography, Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(23), 230503 (2005)
X. F. Ma, B. Qi, Y. Zhao, and H. K. Lo, Practical decoy state for quantum key distribution, Phys. Rev. A 72(1), 012326 (2005)
A. Acín, N. Brunner, N. Gisin, S. Massar, S. Pironio, and V. Scarani, Device-independent security of quantum cryptography against collective attacks, Phys. Rev. Lett. 98(23), 230501 (2007)
S. Pironio, A. Acfn, N. Brunner, N. Gisin, S. Massar, and V. Scarani, Device-independent quantum key distribution secure against collective attacks, New J. Phys. 11(4), 045021 (2009)
L. Masanes, S. Pironio, and A. Acfn, Secure deviceindependent quantum key distribution with causally independent measurement devices, Nat. Commun. 2(1), 238 (2011)
A. Máttar, J. Kolodynski, P. Skrzypczyk, D. Cavalcanti, K. Banaszek, and A. Acfn, Device-independent quantum key distribution with single-photon sources, arXiv: 1803.07089 (2018)
H. K. Lo, M. Curty, and B. Qi, Measurement-deviceindependent quantum key distribution, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108(13), 130503 (2012)
Y. Liu, T. Y. Chen, L. J. Wang, H. Liang, G. L. Shentu, J. Wang, K. Cui, H. L. Yin, N. L. Liu, L. Li, X. Ma, J. S. Pelc, M. M. Fejer, C. Z. Peng, Q. Zhang, and J. W. Pan, Experimental measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution, Phys. Rev. Lett. 111(13), 130502 (2013)
F. H. Xu, M. Curty, B. Qi, and H. K. Lo, Practical aspects of measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution, New J. Phys. 15(11), 113007 (2013)
Z. Y. Tang, Z. F. Liao, F. H. Xu, B. Qi, L. Qian, and H. K. Lo, Experimental demonstration of polarization encoding measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution, Phys. Rev. Lett. 112(19), 190503 (2014)
Y. L. Tang, H. L. Yin, S. J. Chen, Y. Liu, W. J. Zhang, X. Jiang, L. Zhang, J. Wang, L. X. You, J. Y. Guan, D. X. Yang, Z. Wang, H. Liang, Z. Zhang, N. Zhou, X. Ma, T. Y. Chen, Q. Zhang, and J. W. Pan, Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution over 200 km, Phys. Rev. Lett. 114(6), 069901 (2015)
H. L. Yin, W. F. Cao, Y. Fu, Y. L. Tang, Y. Liu, T. Y. Chen, and Z. B. Chen, Long-distance measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with coherent-state superpositions, Opt. Lett. 39(18), 5451 (2014)
C. Wang, X. T. Song, Z. Q. Yin, S. Wang, W. Chen, C. M. Zhang, G. C. Guo, and Z. F. Han, Phase-reference-free experiment of measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution, Phys. Rev. Lett. 115(16), 160502 (2015)
H. L. Yin, T. Y. Chen, Z. W. Yu, H. Liu, L. X. You, Y. H. Zhou, S. J. Chen, Y. Mao, M. Q. Huang, W. J. Zhang, H. Chen, M. J. Li, D. Nolan, F. Zhou, X. Jiang, Z. Wang, Q. Zhang, X. B. Wang, and J. W. Pan, Measurement device-independent quantum key distribution over a 404 km optical fiber, Phys. Rev. Lett. 117(19), 190501 (2016)
C. Wang, Z. Q. Yin, S. Wang, W. Chen, G. C. Guo, and Z. F. Han, Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution robust against environmental disturbances, Optica 4(9), 1016 (2017)
X. D. Wu, Y. J. Wang, D. Huang, and Y. Guo, Simultaneous measurement-device-independent continuous variable quantum key distribution with realistic detector compensation, Front. Phys. 15(3), 31601 (2020)
J. Mower, Z. S. Zhang, P. Desjardins, C. Lee, J. H. Shapiro, and D. Englund, High-dimensional quantum key distribution using dispersive optics, Phys. Rev. A 87(6), 062322 (2013)
M. Mafu, A. Dudley, S. Goyal, D. Giovannini, M. McLaren, M. J. Padgett, T. Konrad, F. Petruccione, N. Lütkenhaus, and A. Forbes, Higherdimensional orbital-angular-momentum-based quantum key distribution with mutually unbiased bases, Phys. Rev. A 88(3), 032305 (2013)
T. Zhong, H. Zhou, R. D. Horansky, C. Lee, V. B. Verma, A. E. Lita, A. Restelli, J. C. Bienfang, R. P. Mirin, T. Gerrits, S. W. Nam, F. Marsili, M. D. Shaw, Z. Zhang, L. Wang, D. Englund, G. W. Wornell, J. H. Shapiro, and F. N. C. Wong, Photon-efficient quantum key distribution using time — energy entanglement with high-dimensional encoding, New J. Phys. 17(2), 022002 (2015)
D. Bunandar, Z. S. Zhang, J. H. Shapiro, and D. R. Englund, Practical high-dimensional quantum key distribution with decoy states, Phys. Rev. A 91(2), 022336 (2015)
S. Wang, Z. Q. Yin, W. Chen, D. Y. He, X. T. Song, H. W. Li, L. J. Zhang, Z. Zhou, G. C. Guo, and Z. F. Han, Experimental demonstration of a quantum key distribution without signal disturbance monitoring, Nat. Photonics 9(12), 832 (2015)
H. Z. Bao, W. S. Bao, Y. Wang, R. K. Chen, and H. W. Li, Detector-decoy high-dimensional quantum key distribution, Opt. Express 24(19), 22159 (2016)
H. Chau, C. Wong, Q. Wang, and T. Huang, Qudit-based measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution using linear optics, arXiv: 1608.08329 (2016)
F. T. Tabesh, S. Salimi, and A. S. Khorashad, Witness for initial correlations among environments, Phys. Rev. A 95(5), 052323 (2017)
G. Cañas, N. Vera, J. Cariñe, P. González, J. Cardenas, P. W. R. Connolly, A. Przysiezna, E. S. Gomez, M. Figueroa, G. Vallone, P. Villoresi, T. F. da Silva, G. B. Xavier, and G. Lima, High-dimensional decoy-state quantum key distribution over multicore telecommunication fibers, Phys. Rev. A 96(2), 022317 (2017)
L. Dellantonio, A. S. Sorensen, and D. Bacco, Highdimensional measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution on two-dimensional subspaces, Phys. Rev. A 98(6), 062301 (2018)
G. I. Struchalin, E. V. Kovlakov, S. S. Straupe, and S. P. Kulik, Adaptive quantum tomography of highdimensional bipartite systems, Phys. Rev. A 98(3), 032330 (2018)
S. Wang, Z. Q. Yin, H. F. Chau, W. Chen, C. Wang, G. C. Guo, and Z. F. Han, Proof-of-principle experimental realization of a qubit-like qudit-based quantum key distribution scheme, Quan. Sci. Technol. 3(2), 025006 (2018)
F. M. Wang, P. Zeng, J. P. Zhao, B. Braverman, Y. Zhou, M. Mirhosseini, X. Wang, H. Gao, F. Li, R. W. Boyd, and P. Zhang, High-dimensional quantum key distribution based on mutually partially unbiased bases, Phys. Rev. A 101(3), 032340 (2020)
F. X. Wang, W. Chen, Z. Q. Yin, S. Wang, G. C. Guo, and Z. F. Han, Characterizing high-quality highdimensional quantum key distribution by state mapping between different degrees of freedom, Phys. Rev. A 11, 024070 (2019)
J. Chapman, C. Lim, and P. Kwiat, Hyperentangled time-bin and polarization quantum key distribution, arXiv: 1908.09018 (2019)
Z. X. Cui, W. Zhong, L. Zhou, and Y. B. Sheng, Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with hyper-encoding, Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 62(11), 110311 (2019)
X. L. Wang, X. D. Cai, Z. E. Su, M. C. Chen, D. Wu, L. Li, N. L. Liu, C. Y. Lu, and J. W. Pan, Quantum teleportation of multiple degrees of freedom of a single photon, Nature 518(7540), 516 (2015)
X. M. Hu, Y. Guo, B. H. Liu, Y. F. Huang, C. F. Li, and G. C. Guo, Beating the channel capacity limit for superdense coding with entangled ququarts, Sci. Adv. 4(7), eaat9304 (2018)
F. Z. Wu, G. J. Yang, H. B. Wang, J. Xiong, F. Alzahrani, A. Hobiny, and F. G. Deng, High-capacity quantum secure direct communication with two-photon six-qubit hyperentangled states, Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 60(12), 120313 (2017)
S. S. Chen, L. Zhou, W. Zhong, and Y. B. Sheng, Three-step three-party quantum secure direct communication, Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 61(9), 90312 (2018)
L. Y. Li, T. J. Wang, and C. Wang, The analysis of high-capacity quantum secure direct communication using polarization and orbital angular momentum of photons, Mod. Phys. Lett. B 34(02), 2050017 (2020)
G. Vallone, R. Ceccarelli, F. De Martini, and P. Mataloni, Hyper-entanglement of two photons in three degrees of freedom, Phys. Rev. A 79(3), 030301 (2009)
Q. Liu, G. Y. Wang, Q. Ai, M. Zhang, and F. G. Deng, Complete nondestructive analysis of two-photon six-qubit hyperentangled Bell states assisted by cross-Kerr nonlin-earity, Sci. Rep. 6(1), 22016 (2016)
H. Inamori, Security of practical time-reversed EPR quantum key distribution, Algorithmica 34(4), 340 (2002)
P. Kok, W. J. Munro, K. Nemoto, T. C. Ralph, J. P. Dowling, and G. J. Milburn, Linear optical quantum computing with photonic qubits, Rev. Mod. Phys. 79(1), 135 (2007)
Y. B. Wei, W. Q. Liu, and N. Y. Chen, Implementing two-photon three-degree-of-freedom hyper-parallel controlled phase flip gate through cavity-assisted interactions, Ann. Phys. 532(4), 1900578 (2020)
C. Zhu and G. Huang, Giant Kerr nonlinearity, controlled entangled photons and polarization phase gates in coupled quantum-well structures, Opt. Express 19(23), 23364 (2011)
I. C. Hoi, A. F. Kockum, T. Palomaki, T. M. Stace, B. Fan, L. Tornberg, S. R. Sathyamoorthy, G. Johansson, P. Delsing, and C. M. Wilson, Giant cross-Kerr effect for propagating microwaves induced by an artificial atom, Phys. Rev. Lett. 111(5), 053601 (2013)
K. M. Beck, M. Hosseini, Y. H. Duan, and V. Vuletic, Large conditional single-photon cross-phase modulation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 113(35), 9740 (2016)
D. Tiarks, S. Schmidt, G. Rempe, and S. Dürr, Optical π phase shift created with a single-photon pulse, Sci. Adv. 2(4), e1600036 (2016)
J. Sinclair, D. Angulo, N. Lupu-Gladstein, K. Bonsma-Fisher, and A. M. Steinberg, Observation of a large, resonant, cross-Kerr nonlinearity in a free-space Rydberg medium, arXiv: 1906.05151 (2019)
B. C. Ren, H. R. Wei, M. Hua, T. Li, and F. G. Deng, Complete hyperentangled-Bell-state analysis for photon systems assisted by quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities, Opt. Express 20(22), 24664 (2012)
T. J. Wang, Y. Lu, and G. L. Long, Generation and complete analysis of the hyperentangled Bell state for photons assisted by quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities, Phys. Rev. A 86(4), 042337 (2012)
G. Y. Wang, Q. Ai, B. C. Ren, T. Li, and F. G. Deng, Error-detected generation and complete analysis of hyperentangled Bell states for photons assisted by quantum-dot spins in double-sided optical microcavities, Opt. Express 24(25), 28444 (2016)
Q. Liu and M. Zhang, Generation and complete nondestructive analysis of hyperentanglement assisted by nitrogen-vacancy centers in resonators, Phys. Rev. A 91(6), 062321 (2015)
T. J. Wang and C. Wang, Complete hyperentangled-Bell state analysis for photonic qubits assisted by a three-level A-type system, Sci. Rep. 6(1), 19497 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 11974189 and 12005106, the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province under Grant No. SJCX19-0241, and a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, YF., Zhou, L., Zhong, W. et al. Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution of multiple degrees of freedom of a single photon. Front. Phys. 16, 11501 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-020-1005-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-020-1005-1