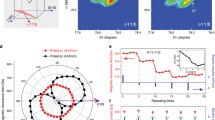
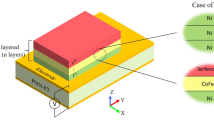
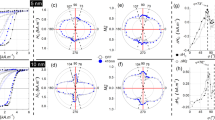
Abstract
Voltage tuning of magnetism is fundamentally and technically important for fast, compact and ultra-low power electronic devices. Multiferroic heterostructures, simultaneously exhibiting distinct ferroelectric and ferromagnetic properties, have caught a lot of attentions because of the capability of controlling magnetism by a voltage via a strain-mediated magnetoelectric (ME) coupling. In these materials, a voltage-induced strain is involved to create an effective magnetic field and change ferromagnetic resonance frequency in the coupled ferromagnetic phases through magnetoelastic interactions. Therefore, the devices made of such materials are compact, ultra-fast and energy efficient, providing new functionalities for microwave components. This paper will review the recent progress of multiferroics and their applications in microwave devices from different aspects, including the creation of the novel laminated multiferroic heterostructures with a strong ME coupling, the realization of the multiferroics based on tunable microwave signal processors and the investigation of nonvolatile tuning of microwave properties using ferroelastic domain switching in multiferroic heterostructures. These tunable multiferroic heterostructures and devices offer great opportunities for realizing the next generation of tunable magnetic microwave components, ultra-low power electronics and spintronics.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Srinivasan G (2010) Magnetoelectric composites. Annu Rev Mater Res 40:153–178
Liu M, Obi O, Lou J et al (2009) Giant electric field tuning of magnetic properties in multiferroic ferrite/ferroelectric heterostructures. Adv Funct Mater 19:1826–1831
Liu M, Zhou Z, Nan T et al (2013) Voltage tuning of ferromagnetic resonance with bistable magnetization switching in energy-efficient magnetoelectric composites. Adv Mater 25:1435–1439
Shi J, Ha SD, Zhou Y et al (2013) A correlated nickelate synaptic transistor. Nat Commun 4:2676
Das J, Song YY, Mo N et al (2009) Electric-field-tunable low loss multiferroic ferrimagnetic-ferroelectric heterostructures. Adv Mater 21:2045–2049
Ramesh R, Spaldin NA (2007) Multiferroics: progress and prospects in thin films. Nat Mater 6:21–29
Vaz CAF, Hoffman J, Anh CH et al (2010) Magnetoelectric coupling effects in multiferroic complex oxide composite structures. Adv Mater 22:2900–2918
Schlom DG, Chen LQ, Eom CB et al (2007) Strain tuning of ferroelectric thin films. Annu Rev Mater Res 37:589–626
Chen X, Hochstrat A, Borisov P et al (2006) Magnetoelectric exchange bias systems in spintronics. Appl Phys Lett 89:202508
Scott JF (2007) Electrical characterization of magnetoelectrical materials. J Mater Res 22:2053–2062
Eerenstein W, Mathur ND, Scott JF (2006) Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature 442:759–765
Cheong SW, Mostovoy M (2007) Multiferroics: a magnetic twist for ferroelectricity. Nat Mater 6:13–20
Spaldin NA, Cheong SW, Ramesh R (2010) Multiferroics: past, present, and future. Phys Today 63:38–43
Dong SX, Zhai JY, Li JF et al (2006) Small dc magnetic field response of magnetoelectric laminate composites. Appl Phys Lett 88:082907
Ma J, Hu JM, Li Z et al (2011) Recent progress in multiferroic magnetoelectric composites: from bulk to thin films. Adv Mater 23:1062–1087
Nan CW, Bichurin MI, Dong SX et al (2008) Multiferroic magnetoelectric composites: historical perspective, status, and future directions. J Appl Phys 103:031101
Wu T, Zhao P, Bao M et al (2011) Domain engineered switchable strain states in ferroelectric (011) [Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3](1−x)-[PbTiO3] x (PMN-PT, x ≈ 0.32) single crystals. J Appl Phys 109:124101
Li N, Liu M, Zhou Z et al (2011) Electrostatic tuning of ferromagnetic resonance and magnetoelectric interactions in ferrite-piezoelectric heterostructures grown by chemical vapor deposition. Appl Phys Lett 99:192502
Srinivasan G, Fetisov YK (2006) Ferrite-piezoelectric layered structures: microwave magnetoelectric effects and electric field tunable devices. Ferroelectrics 342:65–71
Viswanath B, Ramanathan S (2013) Direct in situ observation of structural transition driven actuation in VO2 utilizing electron transparent cantilevers. Nanoscale 5:7484–7492
Liu M, Sun NX (2014) Voltage control of magnetism in multiferroic heterostructures. Philos Trans R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 372:20120439
Ustinov AB, Srinivasan G, Kalinikos BA (2007) Ferrite–ferroelectric hybrid wave phase shifters. Appl Phys Lett 90:031913
Fetisov YK, Srinivasan G (2005) Ferrite/piezoelectric microwave phase shifter: studies on electric field tunability. Electron Lett 41:1066–1067
Tatarenko AS, Srinivasana G, Bichurin MI (2006) Magnetoelectric microwave phase shifter. Appl Phys Lett 88:183507
Wu T, Bur A, Zhao P et al (2011) Giant electric-field-induced reversible and permanent magnetization reorientation on magnetoelectric heterostructure. Appl Phys Lett 98:012503
Zheng RK, Jiang Y, Wang Y et al (2008) Investigation of substrate-induced strain effects in La0.7Ca0.15Sr0.15MnO3 thin films using ferroelectric polarization and the converse piezoelectric effect. Appl Phys Lett 93:102904
Eerenstein W, Wiora M, Prieto JL et al (2007) Giant sharp and persistent converse magnetoelectric effects in multiferroic epitaxial heterostructures. Nat Mater 6:348–351
Aetukuri NB, Gray AX, Drouard M et al (2013) Control of the metal-insulator transition in vanadium dioxide by modifying orbital occupancy. Nat Phys 9:661–666
Hu JM, Li Z, Chen LQ et al (2012) Design of a voltage-controlled magnetic random access memory based on anisotropic magnetoresistance in a single magnetic layer. Adv Mater 24:2869–2873
Liu M, Howe BM, Grazulis L et al (2013) Voltage-impulse-induced non-volatile ferroelastic switching of ferromagnetic resonance for reconfigurable magnetoelectric microwave devices. Adv Mater 25:4886–4892
Thiele C, Dörr K, Bilani O et al (2007) Influence of strain on the magnetization and magnetoelectric effect in La0.7A0.3MnO3/PMN-PT(001) (A = Sr, Ca). Phys Rev B 75:054408
He X, Wang Y, Wu N et al (2010) Robust isothermal electric control of exchange bias at room temperature. Nat Mater 9:579–585
Petrov VM, Srinivasan G, Bichurin MI et al (2007) Theory of magnetoelectric effects in ferrite piezoelectric nanocomposites. Phys Rev B 75:224407
Burdin DA, Chashin DV, Ekonomov NA et al (2012) Multiferroic bending mode resonators and studies on temperature dependence of magnetoelectric interactions. Appl Phys Lett 100:242902
Semenov AA, Kamanenko SF, Kalinikos BA et al (2006) Dual-tunable hybrid wave ferrite–ferroelectric microwave resonator. Electron Lett 42:641–642
Srinivasan G, Fetisov YK (2006) Microwave magnetoelectric effects and signal processing devices. Integr Ferroelectr 83:89
Ustinov AB, Tiberkevich VS, Srinivasan G et al (2006) Electric field tunable ferrite–ferroelectric hybrid wave microwave resonators: experiment and theory. J Appl Phys 100:093905
Fetisov YK, Srinivasan G (2005) Electrically tunable ferrite–ferroelectric microwave delay lines. Appl Phys Lett 87:103502
Liu M, Obi O, Cai ZH et al (2010) Electrical tuning of magnetism in Fe3O4/PZN-PT multiferroic heterostructures derived by reactive magnetron sputtering. J Appl Phys 107:073916
Semenov AA, Karmanenko SF, Demidov VE et al (2006) Ferrite-ferroelectric layered structures for electrically and magnetically tunable microwave resonators. Appl Phys Lett 88:033503
Srinivasan G, De Vreugd CP, Bichurin MI et al (2005) Magnetoelectric interactions in bilayers of yttrium iron garnet and lead magnesium niobate-lead titanate: evidence for strong coupling in single crystals and epitaxial films. Appl Phys Lett 86:222506
Srinivasan G, DeVreugd CP, Flattery CS et al (2004) Magnetoelectric interactions in hot-pressed nickel zinc ferrite and lead zirconante titanate composites. Appl Phys Lett 85:2550–2552
Ustinov AB, Kalinikos BA, Srinivasan G (2014) Nonlinear multiferroic phase shifters for microwave frequencies. Appl Phys Lett 104:052911
Semenov AA, Karmanenko SF, Kalinikos BA et al (2005) Ferrite/ferroelectric layered structures for magnetic and electric field tunable microwave devices. Integr Ferroelectr 77:199–205
Hu J-M, Nan CW (2009) Electric-field-induced magnetic easy-axis reorientation in ferromagnetic/ferroelectric layered heterostructures. Phys Rev B 80:224416
Liu J-M, Nan C-W (2012) Ferroelectricity and multiferroicity: broader way to go beyond. Front Phys 7:373–374
Liu M, Obi O, Lou J et al (2009) Strong magnetoelectric coupling in ferrite/ferroelectric multiferroic heterostructures derived by low temperature spin-spray deposition. J Phys D Appl Phys 42:045007
Shu L, Li Z, Ma J et al (2012) Thickness-dependent voltage-modulated magnetism in multiferroic heterostructures. Appl Phys Lett 100:022405
Nan TX, Zhou ZY, Lou J et al (2012) Voltage impulse induced bistable magnetization switching in multiferroic heterostructures. Appl Phys Lett 100:132409
Liu M, Obi O, Lou J et al (2008) Spin-spray deposited multiferroic composite Ni0.23Fe2.77O4/Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 with strong interface adhesion. Appl Phys Lett 92:152504
Lou J, Insignares RE, Cai Z et al (2007) Soft magnetism, magnetostriction, and microwave properties of FeGaB thin films. Appl Phys Lett 91:182504
Zhou HM, Li C, Zhu FJ et al (2013) A generalized lumped element modeling of electrically and magnetically dual-tunable microwave magnetoelectric resonators. J Appl Phys 114:083902
Martin F, Falcone F, Bonache J et al (2003) Miniaturized coplanar waveguide stop band filters based on multiple tuned split ring resonators. IEEE Microw Wirel Compon Lett 13:511–513
Yun TY, Chang K (2001) Uniplanar one-dimensional photonic-bandgap structures and resonators. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 49:549–553
Fetisov YK, Srinivasan G (2006) Electric field tuning characteristics of a ferrite-piezoelectric microwave resonator. Appl Phys Lett 88:143503
Murthy DVB, Srinivasan G (2012) Broadband ferromagnetic resonance studies on influence of interface bonding on magnetoeletric effects in ferrite-ferroelectric composites. Front Phys 7:418–423
Pettiford C, Dasgupta S, Lou J et al (2007) Bias field effects on microwave frequency behavior of PZT/YIG magnetoelectric bilayer. IEEE Trans Magn 43:3343–3345
Dudek P, Szczepanski S, Hatfield JV (2000) A high-resolution CMOS time-to-digital converter utilizing a Vernier delay line. IEEE J Solid-State Circuit 35:240–247
Poon JKS, Scheuer J, Xu Y et al (2004) Designing coupled-resonator optical waveguide delay lines. J Opt Soc Am B Opt Phys 21:1665–1673
Hristoforou E, Ktena A (2007) Magnetostriction and magnetostrictive materials for sensing applications. J Magn Magn Mater 316:372–378
Ozgur U, Alivov Y, Morkoc H (2009) Microwave ferrites, part 1: fundamental properties. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 20:789–834
Geiler AL, Gillette SM, Chen Y et al (2010) Multiferroic heterostructure fringe field tuning of meander line microstrip ferrite phase shifter. Appl Phys Lett 96:053508
Bichurin MI, Viehland D, Srinivasan G (2007) Magnetoelectric interactions in ferromagnetic-piezoelectric layered structures: phenomena and devices. J Electronceram 19:243–250
Tatarenko AS, Murthy DVB, Srinivasan G (2012) Hexagonal ferrite-piezoelectric composites for dual magnetic and electric field tunable 8–25 GHz microstripline resonators and phase shifters. Microw Opt Technol Lett 54:1215–1218
Yang GM, Lou J, Wu J et al (2011) Dual H- and E-field tunable multiferroic bandpass filters with yttrium iron garnet film. In: 2011 IEEE MTT-S international microwave symposium digest (MTT), 5–10 June 2011, pp 1–4
Zhang S, Zhao YG, Li PS et al (2012) Electric-field control of nonvolatile magnetization in structure at room temperature. Phys Rev Lett 108:137203
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National 111 Project of China (B14040), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and the Recruitment Program of Global Youth Experts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
SPECIAL TOPIC: Multiferroic Materials
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M. Novel laminated multiferroic heterostructures for reconfigurable microwave devices. Chin. Sci. Bull. 59, 5180–5190 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0627-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0627-5