Abstract
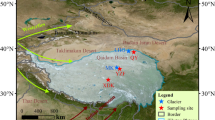
Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic tracer was applied, for the first time, to identifying the sources of the particles in the East Rongbuk ice core from Mt. Qomalangma (Everest). The results show that the particles in the dirty layers originate mainly from local sources, while the particles in the non-dirty layers are consistent with the features of dust from the arid regions in northwestern India. The HYSPLIT model shows that the air trajectory goes first through northwestern India before reaching the drilling site of ice core when dust storms occur in northwestern India, confirming northwestern India as a possible source of dust in the East Rongbuk ice core.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruth U, Wagenbach D, Steffensen J P, et al. Continuous record of microparticle concentration and size distribution in the central Greenland NGRIP ice core during the last glacial period. J Geophys Res, 2003, 108(D3): 4098–4110
Steffensen J P. The size distribution of microparticles from selected segments of the Greenland Ice Core Project ice core representing different climatic periods. J Geophys Res, 1997, 102(C12): 26755–26763
Ram M, Koenig G. Continuous dust concentration profile of pre-Holocene ice from the Greenland Ice Sheet Project 2 ice core: Dust stadials, interstadials, and the Eemian. J Geophys Res, 1997, 102(C12): 26641–26648
Delmonte B, Basile-Doelsch I, Petit J R, et al. Comparing the EPICA and Vostok dust records during the last 220,000 years: Stratigraphical correlation and provenance in glacial periods. Earth Sci Rev, 2004, 66(1–2): 63–87
Petit J R, Jouzel J, Raynaud D, et al. Climate and atmospheric history of the past 420000 years from the Vostok ice core, Antarctica. Nature, 1999, 399: 429–436
Mahowald N, Kohfeld K E, Hansson M, et al. Dust sources and deposition during the Last Glacial Maximum and current climate: A comparison of model results with paleodata from ice cores and marine sediments. J Geophys Res, 1999, 104: 15895–16436
Chen J, Li G J, Yang J D, et al. Nd and Sr isotopic characteristics of Chinese deserts: Implications for the provenances of Asian dust. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 2007, 71:3904–3914
Rao W B, Yang J D, Chen J, et al. Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry of eolian dust of the arid-semiarid areas in China: Implications for loess provenance and monsoon evolution. Chin Sci Bull, 2006, 51(4): 1401–1412
Grousset F E, Biscaye P E. Tracing dust sources and transport patterns using Sr, Nd and Pb isotopes. Chem Geol, 2005, 222: 149–167
Grousset F E, Biscaye P E, Revel M, et al. Antarctic (Dome C) ice-core dust at 18 ky BP-Isotopic constraints on origins. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 1992, 111(1): 175–182
Biscaye P E, Grousset F E, Revel M, et al. Asian provenance of glacial dust (stage 2) in the Greenland Ice Sheet Project 2 ice core, Summit, Greenland. J Geophys Res, 1997, 102(C12): 26765–26781
Svensson A, Biscaye P E, Grousset F E, Characterization of late glacial continental dust in the Greenland Ice Core Project ice core. J Geophys Res, 2000, 105: 4637–4656
Xu J, Hou S, Qin D, et al. Dust storm activity over the Tibetan Plateau recorded by a shallow ice core from the north slope of Mt. Qomolangma (Everest), Tibet-Himal region. Geophys Res Lett, 2007, 34: L17504
Chen F, Li X H, Wang X L, et al. Zircon age and Nd-Hf isotopic composition of the Yunnan Tethyan belt, southwestern China. Int J Earth Sci, 2007, 96: 1179–1194
Najman Y. The detrital record of orogenesis: A review of approaches and techniques used in the Himalayan sedimentary basins. Earth Sci Rev, 2006, 74: 1–72
Gariepy C, Allegre C J, Xu R H, The Pb-isotope geochemistry of granitoids from the Himalaya-Tibet collision zone: Implications for crustal evolution. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 1985, 74: 220–234
Tripathi J K, Bock B, Rajamani V, et al. Is river Ghaggar, Saraswati? Geochemical constraints. Curr Sci, 2004, 87(8): 1141–1145
Ye T Z, Gao Y X. The Meteorology of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 1979. 165
Zhuo G. Preliminary study about Xigaze area sand dust weather (in Chinese). Tibet Sci Technol, 2007, 2: 59–63
Chen B, Hiroyuki K, Jie D, et al. Dust transport from northeastern China inferred from carbon isotopes of atmospheric dust carbonate. Atmos Environ, 2008, 42(19): 4790–4796
Argles T, Foster G, Whittington A, et al. Isotope studies reveal a complete Himalayan section in the Nanga Parbat syntaxis. Geology, 2003, 31(12): 1109–1112
Middleton N J. A geography of dust storms in south-west Asia. J Climatol, 1986, 6: 183–196
Prospero J M, Ginoux P, Torres O, et al. Environmental characterization of global sources of atmospheric soil dust identified with the nimbus 7 total ozone mapping spectrometer (TOMS) absorbing aerosol product. Rev Geophys, 2002, 40(1): 1002
Goudie A S, Middleton N J. Desert Dust in the Global System. Berlin: Springer, 2006. 117–133
Middleton N J. Climatic controls on the frequency, magnitude and distribution of dust storms: Examples from India/Pakistan, Mauritania and Mongolia. In: Leinen M, Sarnthein M, eds. Paleoclimatology and Paleometeorology: Modern and Past Patterns of Global Atmospheric Transport. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1989. 97–132
Nair V S, Krishna Moorthy K, Alappattu D P, et al. Wintertime aerosol characteristics over the Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP): Impacts of local boundary layer processes and long-range transport. J Geophys Res, 2007, 112: D13205
Hegde P, Pant P, Naja M, et al. South Asian dust episode in June 2006: Aerosol observations in the central Himalayas. Geophys Res Lett, 2007, 34: L23802
Marinoni A, Cristofanelli P, Laj P, et al. Observations of dust mixed with pollution transport event from Pakistan area to Himalayas. Geophys Res Abst, 2008, 10: EGU2008-A-10068
Prasad A K, Singh R P. Changes in aerosol parameters during major dust storm events (2001–2005) over the Indo-Gangetic Plains using AERONET and MODIS data. J Geophys Res, 2007, 112: D09208
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported jointly by National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2007CB411501), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 90411003) and Hundred Talents Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. KZCX3-SW-344)
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Hou, S., Chen, F. et al. Tracing the sources of particles in the East Rongbuk ice core from Mt. Qomolangma. Chin. Sci. Bull. 54, 1781–1785 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0050-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0050-5