Abstract
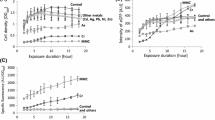
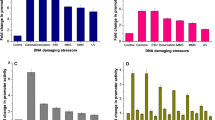
Based on a genetically modified radioresistant bacteria Deinococcus radiodurans, we constructed a real time whole cell biosensor to monitor radioactivity and genotoxicity in highly radioactive environment. The enhanced green fluorescence protein (eGFP) was fused to the promoter of the crucial DNA damage-inducible recA gene from D. radiodurans, and the consequent DNA fragment (PrecA-egfp) carried by plasmid was introduced into D. radiodurans R1 strain to obtain the biosensor strain DRG300. This engineered strain can express eGFP protein and generate fluorescence in induction of the recA gene promoter. Based on the correlation between fluorescence intensity and protein expression level in live D. radiodurans cells, we discovered that the fluorescence induction of strain DRG300 responds in a remarkable dose-dependent manner when treated with DNA damage sources such as gamma radiation and mitomycin C. It is encouraging to find the widely detective range and high sensitivity of this reconstructed strain comparing with other whole cell biosensors in former reports. These results suggest that the strain DRG300 is a potential whole cell biosensor to construct a detective system to monitor the biological hazards of radioactive and toxic pollutants in environment in real time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daly M J. Engineering radiation-resistant bacteria for environmental biotechnology. Curr Opin Biotechnol, 2000, 11(3): 280–285
Belkin S. Microbial whole-cell sensing systems of environmental pollutants. Curr Opin Microbiol, 2003, 6(3): 206–212
Kohler S, Belkin S, Schmid R D. Reporter gene bioassays in environmental analysis. Fresenius J Anal Chem, 2000, 366(6–7): 769–779
Vollmer A C, Belkin S, Smulski D R, et al. Detection of DNA damage by use of Escherichia coli carrying recA’::lux, uvrA’::lux, or alkA’::lux reporter plasmids. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1997, 63(7): 2566–2571
Davidov Y, Rozen R, Smulski D R, et al. Improved bacterial SOS promoter∷lux fusions for genotoxicity detection. Mutat Res, 2000, 466(1): 97–107
Kostrzynska M, Leung K T, Lee H, et al. Green fluorescent protein-based biosensor for detecting SOS-inducing activity of genotoxic compounds. J Microbiol Methods, 2002, 48(1): 43–51
Norman A, Hestbjerg H L, Sorensen S J. Construction of a ColD cda promoter-based SOS-green fluorescent protein whole-cell biosensor with higher sensitivity toward genotoxic compounds than constructs based on recA, umuDC, or sulA promoters. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2005, 71(5): 2338–2346
Minton K W. DNA repair in the extremely radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. Mol Microbiol, 1994, 13(1): 9–15
Battista J R, Earl A M, Park M J. Why is Deinococcus radiodurans so resistant to ionizing radiation? Trends Microbiol, 1999, 7(9): 362–365
Cox M M, Battista J R. Deinococcus radiodurans-the consummate survivor. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2005, 3(11): 882–892
Lange C C, Wackett L P, Minton K W, et al. Engineering a recombinant Deinococcus radiodurans for organopollutant degradation in radioactive mixed waste environments. Nat Biotechnol, 1998, 16(10): 929–933
Daly M J, Ouyang L, Fuchs P, et al. In vivo damage and recA-dependent repair of plasmid and chromosomal DNA in the radiation-resistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. J Bacteriol, 1994, 176(12): 3508–3517
Brim H, McFarlan S C, Fredrickson J K, et al. Engineering Deinococcus radiodurans for metal remediation in radioactive mixed waste environments. Nat Biotechnol, 2000, 18(1): 85–90
Lippincott-Schwartz J, Snapp E, Kenworthy A. Studying protein dynamics in living cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2001, 2(6): 444–456
Meima R, Lidstrom M E. Characterization of the minimal replicon of a cryptic Deinococcus radiodurans SARK plasmid and development of versatile Escherichia coli-D. radiodurans shuttle vectors. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2000, 66(9): 3856–3867
Bonacossa A C, Coste G, Sommer S, et al. Quantification of RecA protein in Deinococcus radiodurans reveals involvement of RecA, but not LexA, in its regulation. Mol Genet Genomics, 2002, 268(1): 28–41
Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem, 1976, 72: 248–254
Lipton M S, Pasa-Tolic L, Anderson G A, et al. Global analysis of the Deinococcus radiodurans proteome by using accurate mass tags. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002, 99(17): 11049–11054
Huan C, Zhenjian X, Bing T, et al. Transcriptional profile in response to ionizing radiation at low dose in Deinococcus radiodurans. Prog Nat Sci, 2007, 17(5): 529–536
Zhang C, Wei J, Zheng Z, et al. Proteomic analysis of Deinococcus radiodurans recovering from gamma-irradiation. Proteomics, 2005, 5(1): 138–143
Appukuttan D, Rao A S, Apte S K. Engineering of Deinococcus radiodurans R1 for bioprecipitation of uranium from dilute nuclear waste. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2006, 72(12): 7873–7878
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Basic Research Program (Grant No. 2004CB19604), National Hi-Tech Development Program (Grant No. 2007AA021305), Distinguished Young Scientist (Grant No. 30425038) and key project from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30330020)
About this article
Cite this article
GuanJun, G., Lu, F., HuiMing, L. et al. Engineering Deinococcus radiodurans into biosensor to monitor radioactivity and genotoxicity in environment. Chin. Sci. Bull. 53, 1675–1681 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0224-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0224-6