Abstract
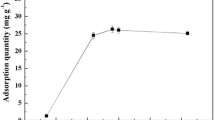
Experimental studies were conducted on the feasibility of aerobic granular biomass as a novel type of biosorbent for Pb2+ removal. The results show that the initial pH, Pb2+ concentration (C 0) and biomass concentration (X 0) affected the biosorption process significantly. Both the Freundlich and Langmuir isotherm models describe the biosorption process accurately, with correlation coefficients of 0.932 and 0.959 respectively. The Pb2+ biosorption kinetics is interpreted as having two stages, with the second stage described reasonably well by a Lagergren pseudo-second order model. Moreover, the surface change of granular biomass after the Pb2+ biosorption process appears to be caused by ion exchange and metal chelation according to the analysis results of Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy (ESEM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen W, Yang S L, Li X K, et al. The mechanism of Pb(II) sorption by living cell of Trichoderma sp. HR-1(in Chinese). Chin Environ Sci, 2006, 26(1): 101–105
Yu J X, Tong M, Sun X M, et al. Cystine-modified biomass for Cd(II) and Pb(II) biosorption. J Hazard Mater, 2007, 143(1–2): 277–284
Tokcaer E, Yetis U. Pb(II) biosorption using anaerobically digested sludge. J Hazard Mater, 2006, 137(3): 1647–1680
Al-Qodah Z. Biosorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by activated sludge. Desalination, 2006, 196(1-3): 164–176
Li Q, Chen M, Cui F C, et al. Adsorption mechanism of chromium cation by Floc-Type Biosorbent ZL 5-2 (in Chinese). Environ Sci, 2006, 27(2): 343–346
Zhou D Q, Wei D Z. Biosorptive-flotation and desorption operation of heavy metals from wastewater effluents by Gordona amarae. Environ Sci (in Chinese), 2006, 27(5): 960–964
Wang X J, Chen L, Xia S Q, et al. Biosorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solutions by dried activated sludge. Miner Eng, 2006, 19(9): 968–971
Liu L L, Wang Z P, Yao J, et al. Investigation on the formation and kinetics of glucose-fed aerobic granular sludge. Enzyme Microb Tech, 2005, 36(5–6): 712–716
Lei Q, Yu L. Aerobic granulation for organic carbon and nitrogen removal in alternating aerobic-anaerobic sequencing batch reactor. Chemosphere, 2006, 63(6): 926–933
Yang F L, Wang F, Zhang X W, et al. Characteristic of the strain of simultaneous denitrification bacteria aerobic granule sludge in SBAR (in Chinese). Chin Environ Sci, 2005, 25(2): 218–221
Wang Z W, Liu Y, Tay J H. The role of SBR mixed liquor volume exchange ratio in aerobic granulation. Chemosphere, 2006, 62(5): 767–771
Qin L, Liu Y, Tay J H. Effect of settling time on aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactor. Biochem Eng J, 2004, 21(1): 47–52
Qin L, Tay J H, Liu Y. Selection pressure is a driving force of aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactors. Process Biochem, 2004, 39(5): 579–584
Zhang L L, Chen X, Chen J M, et al. Role mechanism of extracellular polymeric substances in the formation of aerobic granular sludge (in Chinese). Environ Sci, 2007, 28(4): 795–799
Hawari A H, Mulligan C N. Biosorption of lead (II), cadmium (II), copper (II) and nickel (II) by anaerobic granular biomass. Bioresour Technol, 2006, 97(4): 692–700
Kiran I, Akar T, Tunali S. Biosorption of Pb (II) and Cu (II) from aqueous solutions by pretreated biomass of Neurospora crassa. Process Biochem, 2005, 40(11): 3550–3558
Liu H, Wang J L, Wen X H. Study on biosorption of heavy metal ion-Lead by Yeast. Res Environ Sci (in Chinese), 2002, 15(2): 26–29
Sun W L, Ni J R. Applicability of Langmuir equation to copper sorption by loess. Environ Chem (in Chinese), 2002, 21(1): 37–41
Cao X, Jin C J, Liu X C, et al. Adsorption characteristics of Copper ions on alkaline sludge. Environ Chem (in Chinese), 2006, 25(4): 414–419
Pan X L, Wang J L, Zhang D Y, et al. Zn2+ sorption and mechanism by EPS of mixed SRB population. Res Environ Sci (in Chinese), 2005, 18(6): 53–55
Cabuk A, Akar T, Tunali S, et al. Biosorption of Pb (II) by industrial strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae immobilized on the biomatrix of cone biomass of Pinus nigra: Equilibrium and mechanism analysis. Chem Eng J, 2007, 131(1–3): 293–300
Sag Y, Ozer D, Kutsal T. A comparative study of the biosorption of lead(II) ions to Z. ramigera and R. arrhizus. Process Biochem, 1995, 30(2): 169–174
Chen C, Wang J L. Biosorption of heavy metal ions by a brewery’s waste: Kinetic and equilibrium. Acta Sci Ciru (in Chinese), 2007, 27(4): 544–553
Guo P, Kang C L, Bao G Z, et al. Thermodynamics and kinetics of Pb2+ and Cd2+ adsorption onto immobilized dominant bacteria. J Jilin Univ (in Chinese), 2006, 44(6): 1019–1022
Pamukoglu A Y, Kargi F. Batch kinetics and isotherms for biosorption of copper (II) ions onto pre-treated powdered waste sludge (PWS). J Hazard Mater, 2006, 138(3): 479–484
Xuan Z X, Tang Y R, Li X M, et al. Study on the equilibrium, kinetics and isotherm of biosorption of lead ions onto pretreated chemically modified orange peel. Biochem Eng J, 2006, 31(2): 160–164
Iyer A, Mody K, Jha B. Biosorption of heavy metals by a marine bacterium. Mar Pollut Bull, 2005, 50(3): 340–343
He B Y, Yin H, Peng H, et al. Cell physiology metabolism and morphology study of chromium biosorption by Yeast. Environ Sci (in Chinese), 2007, 28(1): 194–198
Davis T A, Volesky B, Mucci A. A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Res, 2003, 37(18): 4311–4330
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Instrumental Analysis Fund of Peking University
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, L., Ye, Z., Wang, Z. et al. Characteristics of Pb2+ biosorption with aerobic granular biomass. Chin. Sci. Bull. 53, 948–953 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0103-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0103-1